From this article you will learn:
- What is ROI?
- Who will benefit from ROI?
- How to Calculate ROI
Return on investment involves a complex process of planning, calculations and analysis. Several procedures, as well as an understanding of norms and indicators, allow you to determine the timing. To get a return on your investment, you need to have experience and certain knowledge, otherwise this task will be very difficult. Next, we will talk in detail about how to calculate the return on investment rate.
About the return on investment indicator in more detail
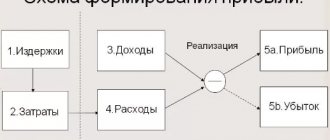
The ROI (Return On Investment) indicator is the return on investment ratio, indicating the return on investment. It is usually presented as a percentage: if it is more than 100%, it demonstrates profitability, and if it is below 100%, it shows the unprofitability of investing money in a particular project. To calculate this indicator, you need to know the following data:
- Cost of supply, that is, all costs for the purchase of parts for products, delivery to the warehouse, production, payment of personnel, etc.
- Revenue is the final profit from the sale of a product or service.
- The amount of investment or the total amount of money invested, for example, the budget for contextual advertising.
Based on ROI, it is possible to make or cancel a number of economic decisions:
- acquisition of an asset (business);
- the feasibility of investing in business development (modernization, entering new markets);
- effectiveness of the advertising campaign (increase in the volume of goods sold);
- purchasing securities on the stock market;
- obtaining a bank loan for investment purposes.
Therefore, the ROI indicator is necessary for both the owner of the enterprise and the investor. If an investor is considering investment options, this figure will guide him in terms of possible income from investments. Let’s say a comparison of the ROI of a clothing boutique and a shoe store will show which is more profitable to invest in.
The owner of an enterprise needs this indicator when searching for investors - it clearly shows that a potential investor can increase his capital, for example, by 20% over a certain period. As a result, the company's attractiveness from the point of view of investment opportunities increases.
However, you need to understand that the opposite is also true. Too low, zero or negative ROI indicates that the company is not attractive to investors, so the owners will be forced to reconsider the organization of their business. ROI is not as clear-cut as profit, but still shows how a business can perform over the long term.
Types of ROI calculations
Usually there are two ways to calculate the payback period of an investment. They are divided on the basis of taking into account the change in the value of the invested funds or the lack thereof.
1. Simple calculation method.
This method appeared first and is still quite often used in practice. However, you need to understand that it allows you to obtain information subject to certain rules:
- Only projects with the same duration can participate in the analysis of a number of projects at once.
- Funds are invested in a lump sum at the very beginning.
- Profits from investments come in approximately equal amounts.
In this case, you will receive an exact period of time during which your investment will pay off.
Why is this method still used? It is valued for its simplicity and transparency. It is also good for superficially comparing investment risks existing in several projects. The higher the indicator, the greater the risk of such an investment. And vice versa: the lower the indicator, the greater the benefit the investor will receive, since he will be able to return the investment in large parts and relatively quickly. And this is necessary to maintain business liquidity.
The simple method has significant disadvantages, since it does not take into account important processes:
- constant change in the value of funds;
- the profit from the project that the company will receive after returning the invested funds.
Therefore, they often resort to a more complex method for assessing the return on investment indicator.
2. Dynamic or discounted method.
This approach allows you to determine the time from investment to return of funds, taking into account discounting. We are talking about the point in time when the net present value loses its negative value and remains so.
It is important to understand that since the dynamic coefficient implies taking into account changes in the cost of finance, it turns out to be higher than the coefficient obtained by calculation in a simple way.
Whether it will be convenient for you to use this method depends on whether financial income is constant. If amounts of different amounts are received at different frequencies, it is better to use calculations using tables and graphs.
Next, let's talk about possible formulas for calculating the return on investment period.
Top 3 articles that will be useful to every manager:
- Financial control at the enterprise
- Net profitability of the enterprise
- How to build a company's financial structure
Where can I get data to calculate the profitability of an enterprise?
We know that in order to calculate the profitability of an activity, the formula must contain information about the profit, revenue, assets, capital and borrowings of the enterprise. All this information can be gleaned from financial statements: the balance sheet and income statement.
For more information about the balance sheet, see the article “Filling out form 1 of the balance sheet (sample)” , and for form 2 - in the article “Filling out form 2 of the balance sheet (sample)” .
But on their basis, only fairly aggregated, general indicators can be calculated. A more detailed and in-depth analysis requires more detailed information. For example, to calculate the profitability of a particular type of product, we need figures for the profit and cost of a specific product; the profitability of sales can be calculated not for the organization as a whole, but for the type of activity, and for this we need to know the amount of revenue and profit specifically for the line of business that interests us. This means that in order to calculate the profitability of an enterprise, the formula must be supplemented with data from accounting analytics or management accounting.
How to calculate return on investment: formulas and examples
So we need to know what the ROI is. The formula for calculating in a simple way looks like this:
Payback period = investment size / net annual profit.
Or
PP = K0 / PChsg.
We take into account that PP is the payback period expressed in years.
K0 – the amount of invested funds.
PChsg – net profit on average for the year.
Example.
You are considering the option of investing 150 thousand rubles in a project. It is assumed that the annual net profit will average 50 thousand rubles.
The simplest calculations show that the investment can be returned in three years - for this we divide 150,000 by 50,000. But in this case we receive information that does not take into account that the project can both generate income for all these three years and require new ones expenses. For this reason, we recommend using the second formula, where you need to obtain the IFg value. To calculate it, subtract the average expense for the year from your average income. Let us consider this in more detail using the second example.
Example 2.
During the implementation of the project that is already familiar to us, 20 thousand rubles will be spent every year on various types of expenses. That is, we get the value of PChsg by subtracting 20 thousand expenses from 50 thousand rubles of net annual profit.
In this case, the formula will look like this:
PP (payback period) = 150,000 (investment) / 30,000 (average annual net profit).
As a result, the return on investment will be already 5 years. That is, taking into account average annual costs, the payback period increases by as much as two years, which is much more similar to reality.
Let us recall that this calculation can be used if we are talking about the same income for all periods. However, practice shows that the amount of income varies from year to year. And to take this into account, let's take the following steps.
We find the integer number of years it will take for the final income to be as close as possible to the amount of funds invested in the project.
We find the amount of investments that remain uncovered by profit, and it is assumed that income flows evenly throughout the year. We find the number of months required to achieve a full return on investment.
Let's consider everything that has been said with an example.
Example 3.
The conditions are similar: you need to invest 150 thousand rubles in the project. During the first year, the income will be 30 thousand rubles, in the second - 50 thousand, in the third - 40 thousand, in the fourth - 60 thousand rubles.
Thus, the income for three years will be 30+50+40 = 120 thousand rubles. And in 4 years the amount of profit will increase to 180 thousand rubles. We invested 150 thousand, which means that the payback period for the investment will occur between the third and fourth years of the project. But this information is not enough, so we proceed to the second stage. Now we need to find out what part of the invested funds remains uncovered after the third year:
150,000 (investments) – 120,000 (income for 3 years) = 30,000 rubles.
We move on to the third stage, at which we must determine the fractional part for the fourth year. Let us remind you that there are 30 thousand left to cover, and the income for the year will be 60 thousand. This means we divide 30,000 by 60,000 and get 0.5 (in years).
Thus, taking into account the uneven influx of money across periods (but uniform across months in a period), the return on investment in the project for us will be three and a half years (3 + 0.5 = 3.5).
Profitability of “tax” value - is this possible?
So, we found out that profitability can be used to judge the effectiveness of a company. This implies a circle of people to whom this indicator may be useful. Obviously these include:
- company owners who need to know how their money works;
- managers, because they are responsible for the work of the company, including to the owners;
- potential investors - you should understand where you are investing;
- analysts, economists, financiers - they work with numbers, make forecasts, look for growth reserves, and fight the inefficient use of resources.
At first glance, that's all. Meanwhile, tax specialists should also be included in the circle of interested parties. Yes, yes, the inspection is also interested in your profitability, namely the profitability indicators of products and assets. They track the average profitability by industry - the data can be found in Appendix No. 4 to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated May 30, 2007 No. MM-3-06 / [email protected] (information is supplemented annually). And compare your profitability with them. A deviation of more than 10% may be a signal for the company to be included in the on-site audit plan (see 11th of the publicly available criteria for taxpayers’ self-assessment of tax audit risks). This means that employees of accounting and tax services of organizations should also pay attention to profitability.
The details of comparing the organization’s profitability with industry averages, including using the tax service’s Internet service, were provided by ConsultantPlus experts. If you don't have access to the system, get it for free and proceed to the directions.
Calculation formula for the dynamic method
This method is more complicated, because it takes into account that during the payback period the cost of funds does not remain stable. To do this, enter an additional value - the discount rate.
Let's take the conditions where:
Kd – discount factor;
d – interest rate;
nd – time.
Then kd = 1/(1+d)^nd.
Discounted term = amount of net cash flow / (1+d) ^ nd.
Since this formula is much more complicated than the previous ones, we will discuss one more example. To make it easier, let’s keep the familiar conditions of the problem, and the discount rate will be equal to 10%, which approximately corresponds to reality.
We start by calculating the discount factor, that is, discounted earnings for each year:
- 1 year: 30,000 / (1+0.1) ^ 1 = 27,272.72 rubles.
- Year 2: 50,000 / (1+0.1) ^ 2= 41,322.31 rubles.
- Year 3: 40,000 / (1+0.1) ^ 3 = 30,052.39 rubles.
- Year 4: 60,000 / (1+0.1) ^ 4 = 40,980.80 rubles.
We add up the indicators and find out that the profit for the first three years is 139,628.22 rubles.
It becomes obvious that this is not enough to cover our investment. In other words, taking into account the change in the value of money, we will not be able to return our funds even in 4 years. But let's finish the calculation. In the conditions, we had no profit from the project in the fifth year of its existence, so let’s denote it equal to the fourth – 60,000 rubles.
- Year 5: 60,000 / (1+0.1) ^ 5 = 37,255.27 rubles.
If we add the total to the already existing amount, over five years we get 176,883.49. This exceeds our investments at the start, so we can safely assume that the payback period is between the fourth and fifth years of the project.
To find out the specific period, you need to calculate the fractional part. To do this, subtract the amount for 4 whole years from the amount invested: 150,000 – 139,628.22 = 10,371.78 rubles.
We divide the result by discounted revenues for the fifth year:
13 371,78 / 37 255,27 = 0,27
It turns out that we are 0.27 from the fifth year short of full payback, and the entire payback period with the dynamic calculation method will be 4.27 years.
As we have already said, the indicator of the payback period of investments using the discounted method differs greatly from the calculation using the simple method. But it allows you to more accurately imagine the result that you will get under specific conditions.
What is internal rate of return?
No one can calculate with 100% probability what income will be received from the invested funds. There are too many variable factors that can affect the implementation of a business project financed by an investor. However, you can minimize the risk of inaccuracy if you use a relative rather than an absolute assessment.
Is it possible to use internal rate of return as a discount factor ?
The interest rate at which the investor is guaranteed to recoup his investment, but will not receive a profit, is called the internal rate of return (IRR). The norm is that all cash flows of a given investment project will be offset in total. In other words, the costs of an investment project at some point in time are balanced by the income received (they say that the project “broke to zero”).
IMPORTANT! The word “internal” in the definition of this investment rate means its dependence on the properties of the project itself, and not on external factors.
How is the internal rate of return used when assessing the effectiveness of investment projects ?
Experts may call the internal rate of return differently. The following names :
- VND is a Russian abbreviation;
- IRR is an English abbreviation for “Internal Rate of Return” - “internal rate of return”;
- internal rate of return;
- internal rate of return;
- internal rate of return on investment;
- maximum efficiency of capital investments;
- percentage rate of return;
- discounted flow of real money;
- financial rate of return;
- own rate of return.
ATTENTION! This norm can be considered the limit, since going beyond its limits already means a loss for the investor.
Business valuation based on return on investment
When analyzing return on investment, you should not rely solely on ROI, since this is often not enough to obtain reliable results. In assessing the attractiveness of a company from an investment point of view, an equally important factor is the time period. It would seem that an ROI of 30% looks better than an ROI of 20%. However, this 30% could be obtained in 3 years, and 20% in a year, which means, in terms of one year, the return on investment ROI in the second case will be higher. But you need to understand that investing for a year sometimes entails great risks, and an investor may be attracted to a longer-term and less dangerous project.
The payback period is one of the key indicators for an entrepreneur if he plans to invest his own funds and chooses the most profitable one among possible projects. But the investor himself decides how exactly he will make the calculations.