Margin (English margin - advantage, difference) is the difference between the selling price of a product and its cost. In business, a metric shows the amount of money a company will receive after selling a product or service.
The concept of margin is also used in banking, insurance, stock exchange and other areas of activity, each of which has its own characteristics in determining the indicator and its calculation. Therefore, we will consider what margin is only in relation to the sale of goods or services.
Margin calculation formula
Margin is measured in monetary units and calculated using the formula:
Margin = Selling Price – Cost
Cost includes all variable costs associated with the production or purchase of goods or services.
A simple example.
The company purchased a batch of sneakers at a price of 1,200 rubles per pair. They sold shoes for 2,000 rubles. Let's calculate the margin:
2,000 – 1,200 = 800 (rub.)
It turns out that the amount of income per unit of goods was 800 rubles.
However, in reality, calculating margin is not always easy, since it is important to correctly determine variable costs.
Complex example.
The company produces products independently. To do this, it purchases raw materials, produces goods using its own equipment, then packages and sells them. In this case, workers receive a percentage of each unit of goods produced in addition to their fixed earnings.
In this case, variable costs include:
- cost of raw materials;
- resource costs for equipment operation (electricity, etc.);
- percentage of wages for production volume;
- expenses on packaging and logistics.
Expenses for fixed salaries of employees and rent of premises, fixed costs for electricity and equipment maintenance are not included in the cost price. These are constant expenses, the amount of which does not change depending on the volume of production of goods.
Having calculated all the variable costs for the production of a batch of goods, we divide the resulting amount by the number of units produced and find out the cost of one product. Then you can calculate the margin using the standard formula - subtract the cost from the selling price.
The margin indicator is useful for calculating many other metrics. For example, it is used to determine LTV - customer lifetime value:
LTV = average check × average number of orders per month × average time of cooperation with a client × average margin
For a quick calculation, you can use the LTV calculator, which will help you find out how much money a client brings in on average over the period of cooperation with the company.
Margin is an absolute indicator, the value of which is difficult to judge the efficiency of a business. For example, monthly monitoring shows a stable increase in margin. But as a result of a more detailed study, it turns out that variable costs are also growing. Consequently, the effectiveness of the activity remains in question. To understand, you need to determine the margin.
Analysis of indicators
The company manager can use the obtained data to formulate a competent and highly effective marketing strategy. This is necessary in order to increase turnover by increasing sales levels.
Margin analysis helps to select the optimal pricing policy, as well as make a forecast of possible risks. This method is also effective in the sense that it allows you to find the difference between the company’s variable and fixed costs, as well as calculate the consequences for the company if the volume of production is adjusted.
Margin analysis is a tool that allows you to perform financial planning. The main purpose of its use is to increase the value of the enterprise.
Using analysis you can determine:
- does the size of the company’s margin depend if production volumes increase;
- volume of trade turnover affecting profit growth;
- volume of sales that is necessary to achieve break-even for the enterprise and establish the optimal price threshold;
- How do all of these factors affect production profitability?
What kind of profitability can be considered good? It is impossible to answer this question unequivocally, since in Russian practice there are no accurate research results. Foreign studies, on the contrary, indicate that this figure should be 20−25%. But the optimal margin size will be considered to be 10% profitability.
Margin analysis takes place in 3 stages:
- Determination of indicators: revenue, costs, both fixed and variable, marginal income, as well as revenue from the sale of goods. It is important to track these numbers over time to compare production profitability.
- Calculation of the marginal income ratio. For this, the formula is used: K = MD / V * 100%. If you know the coefficient, you can determine what share of the proceeds from product sales will be used to cover costs.
- Factor analysis. As part of this stage, indicators are determined, in particular, the volume of products sold, the cost of goods, profit, financial losses, as well as costs of a constant or variable nature.
Is it possible to control profitability indicators? It’s very difficult, but every entrepreneur can automate the control process, which will simplify the analysis.
How and why to calculate margins
Margin is the ratio of margin to revenue. The metric shows exactly how much income each ruble earned contains. Marginality is calculated as a percentage using the following formula:
Margin = Margin ÷ Revenue × 100%
Example.
In August, the company sold a batch of goods for 100 thousand rubles at a cost of 50 thousand rubles. The margin was:
100,000 – 50,000 = 50,000 (rub.)
Let's calculate the margin:
50 000 ÷ 100 000 × 100% = 50%
It turns out that the sales margin in August was 50% - each ruble earned brought 50 kopecks of profit.
Now imagine that the same company next month sold goods worth 200 thousand rubles at a batch cost of 120 thousand rubles. Let's calculate the margin:
200,000 – 120,000 = 80,000 (rub.)
The margin figure is higher than in August, and the company appears to have performed more efficiently in September. But let’s calculate the margin:
80 000 ÷ 200 000 × 100% = 40%
It turns out that in September the margin fell by 10% compared to August, which indicates a decrease in efficiency. One ruble earned brought only 40 kopecks of profit.
The terms “margin” and “marginality” are often confused. To avoid mistakes, remember that the first indicator is calculated in money, and the second - in percentage. Margin shows how much profit remains from the revenue after the product is sold, and marginality is the share of profit in the income received.
Marginality helps assess the profitability, or profitability, of a business. It can be both positive and negative. The latter happens when variable costs exceed revenue, leading to negative margins. In such a situation, if there are no errors in the calculations, you need to look for where overspending occurs in the production or procurement process.
The margin cannot be more than 100%, since even with zero cost, the margin cannot be higher than the revenue. When they talk about profitability of more than 100%, in most cases they mean a markup. And the amount of the markup is not limited.
Attitude towards markup
Margin ≠ Markup when expressed as a percentage. The formula is the same with the only difference – the divisor is the cost of production:
N = (CP - C) / C x 100
Table 2. Comparison of indicators
| Product | CPU, rub. | C, rub. | M | N | M to N, % | ||
| rub. | % | rub. | % | ||||
| NV "Scarlet Sails" (Snow White) | 2240 | 1760 | 480 | 21,4 | 480 | 27,3 | -5,8 |
| NV "Red Tulips" (Aries) | 669 | 450 | 219 | 32,7 | 219 | 48,7 | -15,9 |
| HB Pillow “Anemones” (Vervaco) | 1667 | 954 | 713 | 42,8 | 713 | 74,7 | -32,0 |
| NV "Reconciled girls" (Luca-S) | 464 | 328 | 136 | 29,3 | 136 | 41,5 | -12,2 |
| NV "Brugmanzia" (MI) | 228 | 180 | 48 | 21,1 | 48 | 26,7 | -5,6 |
Thus, if we count as a percentage, the markup is always greater than the margin. It can be higher than 100%. These are two dependent indicators and for each of them you can find the second one.
Types of margin when assessing business profitability
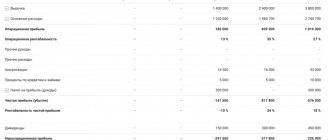
In accounting and finance, when assessing the profitability of a business, three main types of profit, or margin, are taken into account:
- Gross profit, or gross margin
, is total revenue minus cost of goods sold. - Operating profit, or operating margin
, is revenue minus cost of goods sold and operating expenses. - Net profit, or net margin
, is revenue minus all expenses, including interest and taxes.
Excerpt from the consolidated statement of profit or loss. Source
However, profit values alone do not allow us to assess the real financial condition of the company. Therefore, relative indicators are calculated on their basis.
profit
margin shows what percentage of income remains for the company after paying all direct costs associated with the production or purchase of goods:
MVP = Gross profit ÷ Revenue × 100%
operating profit
margin shows the income remaining after deducting direct expenses and operating costs (rent of premises, utilities, employee salaries and other fixed expenses):
Mop = Operating profit ÷ Revenue × 100%
profit
margin shows the share of profit remaining after deducting operating, overhead and all other expenses:
MPP = Net profit ÷ Revenue × 100%
Margin ratios of different companies can be compared with each other to understand who has higher profitability.
The terms “margin” and “gross (operating, net) profit margin” should not be confused. The correct name of the last term is “gross (operating, net) profit margin ratio.” But in everyday life, the names are often simplified and therefore they say “gross profit margin,” while implying a coefficient.
How to do margin trading correctly: 4 simple tips
Margin lending when trading on the stock exchange helps increase investment returns.
It does not matter whether the market is falling or growing - the investor gets the opportunity to carry out larger-scale operations and transactions than he could carry out only with the involvement of his own funds. Accordingly, you can earn more. There are also risks to consider when using this tool. To avoid a margin call situation and forced closing of positions, it is enough to follow a few simple rules:
- it is important to always monitor the market situation and control whether the account balance is sufficient to cover transactions and positions;
- if the position is unprofitable, it is better to get rid of it;
- if the market situation develops unfavorably, you may receive messages from the broker - you need to respond to them promptly;
- optimize margin trading - the Single Cash Position service helps you do this; when you use it, the costs of securing transactions will be lower.
Why do you need to know your net profit margin?
Net profit margin is a key success metric that shows how efficient a company is and how well it controls its costs. A low value may indicate too high operating costs or errors in pricing. Also, the lower the net margin, the smaller the margin, and even minor negative changes in trading or the economy can result in losses.
Knowing a business's net margin helps investors evaluate a company's performance and understand whether it generates enough profit on sales to adequately cover operating and overhead costs. A good sign for investors is the stable growth of this indicator.
Because net profit margin is expressed as a percentage rather than in monetary units, it can be used to compare the profitability of different companies in similar industries.
Margin trading optimization
When using margin lending, traders face various restrictions.
One of the main ones is the division of resources across different markets. For example, the Moscow Exchange has stock, derivatives and foreign exchange markets. And to use margin loans, an investor previously needed to have the resources to secure transactions in each of these markets - this is physically not very convenient, plus it increases the cost of securing positions. In our trading system called MATRIx, clients have access to a single cash position (SMP) service. Thanks to it, the restrictions of different markets can be circumvented. As part of the EDP service, investors receive a common account that combines:
- Stock market of the Moscow Exchange (all instruments traded in T+2 mode)
- Moscow Exchange derivatives market (futures, options)
- Foreign exchange market and precious metals market of the Moscow Exchange (non-deliverable mode)
- Foreign securities market of the St. Petersburg Exchange
Assets that were purchased on one market trading platform can then be used as collateral in other markets on the list.
This opens up opportunities for investors to use general risk management (the function is available in the SMARTx trading terminal), build complex arbitrage strategies, and finally, the amount of guarantee for operations is lower than with a strict division of brokerage accounts into different markets, and the available leverage also increases.
What margin is considered good?
It is impossible to determine the optimal net margin value. The reason is that the value of the indicator highly depends on the industry and the characteristics of the company.
Example of net profit margin indicators by industry. Source
Financial publications sometimes mention that a good net margin is 10-20%. However, a study by Yahoo! Finance, which looked at companies from 212 different industries, found the average to be no more than 7.5%.
In general, the higher the net profit margin, the better. But in order to objectively assess the effectiveness of a business, it is better to compare the obtained percentage not with average values, but with the indicators of real competitors and the most similar companies.
How to calculate margin using Excel: step-by-step instructions
It also happens that the Internet is not at hand. But if you have a working PC, Microsoft Excel will help you calculate your profit margin, just create a table and enter the correct formula. Don't forget to save the step-by-step instructions for calculating margin in Excel.
- Create a new table in Microsoft Excel. Enter the following data into the table: column A - Sales price; column B - Cost; column C - Profit; Column D - Margin.
- Enter the appropriate numbers in each column.
- In column C we calculate the profit. We will need these results to calculate the margin. To do this, select cell C2, enter in the formula bar: =(A2-B2), then press Enter.
4. Now let’s calculate the margin in column D. To do this, in cell D2, enter the formula: =C2/A2*100 and press Enter. This formula will calculate the margin percentage.
Running a business today is not the easiest task for an entrepreneur. But to make this as comfortable as possible, there are many ways, for example online services like Logaster. Today we talked about important concepts and techniques for applying them in practice. We hope that we were able to give you confidence and give you several tools for even more effective management of your business.
Published byAnna Kuznetsova Updated May 1, 2022 Posted inHow To, General
Content marketer at Logaster. He knows everything about business and willingly shares this knowledge with readers. Interested in success stories of famous brands. Chief interviewer of successful Logaster clients.
Conclusion
- Income is all the finances that go to the accounts of the enterprise. It is customary to distinguish between the main income and the accompanying (non-operating) income, for example, from renting out real estate.
- Revenue is the part of the income that the company received from its main activities. It is customary to distinguish between gross and net revenue (after taxes). Revenue can be less than or equal to income.
- Profit is the company's income minus all expenses. This criterion is an indicator of the company's success. It can be positive, zero or negative.
- Calculating profits is necessary in order to know how the business is developing and what its prospects are.