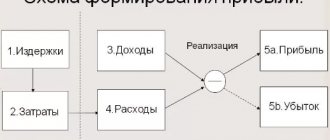
What is profit
Profit is an indicator that determines the financial success of a business, the goal of entrepreneurial activity. This concept is used to evaluate the profitability of a business and its economic efficiency. Revenue and profit are related phenomena, but not equivalent.
Attention!
Profit is the difference between revenue (financial benefit) and the costs required to obtain it.
Expenses include all costs incurred in the course of business activities. Such as: purchase or production of goods, rental of premises, utilities, wages to employees, delivery, etc.
Profit is calculated using the formula: Income (Revenue) – Expenses (Costs) = Profit.
Calculation example: Alexander Petrov produces homemade cheese. In one month, revenue from the sale of his products amounted to 100,000 rubles. During this time spent:
- for the purchase of homemade milk 30,000 rubles;
- for cheese production 5,000 rubles;
- for utilities – 5,000 rub.,
- for salary - 2,0000 rubles;
- for delivery to the buyer - 10,000 rubles.
The amount of expenses was: 30,000 + 5,000 + 5,000 + 20,000 + 10,000 = 70,000 rubles.
Profit amounted to: 10,0000 rubles. – 70,000 rub. = 30,000 rub.
Distribution options
The company has several directions for distributing net profit:
- Creation of reserves
Not only a competent investor, but also an enterprise that thinks about its future has a safety net. Part of the net profit can be used to create a reserve fund, money from which will help pay creditors in difficult times or cover losses in the event of emergencies.
- Own development
The company's development is impossible without a program to increase and improve its own assets. Using net profit, new machinery and equipment is purchased, old equipment is modernized, research and development work and retraining of workers are carried out, environmental protection measures are financed, etc.
- Implementation of social events
Unfortunately, at most enterprises, money for social activities is the last thing to go. This policy is understandable; many companies do not live, but survive. The practice of maintaining kindergartens and health camps, sanatoriums and residential buildings for workers at the expense of the organization has long been forgotten. These were the first objects in the 90s of the last century that enterprises tried to get rid of. I know there are exceptions. But the general practice is negative.
Now social policy mainly comes down to the following measures: reducing the cost of food, organizing transportation of workers to and from work, paying financial assistance and incentives for various achievements, full or partial financing of recreational activities (for example, team games, fitness and gym, swimming pool), voluntary health insurance.
- Dividend payment
This article is of most interest to investors who follow a dividend investment strategy. Dividends are often paid to shareholders from net profits. But if they are not there, this is not a reason to refuse to buy shares. Dividend companies are more interested in maintaining market share and maintaining their customer base; they do not conduct large-scale investment activities to capture new markets. And the so-called growth companies invest all their net profits in further development, which ultimately leads to an increase in the value of shares, sometimes significantly more than the amount of dividends.
Functions and role of profit received
The main function of profit is an indicator of the economic effect of the enterprise's activities. Additional functions:
- Estimated. Shows the level of development of the enterprise, gives an assessment of economic activity as a whole.
- Stimulating. Stimulates the growth of enterprise efficiency.
- Reproductive. Illustrates the difference between income and expenses.
- Test. Criterion for assessing the activities of an enterprise.
- Fiscal. Contributions to the state budget are made from profits.
The main role of profit is to show the result of the operation of an economic entity in monetary terms. This is a marker of the level of quality, demand and success of promotion of manufactured products. The profit received is distributed to expand production, improve working conditions, encourage employees, and improve the well-being of owners.
Factors affecting the calculation
Net profit depends on a number of factors, which include:
- comparability. Low net margins in one industry, such as food, may be acceptable because inventories move quickly. Conversely, there may be a need to generate high net profits in other industries simply to generate sufficient cash flow to purchase fixed assets or finance working capital;
- leverage A company may choose to grow through debt financing rather than the equity option. In this case, it will incur significant interest expenses, which will lead to a decrease in net income. Thus, the financing decision affects the amount of net profit;
- accounting compliance. A company may accumulate items of income and expense according to different accounting standards, but this may give a misleading picture of its cash flows. High depreciation and amortization expenses can result in a low net profit margin even if cash flows are high;
- non-performing assets. Net profit margins may be radically distorted by the presence of unusually large non-operating gains or losses. For example, large proceeds from the sale of a division may create a large net profit margin even if the company's operating results are poor;
- short term focus. Company management may deliberately cut costs that reduce the business's ability to compete in the long term, such as equipment maintenance, research and development, and marketing, in order to increase net profit margins;
- taxes. If a company can apply its net operating loss carryforward to its pre-tax earnings, it can record a larger net profit margin. On the other hand, management may attempt to accelerate the recognition of non-cash expenses in order to minimize the amount of the tax liability. Thus, a particular tax scenario can significantly affect the rate.
Types of profit
Profit can be made in different ways. Depending on the conditions of formation, several types of this concept are distinguished:
- Gross profit. The difference between the cost of production and the income from its sale. Includes the cost of paying tax contributions.
- Operating room. The financial result remaining after deducting all operating expenses, including equipment depreciation and operating expenses.
- Clean. The funds remaining after taxes, debt obligations, and manufacturing and selling expenses have been paid.
- Marginal. The company's income, which ensures its break-even operation. The calculation does not take into account VAT and unplanned costs.
- Unallocated. The profit remaining after subtracting all expenses, paying taxes, and paying other financial obligations, including stock dividends. It is not spent, but accumulated in the accounts of the enterprise.
- Balance sheet. Total profit before taxes. Used as a basis for taxation.
- Accounting. The difference between confirmed income and manifest expenses. The concept is used to balance the balance sheet.
- Economic. The amount remaining after subtracting implicit expenses from net income. Implicit expenses include lost income and unplanned expenses.
In addition, according to the final result, profit can be:
- provided (planned);
- maximum or minimum permissible;
- lost and negative (unprofitable).
Depending on the methods of earning, profit is divided into:
- Income from financial activities. Capital investments with favorable conditions.
- The result of the production and marketing of goods.
- Funds received through investments. Investments in securities and bank deposits.
Depending on the frequency of receipt of profit, it is:
- normalized;
- seasonal;
- excessive;
- marginal or additional.
In order to understand the main types of profit, it is worth considering them in more detail.
General information about income tax
Payers of income tax are Russian and foreign business entities registered as legal entities and operating in the Russian Federation.
An analogue of income tax for individuals, including individual entrepreneurs, is personal income tax.
Exempt from tax:
- enterprises entitled to a zero rate on income taxes;
- business entities working in the gambling business;
- business entities operating under the tax system of the Unified Agricultural Tax and the simplified tax system.
The following business entities have the right to a zero rate (subject to the conditions provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- participating in the Skolkovo project (Article 246.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- working in the field of healthcare or education (Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 917 of November 10, 2011 “On approval of the list of types of educational and medical activities carried out by organizations for the application of a tax rate of 0 percent on corporate income tax”);
- those working in the field of social services (Article 284.5 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- working in the hotel business in the Far Eastern Federal District (Article 284.6 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- sellers of their own agricultural products or processed products (Article 284.6 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Gross profit
Gross profit (GP) is the balance between income from sales of a product and the cost of this product. VP is considered until debt and tax obligations are paid off. The indicator is influenced by factors that depend and do not depend on the actions of management and the team:
- growth in production volumes;
- implementation methods;
- improving product quality;
- expansion of the range;
- reduction in cost;
- advertising company;
- location of the company;
- ecology of the location area;
- features of current legislation;
- unforeseen situations affecting logistics;
- economic situation in the country and in the world.
Attention!
Formula for calculating gross profit: VP = PE – S.
Where C is the cost of a unit of goods, and PE is net profit minus the costs of returning goods and discounts on products.
Total revenue value
Revenue shows how much money a company earned over a certain period of time. If the indicator grows from year to year, it means that the company is developing successfully. If revenue decreases, something needs to change.
Total revenue includes only income from product sales. If a company invests part of its profits or rents out an office, income from these activities is not included in the revenue figure.
What is gross revenue
Gross revenue is the result of the financial activities of an enterprise or company. The indicator includes income from any type of commercial activity, from the sale of manufactured products and any services. Let's consider the VP of a company that has a basis and additional sources of income.
Calculation example: The company produces and sells T-shirts with original inscriptions. The cost of the product is 500 rubles. Production costs:
- purchase of material, paints - 100,000 rubles. for 12 months of work;
- expenses for obtaining copyrights for drawings – 10,000 rubles. in year.;
- salary fund - 1 million rubles. in year;
- advertising expenses – 50,000 for 12 months;
- delivery – 40,000 rub. year.
Enterprise income (gross revenue) is formed from several sources:
- sale of fashionable T-shirts – 1 million rubles. in year;
- income from the rental of real estate - 50,000 rubles. in year;
- receipt of funds from investments RUB 20,0000. in year.
Amount spent: 100,000+10,000+1,000,000+50,000+40,000=1,200,000 rub.
Amount received: 1,000,000+300,000+200,000=1,500,000 rub.
VP = 1,500,000-1,200,000=300,000 rub.
An analysis of expenses and income showed that it was necessary to increase gross profit. You may have to reduce your salary fund or use the amount allocated for investments more rationally.
Operating profit
Operating profit takes into account absolutely all types of costs that support the operation of the enterprise, but differ from the expenses that make up the cost of the product. Including: depreciation of equipment, rent, unplanned expenses and other types of expenses.
Attention!
Operating profit is calculated using the formula: OP = VP - OR
Where VP is gross profit, and OP is operating expenses. Operating expenses include commercial and administrative expenses.
Calculation example:
The company buys small household appliances from the manufacturer and sells them in a store located in a shopping center. During the reporting period, goods worth 150,000 rubles were purchased. Sales revenue amounted to 300,000 rubles.
Expenses for the store's activities amounted to:
- rent – 25,000 rub.;
- salary - 50,000 rubles;
- wear and tear of the cash register and display cases – 2,000 rubles;
- other expenses – 3,000 rub.
Operating profit = 300,000 – 150,000 – 25,000 – 50,000 – 2,000 – 3,000.
Total OP = 70,000 rub.
We will reflect it in accounting
For intermediate calculations, data from synthetic accounts is used. To determine what the accounting profit is equal to in the reporting period, the accountant analyzes accounting account 99 (Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 94n dated October 31, 2000).
Account 99 reflects profitability or losses from the main and other activities of the enterprise every month. It also forms the final accounting records. Here are the main wiring:
| Wiring | Operation description |
| Dt 90.9 Kt 99 | Accounting profit from main activities is taken into account |
| Dt 99 Kt 90.9 | Loss from core activities |
| Dt 91.9 Kt 99 | Profitability from other income and expenses |
| Dt 99 Kt 91.9 | Loss from other income and expenses |
| Dt 99 Kt 84 | Total accounting profit for the year |
| Dt 84 Kt 99 | Total loss for the year |
Profitability for the selected period (as of the date of report generation) is calculated as follows: BP = balance of account 99 + balance of account 84.
Net profit. How to calculate
The definition of net profit (NP) includes an additional parameter - mandatory payments, including tax and other payments.
Attention!
Formula for calculating net profit. PE = GR (gross income) – P (explicit expenses, including tax and debt obligations).
Calculation example:
Entrepreneur Kuznetsova sells fresh baked goods. The cost of a bun is 20 rubles, the cost price is 10 rubles. Other expenses amount to 3 rubles. on a bun. In order to calculate the net profit from the sale of 1 confectionery product, you need to sum up the expenses 10 + 3 = 13 rubles. and deduct them from your income. 20 – 13 = 7 rub.
If an individual entrepreneur sells 50,000 buns in a year, the state of emergency will be: 50,000 * 7 = 350,000 rubles.
Where to find the indicator
The detailed calculation of net profit is carried out by accountants at the enterprise. This makes no sense to ordinary people. The finished results are in the financial reports. Public companies are required to publish them in the public domain.
RAS
RAS are Russian accounting standards. Enterprises that are subject to the general taxation system (and these are all our large companies) are required to prepare financial statements in accordance with RAS. And public ones also publish them on their websites.
In order not to search for websites and documents on them, I always use the service of the Corporate Information Disclosure Center. There are all types of reporting and a lot of other useful information. The main document where you can find all types of profit, including net profit, is the Profit and Loss Statement. It changed its name to Statement of Financial Results, then returned to its original name, so you can see both names.
Using the example of the Detsky Mir company, let’s look at the formation of net profit. The Report always shows results for the current and previous years. But to obtain objective data about the company’s activities, it is better to analyze the indicator for 3–5 years. As you can see, profit from 48.6 billion rubles. decreased by the end of the report by almost 6 times and became 8.2 billion rubles. More than 50% of it was “eaten up” by commercial expenses, which turned out to be almost 27 billion rubles. The positive thing is that compared to 2022, the company managed to improve its results.
IFRS
IFRS – international financial reporting standards. Companies constitute it if they interact not only with Russian suppliers, buyers, investors, but also with foreign ones. It includes information that is understandable to everyone and is considered universal. IFRS reporting can also be found on the website of the Center for Corporate Information Disclosure.
Net profit is formed in the Statement of Profit and Loss and Other Comprehensive Income. The process does not match Russian standards, so the results differ.
Marginal profit rate
To determine when a company will reach the break-even point, it is necessary to calculate the marginal profit rate (MPR). The NPP indicator helps to understand what type of costs need to be reduced in order to improve business efficiency.
NPP is profit taking into account all types of costs.
Attention!
Calculation of NPP is possible using the formula: B – PI/B*100%. Where B is sales revenue, PI is variable costs.
The rate of marginal profit is expressed as a percentage and means the portion of profit that remains from revenue minus variable costs.
Calculation example:
The company sold the goods it produced in the amount of RUR 5,000,000. Variable costs for products sold amounted to half of the revenue, i.e. RUB 2,500,000
NPP = (10,000,000 – 5,500,000)/10,000,000*100% = 4,500,000/10*100% = 45%
A high marginal profit margin does not guarantee a high net profit because, in practice, profit markers are affected by fixed and variable costs.
In their book, MBA Short Course, Neil Thomas and Barry Pearson gave the example of a company that was forced to produce products at a very high cost level.
A large electronics company has adopted a small organization that produces electronic chips. Significant sums were spent on production and trained personnel. In the third year of operation, the NPP reached 74%, with the variable costs indicator being 24%. But the enterprise’s capacity was not fully utilized; fixed costs reached the level of 205% of revenue. The company spent 2.5 rubles. more money than she earned. The following year, demand for products using chips produced by the company increased. Sales increased 3 times, profit appeared.
Knowledge of GMP for each type of product/service allows you to increase profits in the following ways:
- If a certain type of product or service shows a high marginal profit margin, it is necessary to promote this particular product/service.
- Reduce costs in the production of goods that provide a low GMP indicator.
- Ensuring an average level of GMP for new products launched into production.
Important components of competent profit management:
- Orientation to the payback point of the enterprise/company.
- Managing the profitability (profitability) of the products or services produced.
- Monitoring the level of profitability achieved with key clients.
- It is inadmissible to set extremely low prices.
For more effective business management, it is necessary to consider the above points in detail.
Payback point and break-even point
The break-even point is the point at which revenue from the sale of a product equals costs. That is, the level of sales at which the company has neither loss nor profit. To determine the indicator, you must have the following information:
- amount of revenue;
- the amount of basic expenses;
- level of fixed and variable costs.
The payback point shows at what income the funds invested in the business will pay off. To calculate the payback point, you need to know the size of investments, income and expenses for a certain calendar period. For example, for a year.
Profitability of a product or service
In practice, the calculation of the profitability of production of a certain type of goods/services is carried out taking into account assumptions. The calculation may be inaccurate due to the fact that the activities of workers or production facilities relate to the production of several goods or services. For accounting, I use approximate data based on actual or “allocated” costs.
Profitability by key clients
As the company develops, the level of customer concentration increases. Large customers appear, purchasing about 5% of the products produced. Regular customers are more demanding. Their maintenance often requires additional costs. Competent sales management involves calculating the marginal profit rate for each wholesale or regular customer.
Negative consequences of setting low prices
When sales are unsatisfactory, some entrepreneurs reduce prices in order to attract buyers. But a significant price reduction does not lead to an increase, but to a sharp drop in business profitability.
The consequences of such actions by entrepreneurs are as follows:
- sales at low prices undermine the efficiency of a business based on correct pricing;
- Dumping and price fights with competitors are possible.
If production capacity is idle, there is a temptation to lower prices. That is, increase the efficiency of excess capacity. In this case, several conditions must be met:
- limiting the period of sales at reduced prices. Carrying out promotions and discounts for a limited period. Otherwise, buyers will like low prices, and business profitability will fall;
- sell goods whose cost is lower than that of conventional products;
- reduce prices for selling goods to other regions, countries or new segments of the target audience.
If the conditions are not met, there is a danger of destroying your own business.
Concept
Net profit margin is a profitability ratio that measures the percentage of net profit to sales. Comparing the net income of two different periods or two different companies can sometimes be inappropriate due to differences in size.
The indicator is used to describe a company's ability to generate profits, as well as to look at different scenarios, such as rising costs, which are considered ineffective. It is widely used in financial modeling and company valuation.
Net profit margin is a strong indicator of a firm's overall success and is usually reported as a percentage. An increase in revenue may lead to losses if it is followed by an increase in expenses. On the other hand, lower revenues, as well as tight cost control, could lead to a further increase in the company's profits.
A high ratio means that a company is able to effectively control its costs and provide goods or services at a price significantly higher than its costs. Therefore, a high ratio may be due to the following factors:
- effective management;
- low costs (expenses);
- strong pricing strategies.
A low net profit margin means that the company has an inefficient cost structure and poor pricing strategy. Therefore, a low indicator value may be due to:
- ineffective management;
- high costs (expenses);
- weak pricing strategies.
Important! Investors should use the net profit margin figure as a general indication of a company's profitability, and begin to dig deeper into the reasons for increasing or decreasing efficiency as appropriate.
Earnings before taxes and interest
Earnings before taxes and interest are an important indicator of business profitability. Illustrates the profit generated by a company. The concept is synonymous with operating profit. Ignoring variables such as capital structure and tax burden, the indicator shows what a company is capable of. The ratio of pre-tax profit to sales varies depending on the industry. In the construction segment - 2-3%, in food trade - 4-5%. In companies providing services to the public, the figure can reach 15%.
The average earnings before interest and taxes is about 10%.
Important!
If your gross profit drops by a few points, you need to check the percentage of expenses versus sales. If it has not changed, then the fall will lead to a decrease in the rate of profit.
If sales levels sharply decline, it is necessary to partially compensate for losses by reducing overhead costs.
How to use it as an investor
An investor uses net income to perform fundamental analysis when selecting stocks for their portfolio. It is considered both in its pure form and as part of various multipliers. Let's look at the most popular of them.
P/E
P/E is the ratio of market capitalization to the company's annual net income or the ratio of the market price of one share to net income per share. With its help, the investor determines how many years the investment will pay off. The lower the number, the better. There are no standards. Compare with other companies in the industry or with the industry average. But such a comparison will be relative.
For example, a small growth company puts all its money into development. Its net profit will be small and its P/E will be high. On the other hand, there is a company that does not have large projects, but has high net profit. It has significantly less growth prospects than the former, but a low P/E. This does not mean that the investor should choose the second company. Everything is very subjective.
Experts believe that a P/E value of up to 6 is normal for the Russian stock market; anything higher is overvalued.
ROE
ROE is an indicator of return on equity. It is defined as the ratio of annual net profit to the amount of equity capital and reflects the efficiency of its use.
The higher the indicator, the more efficiently the company operates. At a minimum, it should be higher than the yield on low-risk assets, for example, bank deposits or OFZs. Otherwise, the investor will prefer to invest in them than in stocks with low profitability, the return on which is unpredictable.
If several companies are compared, they must be from the same industry. Otherwise, the comparison will be incorrect.
ROA
ROA is an indicator similar to the previous one, only the denominator shows the assets of the enterprise (buildings and structures, machinery and equipment, raw materials and supplies, cash, etc.) It reflects the efficiency of managing the company’s assets and the average profitability that the enterprise received from all sources of capital, own and borrowed. The higher the value, the better for the investor.
EPS
EPS is the earnings per share. Defined as the ratio of annual net profit to the number of shares outstanding. It is not necessary to calculate the indicator yourself. It is published at the end of the Profit and Loss Statements, both under RAS and IFRS. The higher this indicator, the better for the investor. I recommend tracking it over a period of 3 to 5 years.
Additional share issues may result in a decrease in EPS. And a buyback, on the contrary, increases it.
Marginal profit
Marginal profit (MP) allows you to find out the profitability of production and assess whether the “margin” can cover costs. The calculation includes such variables as:
- cost of raw materials;
- salaries and bonuses;
- heating and electricity costs.
Attention!
Formula for calculating marginal profit: MP = D (revenue) – PR (variable expenses).
Variable expenses are expenses that a company would cease to make if operations were suspended. They directly depend on the volume of goods produced. The total expenses indicator consists of variable and fixed expenses. Only variables are taken into account in the calculation of MP.
Calculation example:
The enterprise for the production of plastic containers produces containers with a volume of 5 liters. The cost of plastic containers is 25 rubles. Variable costs for its production are 15 rubles. MP = 25 – 15 = 10 rub.
The higher the “margin”, the faster costs are reimbursed, which means the enterprise is more profitable.
In practice, there are other options for deciphering the definition:
- General increase in funds received from the sale of goods.
- Increase in profit from the sale of each additional unit of product.
- The difference between the purchase price and the selling price.
To increase the marginal profit, the sales volume or the markup on the product is increased.
Why do you need a net profit indicator?
- For owners and shareholders, the analysis of PE by period provides an assessment of actions - the higher the PE rate, the more effective the business and dividends. Its growth will allow for new investments, consumers and suppliers.
- For counterparties, an increase in private equity will indicate the financial stability of the counterparty’s business and the ability to pay off debts on time.
- For creditors, an analysis of the creditworthiness and solvency of counterparties will illustrate the ability to pay off obligations: the more PE remains at the disposal of the business, the higher this assessment.
- Investors will be interested in the increase in profitability, on which the investment attractiveness of the entity depends.
- Employees and managers may be interested in the dynamics of the emergency indicator, since the work strategy, implementation of events and KPIs depend on it.
Margin analysis
Using marginal analysis, you can find out which products/services are most profitable. Which ones are profitable to promote and which ones are not.
Margin analysis functions:
- allows you to determine with the greatest accuracy how various factors influence changes in profit;
- clarify the profitability threshold;
- calculate the break-even point;
- plan the sales volume necessary to obtain the desired profit;
- evaluate the company's performance;
- justify changes in assortment, production capacity, and pricing.
MP is calculated according to the given formula separately for each type of product.
retained earnings
If, after receiving the proceeds, all expenses and necessary payments are paid, and part of the profit remains, it can be considered undistributed. Funds are not spent, but accumulated year after year. Dividends on shares or bonds of the company are paid from the profits deferred last year.
Attention!
Retained earnings are calculated using the formula: NP = NPPP (profit from previous years) + PE (net profit) - dividends, if they are provided for by the organization’s charter.
Retained earnings are spent only on the basis of a general decision of the owners.
Submitting a declaration
Business entities are required to submit an income tax return in any case, even if the tax itself is zero or the business entity enjoys the right to a zero rate.
Calculations are submitted and taxes are paid by the 28th day of the month following the end of the reporting period.
For the tax period, you must report by March 28 and pay tax for the year. If a business entity pays income tax every month, then reports are submitted monthly from January to November by the 28th, and the annual report is submitted by March 28.
What is book profit
Balance sheet profit (BP) is the total profit of an enterprise available on the balance sheet for a certain period of time. It includes sums of money generated through production and other activities.
To determine balance sheet profit, it is necessary to have an operating profit indicator.
Attention!
Method for calculating balance sheet profit: BP = OP - interest.
BP illustrates the effectiveness of enterprise management and production decisions.
Accounting and economic types of profit
Accounting and economic types of profit are used in accounting reports and analysis of company performance. Let's look at each type of profit in more detail.
Accounting profit
Accounting profit is the positive difference between the recorded income and expenses of an enterprise or organization. To calculate, you need to know the amount of income actually confirmed by accounting documents and the amount of confirmed expenses.
Attention!
The formula required to calculate the value of BP: BP = D (income) – P (expenses).
Based on accounting profit (AP), the balance sheet of an enterprise or organization is calculated.
Calculation restrictions
Net profit margin can be affected by isolated situations, such as the sale of an asset, which will temporarily increase profits. Net profit margin does not impact sales or revenue growth, nor does it provide insight into whether management is managing its operating costs.
It is best to use several ratios and financial indicators when analyzing a company. Net profit margin is commonly used in financial analysis, along with gross and operating profit margins.
Important! When calculating net profit margin, analysts typically compare the metric to different companies to determine which business performs best.
This indicator can vary greatly between companies in different industries. For example, a company in the automotive industry may report high profit margins but lower revenue compared to a company in the food industry. A company in the food industry may show a lower profit margin but higher revenue.
It is recommended to compare only companies in the same sector with similar business models.
Other limitations include the potential for misinterpretation of net profit margins and cash flow figures. Low net income does not always indicate a poorly performing company. Also, a high rate does not necessarily mean high cash flows.