Image: Unsplash
Anyone who is interested in the field of stock investments has come across references to the concept of margin trading. But what is it and what is this tool for? Let's look at it in our new material.
Note
: any investment activity on the stock exchange is associated with a certain risk, and when trading you can lose money - this must be taken into account. We do not encourage you to use the possibility of margin trading, but we tell you about this tool. In addition, to make investments you will need a brokerage account, which can be opened online. You can study the trading software and practice performing transactions using test access with virtual money.
Investor's Dictionary
Margin
— the amount of collateral that the broker blocks on the account during a transaction with borrowed funds.
Leverage (leverage)
— broker loan size: ratio of borrowed funds to equity.
Risk rate
— the probability of a change in the price of an asset. The rate is determined every day by the National Clearing Center.
Short (short position)
— selling an asset in order to later buy it cheaper and make money on the fall.
Long (long position
) - buying an asset in order to later sell it at a higher price and make money on growth.
Margin call
— forced closure of a losing position by the broker.
Short squeeze
— massive closing of short positions, due to which the demand for purchase becomes greater than supply, and the price of the asset rises sharply.
More on the topic:
Learn to invest
July 20, 2021 Correction: how to preserve capital when stocks fall for 5 minutes
Examples
Knowing how margin is calculated in theory, we will give examples of calculation in numbers.
- For business.
Initial data:
- transaction volume – $1 million;
- prime cost (funds spent on materials, components, logistics, wages, delivery of products, etc.) – $600 thousand;
\[ M=\frac{(1,000,000-600,000)}{1,000,000x100\%}=40\%. \]
- For banking activities.
Initial data:
- bank interest income – $14,363,060,000;
- interest expense – $8,679,068,500;
- assets – $94,733,191,700.
\[ BM=\frac{(14363060000-8679068500)}{94733191700x100\%}=6\%. \]
- Exchange trading (Forex).
Initial data:
- currency pair: euro-dollar;
- contract volume – $2000 or 0.02 lots (trading on the exchange is carried out in lots, the cost of one lot is $100,000);
- leverage – 1/400;
- exchange rate – 1.2 (1 euro equals 1.2 dollars).
\[ M=\frac{2000}{400x1.2}=6\%. \]
What is margin trading
Federal Law No. 39-FZ “On the Securities Market” defines a margin transaction as a transaction that is made using funds or securities lent by a broker to a client.
In essence, margin trading is transactions that an investor carries out on credit: he takes either money or securities from a broker. This is analogous to a loan on the stock market.
Buying instruments with the broker's money is called a long position, or long with leverage. In this case, the investor borrows money from the broker. Selling shares of a broker - a short position, or short. In this case, the investor borrows securities. For margin transactions, the broker takes a commission - a small percentage of the loan you took from him. The percentage depends on the risk rates determined by the clearing organization, for example NCC on the Moscow Exchange.
For a broker, a loan is a risk that the funds will not be returned, so he lends money or shares only for transactions with the most liquid instruments, and reserves the opportunity to execute a margin call, that is, to forcefully close the client’s position. In this way, the broker can protect both himself and the client: in the event of force majeure, it is easier to close a losing position. The list of margin securities is determined by the clearing organization, but each broker has the right to determine for himself which securities from this list to give to his clients for transactions.
Documents for margin trading are drawn up once when signing an agreement or connecting to a service. Then everything works automatically: you simply submit an order, and if execution is possible, the broker will satisfy it.
Download the application in the App Store and Google Play
Download on the App Store Available on Google Play
Kinds
Let's look at the types of margin.
- Gross. An example of calculating gross (or net margin) was given above. This is one of the key indicators of the profitability of an enterprise or an individual transaction. The calculation formula is quite simple. As part of the business profitability analysis, you should calculate the gross margin over time and compare the values over several periods.
- Profit margin shows the ratio of net profit to sales volume, i.e. business profitability taking into account operating and non-operating income and costs.
- Bank interest margin is an indicator of the profitability of banking operations. It is calculated as the ratio of the difference in interest income and expenses to the value of the credit institution’s assets.
- Variation margin is a trader’s profit on the stock exchange from the difference in quotes.
Long and short: let's look at examples
Buying long is a calculation for an increase in the price of an asset
. Such transactions are usually made in two cases: when they want to earn more on speculation or to close the cash gap when settling transactions on different days.
Let's say an investor is waiting for good news after Tesla's report and wants to buy shares of this company. He believes that the probability of growth of the stock is very high, so he plans to buy as much as possible. There are only 100 thousand rubles available in his account for purchase, so he decides to take the broker’s money and buys a Tesla for 200 thousand rubles - 100 of his own and 100 borrowed.
If his expectations are justified and the shares rise, after the transaction is closed, the broker will write off the money he lent, and the investor will receive a profit from the entire amount: twice as much as if he had used only his own funds. If the stock falls, he will receive a loss - also twice as much. This is unpleasant, so it is always worth calculating the risk before entering a trade.
Let's say the investor then decides to sell Tesla stock and buy bonds. The Moscow Exchange operates in two modes: T+2 for shares and T+1 for bonds. This means that at the time of sales his Tesla shares will be blocked in the account, but the money for the sale will be physically credited only two days later. Therefore, to buy bonds, you will have to wait one day for the calculations to come together. At this point, the investor will not be able to complete transactions due to lack of funds. In order not to wait, he can use the broker’s money: take out a loan for one day and pay a small commission for it.
Short, or short position
, is a play to reduce the price of an instrument. In this case, the investor borrows shares from a broker, sells them on the stock exchange, waits for the shares to fall in price, and then buys them cheaper. As a result, he purchases shares at a lower price than he sold, and keeps the profit from the difference for himself. When the trade is closed, the shares are returned back to the broker.
For example, an investor believes that the price of Tesla shares will decline. To make money on this, he borrows securities from a broker and sells them on the market cheaper. Let's say he borrows one share and sells it for $150. In the meantime, the price really went down and within a few weeks Tesla is worth around $100. The investor realizes that he has made good money and decides to exit the deal. He buys the share back for $100. The money for the purchase is debited from the account, but this is 50 dollars less than the 150 he received for the sale. The stock is automatically returned to the broker, the transaction is completed, and there is $50 more in the brokerage account.
conclusions
- Remember: the stock market is not a casino. You don’t come there to play, but to become the owner of an effective business conveniently and technologically.
- Do not use leverage and do not make short sales (don't go short). This is a game, not an investment. If you buy shares without leverage, no one will ever be able to sell them without your permission.
- Remember the words of W. Buffett: “The best time to sell stocks is never.” We at Arsager Management Company add to this: “Shares should only be sold when you have found others that are better.”
What is margin
How much money or shares you can borrow from a broker is shown by the margin level - the amount of collateral that the broker blocks in the account when opening a margin position. The margin is expressed as a percentage of the funds in the account and depends on the number of securities and the size of the loan.
For example, an investor has 100,000 rubles and wants to buy shares of a company at 1,000 rubles each for 200,000 rubles. There are only 200 shares: he will buy one hundred with his own money, and another hundred with credit. The broker will use a special formula to calculate how much money to block in the account so as not to incur a loss.
The risk rate for each security is published by NSD - the National Settlement Depository. For example, for shares that an investor wants to buy, it will be 25% on that day.
This is 50% of the investor’s 100,000 own funds. Margin - 50%.
The trading terminal or application displays two indicators: initial and minimum margin. As a rule, for ease of perception, they are immediately displayed in the transaction currency, although they are calculated as a percentage.
Initial Margin
— the amount of money in the account that the broker takes as collateral for a transaction with a specific security. It is different for each asset. If an investor buys a stock with full leverage and the price declines, the equity level falls below the initial margin. Now he cannot buy additional shares, because the money is blocked. But he can sell part of his assets to free up funds for purchases.
For example, an investor bought shares of two issuers for a portfolio. He purchased the shares of the first issuer with his own money, and to purchase the securities of the second, he borrowed from the broker the entire possible amount for margin trading. The shares of the first issuer rise in price, while the shares of the second fall. The investor wants to buy additional shares of the first issuer and wait out the fall of the second, but his level of initial margin does not allow him to complete the transaction. The broker calculates the margin for the entire portfolio, and not for an individual security that the investor took with leverage. Therefore, in order to purchase additional shares, free funds are needed. You can sell some of the securities or top up your brokerage account.
The minimum margin indicates at what level the broker will ask the investor to top up the account or close the position. This will mean that the broker is at risk of incurring a loss due to the loan. If the margin level has reached the minimum, and the investor does not respond to the broker’s request to exit the transaction or replenish the account, a “margin call” occurs. The broker's employees close the position themselves. This is possible because investors’ funds during margin transactions are pledged to the broker and, according to the agreement, he has the right to dispose of them in the event of force majeure.
Margin Call
The concept of “margin call” - Margin Call - comes from the times when transactions were made over the phone. The broker called the client and informed him that he urgently needed to close the position or top up the account, otherwise there would be a big loss. Now the broker does not call, but sends notifications
More on the topic:
Special project
September 23, 2021 How to build an investment portfolio with reduced risk: 5 tips for investors 7 minutes
For example, an investor bought Tesla shares with leverage and went on vacation. It turned out that the hotel did not have access to the Internet, and while the investor was looking for wi-fi or just relaxing, the price dropped significantly. The investor suffers a large loss. If there were no leverage, it would be possible to wait out the temporary drop, but due to margin funds, there is not enough money in the account to do this. The margin reaches a critical value, the broker sends several notifications, but the investor does not receive them. When the investor returns home, he will see that the deal has been forcefully closed.
Why calculate margin
Margin indicators are calculated by business owners, financial analysts, and investors. Calculations are needed to determine the efficiency of the company or the profitability of the transaction. In simple words, the margin shows how optimal the ratio between income and expenses is, and how net profit will change.
Net profit can be used, for example, to pay dividends to participants. The amount remaining after payment of income is called retained earnings and is recorded in the balance sheet account of the same name.
If net profit decreases before distribution, this indicates that costs are rising. Perhaps some areas of the company's activities are unprofitable. Or maybe this is just a temporary phenomenon, and the investments made at this stage will pay off in the future.
Knowing what the industry margin should be in good years, you should analyze the margin over several periods, as shown in the example above. Thus, it is easy to determine the reason for the drop in profits and take steps to optimize costs.
For some types of business, a factor such as seasonality should be taken into account. In the example we considered, it’s unlikely that much depends on the seasons, because profits declined in the third and first quarters. It is possible that during these periods goods were purchased at a higher cost or costs remained at the same level while sales fell.
How to calculate leverage and risks
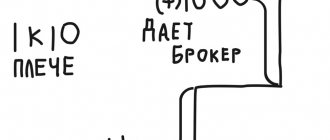
Shoulder
- the size of the loan given by the broker. Leverage shows how many times more money an investor uses than he has.
For example, an investor bought Tesla shares for 100 thousand rubles, but decides to use the broker’s money and makes a deal for 200 thousand. This is twice your net worth: 200 / 100 = 2. Leverage - 2. If he bought 150 thousand shares, his leverage would be 1.5: 150 / 100 = 1.5.
The maximum leverage on the Moscow Exchange is 3 or 6. This depends on the category to which the broker classifies the investor - CRMS or CPUR.
- CRMS is a client with an average level of risk. These are all clients of the broker at the time of opening an account. Such investors are given leverage of no more than 3 and not have access to all trading instruments.
- KPUR is a high-risk client. This is an investor with an account of more than three million rubles and has been trading through a broker for more than six months. Such clients have a maximum leverage of 6.
The profit, loss and commission that the investor will pay depends on the leverage. For example, with leverage 3, if the stock grows by 10%, your profit will be 3 * 10 = 30%.
But the loss in case of a fall will also be 30% - this is already almost a third of all the money in the account.
Commission for margin trading is also important. If an investor takes out a loan for a few days, these losses will not be noticeable. But if the loan rate is 20%, then within a year of being in the position a significant amount will accrue.
How to open buy or sell orders on CEX.IO
Guide to creating an order:
- Specify Take Profit.
There is a PiP indicator nearby. For the BTC/USD pair it is equal to one dollar. We set the expected profit, for example, 3 USD. Next, the system itself will adjust the selling price. - Specify Stop Loss.
The price must be lower than the BID (red line) so that the system does not reject the Stop, but sets it correctly. Using the selection method, you can determine the optimal PiP or specify the price manually.
If you did everything correctly, then you should start to see green trades—profitably closed orders.
Pros and cons of margin trading for investors
Not all investors use margin trading. Whether you need the opportunity to use additional funds can be determined by assessing all the pros and cons.
Source: analytical department of GPB Investments
More on the topic:
Learn to invest
April 21, 2021 IIS vs brokerage account: what is the difference 11 minutes
Real reviews
Traders have varying opinions on margin trading. Some see high leverage and active debt management as only opportunity and potential rewards, while others insist on risks and potential losses.
How to start using margin trading
Beginners should not use margin trading. It requires comprehensive knowledge of the stock market and years of trading experience. It is important for experienced investors to remember the risks, fees and try to avoid the most common mistakes. To do this, you need to adhere to a pre-thought-out strategy:
- Decide on a tool
. For margin transactions, the broker allows the use of only liquid instruments from a special list. - Think in advance where and if something happens the position will be closed
. Margin trading is a risk, so it is better to calculate it in advance. It is necessary to set a time period for the transaction for yourself so as not to lose money on commissions if the price does not move, and also determine how much money the investor is willing to lose and at what price level he will close the position. - Monitor the security price and margin level
. You need to monitor quotes in order to react to changes in time. This will allow you to close your position in time.
Mistakes that lead to losses
Margin lending must be used carefully and with an understanding of the risks. The most common mistakes that are important to avoid:
- Do not determine the exit level of a position and lose money or reach a margin call.
- Use margin trading in any transaction without assessing the risk. This leads to losses on commissions and losses, which are then difficult to recover.
- Hoping that the price of securities will still rise. This tactic is not suitable for margin trading due to losses that are multiples of leverage.
- Do not take into account interest on the loan. If the price stays the same for a long time, you can lose money simply due to the broker's commission.
If you take into account and calculate risks and think through transactions in advance, margin trading can become an additional tool for generating income from investing. But it is important to use it when confidence in the knowledge and understanding of the stock market is confirmed by real many years of trading experience.