Before we start talking about overclocking RX 580/RX 570 video cards, we first need to explain what they are. These graphics chips are nothing more than relabeled RX 480/RX 470 graphics processes with completely identical technical characteristics, which, thanks to a modified technical process, increased the operating frequency by an average of 70 megahertz and the maximum operating voltage by 0.5 volts to ensure stable operation. Thrill-seekers even flash RX 480 video cards with the BIOS from the RX 580, which in most cases work great at higher frequencies. In fact, overclocking the overclocking process for the RX 580/RX 570 is similar to the RX 480/RX 470, just remember that they can run 70 megahertz faster. The easiest way to overclock RX 580/RX 570 video cards is to use the WattMan program, which is installed with the Radeon Software Crimson Edition ReLive Graphics Driver package.
You can find WattMan in “Radeon Settings”, where you must first go to “Games”, then to “Global Settings” and click on “Global WattMan”.
Before you start overclocking, there are a few things you need to know:
- WattMan does not get along well with other utilities for overclocking graphics cards, which can cause settings to be lost and the wrong voltage, frequency, and maximum power consumption level to be set. But at the same time, you can easily use WattMan and third-party monitoring programs for overclocking.
- The heat dissipation of RX 580/RX 570 video cards is more influenced by the voltage on the graphics chip than by the operating frequency.
- What WattMan calls the memory supply voltage is actually the memory controller supply voltage and has virtually no effect on memory overclocking.
- The GPU supply voltage cannot be lower than the memory voltage. If the voltage on the processor is set lower than the voltage of the memory controller, it will automatically rise to the memory voltage.
- BIOS, when increasing the processor frequency, automatically increases the voltage on the processor if you use “Voltage Control” in automatic mode. Therefore, when you start overclocking your video card, switch “Voltage Control” to manual mode, then “BIOS” will not do anything on its own, but will use the voltage specified in WattMan.
Now you need to understand the WattMan interface in order to know what is responsible for what, what needs to be changed when overclocking the video card.
VIDEO CARDS
Reducing the frequency of the video card | Introduction
Typically, most computer enthusiasts are concerned with overclocking the processor, memory and video card: overclocking has long become a kind of sporting competition - who can squeeze the most out of the hardware by increasing, first of all, its clock frequency.
And it is quite natural that many guides have been written on overclocking computer components. The same cannot be said about guidelines for lowering their frequency - meanwhile, it is not so rare to encounter cases when it is necessary to lower the frequency of, for example, a video card. Reducing the frequency of the video card is an excellent way to combat elevated operating temperatures and a means of reducing power consumption. Gamers will be able to achieve the optimal performance per watt ratio and make their system less noisy. It is even more important to lower the frequency of a discrete video card in laptops, where operating temperature conditions are much more difficult.
Reducing the frequency of the video card | Tools
Before you start reducing the frequency of the video card, it is worth remembering that there are no two absolutely identical graphics processors (as well as any other processor), therefore the characteristics of each of them are unique - although they fit within the specified tolerances. This means that the actual performance and stability of different chips may vary, and this is completely normal. In addition, many outdated video cards are not capable of lowering clock speeds using simple software tools - and that is what we will use.
The most popular tool for overclocking video cards - and at the same time reducing their frequency - today can be called the MSI Afterburner utility. It is the de facto gold standard for any such utilities. The fact is that it is built on the basis of the classic Riva Tuner, which is a free utility with free source code designed for overclocking and monitoring the performance of a huge range of graphics accelerators on both the Nvidia and AMD platforms. With its help, you get the opportunity to change many parameters, including processor voltage, frequency and video memory speed, as well as build your own curve of the dependence of cooling system fan speed on temperature. The latest version of MSI Afterburner can be downloaded from here
.
There are other utilities for adjusting video card parameters, including, for example, ASUS GPU Tweak, EVGA Precision XOC or NZXT Cam, and if you wish, you can use any of them - especially if such a utility is included with your video card model. In our examples, MSI Afterburner will be used.
Reducing the frequency of the video card | Setting the Clock Frequency
After installing and launching MSI Afterburner, you will see something like this graphical interface, similar to the dashboard of a car (there are a lot of “skins” for this utility, so in your particular case the appearance may differ quite noticeably). Parameters of memory frequency and speed are displayed in the left “well”, voltage and temperature - in the right. All available adjustments are located between these two “wells”. Temperature is dynamically displayed at the bottom of the window, which is useful for monitoring thermal conditions as settings change.
The slider located approximately in the middle is responsible for adjusting the clock frequency - what we will need in most cases for a little underclocking. When moving the slider to the right, the GPU clock speed will increase to the values set in VBIOS. As you move the slider to the left, the frequency will decrease. We just need to reduce the frequency to the desired parameters and test the system for stability.
Reducing the frequency of the video card | Voltage setting
The core supply voltage is adjusted using the topmost slider, by moving it to the left or right you lower or increase the voltage by a certain amount of millivolts. Some cards only support voltage changes in multiples. For example, for the AMD Radeon R9 390X this number is 6 (i.e. 6, 12, 18, etc.). These settings are set at the firmware and VBIOS level and usually cannot be changed.
Reducing the GPU supply voltage is often done while lowering the clock speed to achieve maximum power efficiency. After selecting the desired frequency and voltage, click the check mark button to apply the changes.
Reducing the frequency of the video card | Setting the cooling fan curve
Theoretically, lowering the clock frequency and supply voltage of the GPU automatically means reducing heat dissipation, but in practice this does not always happen. Therefore, you may need to make changes to the fan speed versus temperature curve. Click on the gear image to the left of the fan speed selection slider and a window with a graph and reference points will open.
A graph close to a 1:1 ratio looks something like the screenshot, and these settings allow you to achieve maximum cooling of the video card. However, the cooling system can be too noisy even at fairly low temperatures, so it makes sense to try changing the ratio to get the best balance between temperature and noise level.
Reducing the frequency of the video card | Concluding remarks
The best way to check the stability of a video card after changing its settings is to run a game or some other application while simultaneously monitoring temperature, frequency and voltage indicators. MSI Afterburner has a mode where the parameters are displayed directly on top of the application window. If you encounter crashes or freezes, change the frequency and, if necessary, the voltage, and repeat the procedure until the system operates stably.
Of course, not everyone may need to reduce the clock speed of their video card - the most obvious categories of such users are gamers with laptops and cryptocurrency miners. However, everyone can experience the benefits of cooler and quieter video cards thanks to simple and intuitive software tools.
What coins can you mine?
As mentioned earlier, the best mined coins are the Ethash and CryptoNightV7 algorithms. Also sometimes the Lyra2REv2 and CryptoNightHeavy algorithms work well.
Next are the algorithms that bring slightly less profit per day, but they can still be considered for mining: NeoScrypt, X16R, X16S.
Mined coins
| Algorithms | Coins |
| Ethash | Ethereum, Ethereum Classic, Ellaism, Metaverse, Expanse, Krypton, Ubiq, Soilcoin, Shift, Pirl, Musicoin, Akroma, Callisto, DubaiCoin, Nilu, MIX, Goldiam, MOAC, Ether1, EtherSocial, WhaleCoin |
| NeoScrypt | Crowdcoin, Dinero, Feathercoin, GoByte, Halcyon, Innova, Vivo, Trezarcoin, Orbitcoin, Phoenixcoin, 01 Coin, Agena, Airin, Akencash, Banq, Cerberus, CharmCoin, Coin2Fly, CoreZ, Desire, GoaCoin, HashRental, IQ Cash, Ignition, Kicker Romm, LuckyBit, Masterbit, Momo Cash, NyxCoin, Onex Cash, Qbic, Qyno, Rapture, Sigil, SimpleBank, Sparks, SunCoin, SuperLumic, Uniform Fiscal Object, ZCore, Zixx |
| CryptoNightV7 | Monero, BBSCoin, Citadel, DigitalNote, Elya, Graft, IntenseCoin, Parsicoin, NXB, MoneroV, Lethean, Kepl, Quantum RL, Superior Coin, Wownero |
| TimeTravel10 | Bitcore |
| Lyra2REv2 | Monacoin, Galactrum, Rupee, Straks, Vertcoin, Verge, Absolute, Exvo, HanaCoin, Kreds, MTI Coin, WeyCoin |
| X16R | Ravencoin, Motion, GPUnion, Gravium, Help The Homeless, Hilux, MoonDEX, XChange, Stone Coin, Sovereign, Proton Coin, OPL Coin, xGalaxy |
| X16S | Pigeoncoin, Rabbit, Reden, RESQ Chain |
| Lyra2z | Actinium, Alpenschilling, Criptoreal, GINcoin, Infinex, MCT+, Taler, Respawn, STIM COIN, Taler, Vertical, Zcoin |
| CryptoNightHeavy | Alloy, Loki, Qwerty coin, RyoCurrency, zBucks |
you can use these algorithms on our website.
You can also .
Creating an Overclocking Profile
All overclocking profiles are created individually for each farm and cannot be used in conjunction with other farms. You can create a profile for the entire farm or a profile for a specific worker. Running settings will always override any farm-wide settings. For example, this way you can set the optimal desired settings for an entire farm, and then fine-tune each setting individually.
To add a new profile, go to the Overclocking Profiles tab of your rig and click the Add Overclocking Profile button. In the “Save overclocking as template” window, specify a profile name and click “Save”.
Create a new overclock profile
You have created a template that will later be used by specific workers or your entire farm. This template can then be copied and modified for different combinations of miners or algorithms.
The template we created will be used by all your GPUs, but the settings are different for Nvidia and AMD. You can have separate sets of settings for both GPU types in the same profile if your setup works with both Nvidia and AMD GPUs, and these will be applied to each GPU type individually.
To change your overclocking profile, click the plus sign next to your profile name and follow the instructions below based on your GPU type.
Editing an OC template
Overclocking the AMD Radeon RX 570 video card occurs using third-party software - MSI Afterburner. The tool allows you to manually edit the current parameters of the video card: increase power, adjust memory frequency, change voltage.
Before you start overclocking, you should save the current settings in a separate profile (for a quick rollback) and check the current state of the card.
If the temperature is already approaching 50 degrees, it is worth taking care of additional cooling. Otherwise, overclocking will end with a forced reboot of the computer or the appearance of a blue screen of death.
If the overclocking ends successfully, you should carefully check the performance in tests and entertainment. At this time, you need to monitor the temperature (an add-on for Afterburner, RivaTuner, will help you find out about the state of things in real time).
Temperature
In the “Temperature” section, users have the opportunity to adjust the temperature limits of the graphics chip, after which the frequencies will be reset or the coolers of the cooling system will spin up more strongly
- “Temperature” will allow you to change the critical temperatures of the GPU. "Max." This is the maximum possible temperature of the chip; when it is reached, the processor goes to a lower operating state, actually reducing the operating frequency and voltage. The “target” temperature is the temperature above which the video card will try to prevent the graphics chip from heating up, gradually spinning up the coolers to the maximum. To make it possible to drag the sliders or manually change the values manually, you need to flip the switch to the “Manual” position.
- “Limiting energy consumption.” allows you to increase the video card power consumption limit as a percentage relative to the values prescribed in the BIOS.
Overclocking the AMD Radeon RX 5600 XT graphics card
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Printed circuit board and cooling system
- Test bench and overclocking
- Gaming Performance Test Results
- Conclusion
Introduction
Recently, in our first review, we looked at the new mid-segment video card AMD Radeon RX 5600 XT using the Sapphire Pulse variant as an example and tested it in normal mode. All that remains is to disassemble the graphics accelerator and take a closer look at the cooling system and printed circuit board, as well as check overclocking and test performance in comparison with overclocked competitors. Let's move straight from words to action and start disassembling.
Printed circuit board and cooling system
The Sapphire Radeon RX 5600 XT Pulse is held together by 11 screws, all located on the back of the video card. Seven of them are responsible for the combination of the front casing and the rear skid plate.
And if they can be unscrewed without risking losing the warranty, then the four remaining ones - actually pressing the radiator to the GPU through the rear thrust cross - are no longer there. Two of them have protective seals, damage to which will void the warranty on the video card.
But when has that stopped us?
Having unscrewed all the screws at once (for this you will need two types of small Phillips screwdrivers, because the quartet of screws in the “backplate” are different in size from the rest), first remove the back plate, and then the casing.
The first one is prudently covered from the inside with an insulating film and even contains one thermal pad - a unique phenomenon!
But the radiator, in fact, doesn’t hold anything except thermal paste and a few thermal velcro strips. It is also easy to remove.
We have before us a fairly advanced design, which is based on three copper heat pipes. They are flattened at the base and soldered both to it and to the aluminum fins of the radiator.
The entire radiator is nickel-plated, except for the base, which is left copper. It is quite large for such a GPU, although its polishing quality is not the most ideal.
The heat dissipator itself contains many separate areas for removing heat from other elements. First of all, these are memory chips and power system mosfets. Adjacent batteries are equipped with their own small heatsinks, which are already visible on the board itself:
The power supply system is made according to a 4+1 scheme (GPU and memory). The GDDR6 chips remained covered with thermal Velcro, and I did not touch them so as not to damage them.
But it’s already clear that six out of eight sites have Micron GDDR6 chips soldered on – as, in my opinion, on all the latest video cards in all price segments.
AMD doesn't bother labeling its GPUs. But we already know that this is Navi 10 PRO. Exactly the same as the Radeon RX 5700 model. This is undoubtedly the main asset of the Radeon RX 5600 XT video card.
Sapphire does not betray itself in using fans with simple fastening with a single screw. Before us is the long-familiar model FD10015M12D on a ball bearing - reliable and with an adequate noise profile. And most importantly, it is widespread: if necessary, it will not be difficult to find a similar replacement in Chinese online stores.
In conclusion, we note that the manufacturer used a high-quality thermal interface. Because when re-testing after assembling the video card with our standard Gelid GC-Extreme, I got exactly the same temperatures in all modes. This is not Zotac, which uses a more effective thermal paste, but it is also a worthy solution, especially considering the not-so-expensive segment of the new product.
That's all, you can move on to the tests.
Test bench and overclocking
Let me remind you that the video card was tested as part of the following system:
- Central processor: Intel Core i9-9900K;
- CPU cooling system: Deepcool Captain 240 Pro;
- Motherboard: ASRock Z390 Phantom Gaming 7;
- RAM: G.Skill Trident Z Royal DDR4-3600 16 GB (8 x 2);
- Storage: Galax Hall of Fame (HOF M.2 SSD) 2 TB;
- Power supply: SilverStone Strider Titanium 1500W, 1500 W;
- Software versions: Microsoft Windows 10 Pro 64 bit (ver.1903), NVIDIA drivers 441.87; AMD 20.1.1.
And the following were still used as competitors for the tested Sapphire Radeon RX 5600 XT 6 GB:
- ASUS GeForce RTX 2060 Strix;
- KFA2 GeForce GTX 1660 Ti;
- Sapphire Radeon RX 5500 XT Pulse 4 GB;
- AMD Radeon RX 5700 reference.
The central processor was overclocked to 5.0 GHz for the first four cores and to 4.8 GHz for the rest.
Video cards were tested in two modes: standard and overclocked. The overclocking itself was carried out using AMD Radeon Software (Radeon RX 5600 XT and Radeon RX 5700) and MSI Afterburner (others). The efficiency of cooling systems and power consumption were tested in MSI Kombustor (analogous to FurMark).
The noise level was measured with a sound level meter (model TM-104 with a stated lower measurement limit of 30 dB) from a distance of 100 cm from the plane of the video card fans. The measured background noise level was exactly this amount – 30 dB – with the CPU cooling system running at low speed when idle (the power supply’s fan is completely turned off at low loads).
Energy consumption was measured in total for the entire system, how much it consumes “from the outlet,” including the consumption of other components and the efficiency of the power supply. And the final value was rounded to 10 W. But considering that in the test bench only the video cards and their operating modes differed, the difference in the values on the graphs makes up the difference in the power consumption of the video cards.
If in order to get correct testing results, at least in normal mode, I had to flash the BIOS to an updated one - with increased frequencies - immediately, then I did not have time to overclock it during the first day of testing. But this time I’ll tell you about him. Actually, you won’t have to describe it for a long time. MSI Afterburner does not work adequately with the latest AMD models. But fortunately, AMD Radeon Software offers advanced overclocking functionality.
The only thing that confuses us is the low overclocking limits specifically for the Radeon RX 5600 XT. I have a theory that they were asked even before the manufacturer, just before the release of real models, decided to significantly increase the frequencies (and forced users to update the firmware en masse). And perhaps the limits will be increased further in future versions. In the meantime, even the MorePowerTool utility does not work with the Radeon RX 5600 XT.
So you have to be content with what you have: a maximum of 1820 MHz GPU Boost Clock and 1860 MHz memory versus the standard 1750 MHz in both versions. Of course, not forgetting to raise the Power Limit to the available limit.
With these settings, the Sapphire video card remained completely stable in all tests - its overclocking potential is clearly higher.
You can test the temperature and noise conditions to see how well the Sapphire Radeon RX 5600 XT cooling system copes with such overclocking.
Here, to ensure the GPU temperature did not exceed 75 degrees (let me remind you that the room temperature in all my tests was maintained at 23–24°C), the fans had to spin up to more than 1600 rpm. This could not but affect the noise level; from a distance of one meter it was 39 dB. The nature of the noise of the local fans is not annoying - it is a uniform aerodynamic rustle. However, in a really quiet system unit, the video card in this mode will already be audible. However, that’s what acceleration is for.
The energy consumption of the entire system during overclocking also increases significantly and amounts to 290 W (versus, let me remind you, 250 and 220 W in normal mode with high-performance and quiet BIOS versions).
You can see that the actual GPU operating frequency has increased by more than 100 MHz compared to the MSI Kombustor test in normal mode. Coupled with a noticeable overclocking of video memory, this allows us to hope for an increase in gaming performance. I won’t completely duplicate the testing methodology for the second time in three days; you can easily find it in the Radeon RX 5600 XT review. And if you haven’t read it, it’s better to fill this gap now.
BIOS firmware
Thematic forums (for example, bitcointalk.org) provide users with ready-made stock firmware to increase mining performance on 570 series video cards. The manual configuration option using MSI's Afterburner utility is more productive and secure. The program coordinates the values of timings, power consumption and hashrate so that the board continues to efficiently mine cryptocurrency.
The final performance after flashing the BIOS depends on the manufacturer:
- Video cards with memory modules from Nitro, Expedition or ASRock can accelerate to 31.7 megahash per second.
- RX 570 video adapters with RAM from Gigabyte, AORUS or Gaming with four gigabyte memory cards provide a hashrate of up to 30.5 megahash after overclocking.
- Boards from Asus Strix can be accelerated up to 29.9 megahash in one second.
It is recommended to use GPU resources at 95% maximum to ensure stable operation of the board and avoid premature hardware replacement. Partially, the efficiency of production when installing the RX 570 can be increased by installing the Hive operating system, adapted for the operation of the farm.
How to overclock a video card?
Most modern video cards are slightly overclocked right at the factory, and some models, such as products from Inno3D and Zotac, are overclocked quite a lot. But even more hidden from the graphics accelerator with your own hands. Overclocking will help increase the frame rate in games by 10 - 20 percent, but perhaps this is just enough to achieve a comfortable 30 or 60 FPS, and thereby allow you to hold off on an expensive upgrade. It's definitely worth a try!
Preparing for overclocking
In theory, overclocking a video card resembles the same procedure with a central processor: it is necessary to find the optimal balance between the frequency of the processor cores (graphics core), RAM (video memory) and supply voltage (power consumption limit). In practice, unlike overclocking the processor, which is done through the BIOS menu of the motherboard, overclocking the video card is carried out using Windows applications.
Almost all major video card vendors have their own proprietary overclocking utilities: ASUS GPU Tweak II, Palit ThunderMaster, Sapphire TriXX, etc. The most popular due to their versatility (they support overclocking of their own and others’ models) are the paid EVGA Precision (sold on Steam) and free MSI Afterburner. It is using the second example that we will give advice on overclocking.
In addition to the overclocking utility, you will need a “warm-up” application that loads the video card to capacity. This could be MSI Kombustor, AIDA64, FurMark, Unigine Valley or any modern demanding game, preferably with a built-in benchmark. The advantage of the gaming benchmark is that it repeats the same scene over and over again, which allows you to accurately measure the frame rate before and after overclocking. In games without a benchmark, it is almost impossible to repeat the same actions twice.
General principles
When you launch MSI Afterburner for the first time, you must uncheck the box next to “Startup” so that the program does not start automatically after loading the operating system. This will allow you, in case of unsuccessful overclocking and the PC freezes, to simply reboot the system and return the video card settings to standard values.
Beginning overclockers are recommended to overclock exclusively in safe mode - without increasing the voltage of the graphics chip. By default, voltage changes are disabled in Afterburner. If you still decide to experiment with voltage, in the “Settings - General” menu, activate the “Unlock voltage control” option and restart Afterburner.
Control of the maximum power power (the “Power Limit” slider) and the maximum permissible temperature (“Temp. Limit”) is blocked in Afterburner for most modern video cards. You can use it either in proprietary configuration applications from the graphics chip manufacturer (this will be discussed below), or by flashing it to an unofficial BIOS version.
The main sliders we are interested in in Afterburner are the “Core Clock” (graphics core frequency) and “Memory Clock” (video memory frequency). We will promote them. You can find out the approximate overclocking potential of your video card model from text reviews on specialized hardware sites or video reviews on YouTube.
It is also worth considering that overclocking is always a lottery: the same video card model, depending on the success of a particular instance (ASIC current leakage coefficient), can overclock better or worse. Reviewers often receive test samples directly from manufacturers. Naturally, the best quality specimens are selected for testing, while everything goes into retail sale. Accordingly, it is better to set the core and memory overclocking frequency a little lower than what is stated by the reviewer.
Afterburner indicates the actual real memory frequency (for example, for the GeForce GTX 1050 Ti it is 1750 MHz), while the video card specifications and reviews indicate an effective frequency that is four times higher (7000 MHz). Accordingly, if you want to get a memory overclock of 400 MHz, as in the review, then you only need to add 100 MHz to Afterburner.
Having set the overclocking frequency, click the “Apply” button. If you made a mistake, click “Reset”. Now we need to test the efficiency and, most importantly, the stability of overclocking. This can be done using the above-mentioned “warm-up” utilities or games. It is recommended not to exceed a temperature of 85°C (displayed in the graphs at the bottom of the Afterburner window). If the norm is exceeded, either increase the speed of the video card fans (the “Fan Speed” slider), or slightly lower the overclocking frequency so that the PC continues to remain quiet.
If you overclock the overclocking frequency, Windows may display the error “The video driver has stopped responding and has been restored” or even show a “blue screen” (BSOD). In this case, simply restart the PC using the button on the case. Through trial and error, having selected the optimal combination of increased frequency and stable operation under load, click the “Save” and “Startup” buttons so that in the future Afterburner will start together with the OS immediately with active overclocking.
AMD Radeon Features
On average, Radeon video cards are more energy-hungry and hotter than GeForce of the same year. Therefore, they are characterized by a strict limitation of maximum power. Sometimes it gets ridiculous: some Radeon RX 480 models, for example HIS, by default operate at a frequency lower than stated. And all because the manufacturer has set too strict a power limit.
You can remove the limitation using the Crimson application (formerly known as Catalyst), which is part of the AMD graphics driver package. The WattMan function is responsible for tuning the Radeon 400, 500 and Vega series models, and the OverDrive function for the Radeon 7000, 200 and 300 series. As a result, the maximum permissible overclocking frequency and the heating level of the video card increase. Therefore, it is worth monitoring the temperature even more carefully.
Features NVIDIA GeForce
GeForce 600, 700, 900 and 1000 series video cards, in addition to the nominal core frequency, also have an automatic Boost overclocking frequency. Simply put, if the temperature and power consumption are within normal limits, the video card overclocks itself.
The latest NVIDIA 1000-series has especially strong auto-overclocking – at 300 – 500 MHz. This partly neutralizes the benefit of manual overclocking: we increase the nominal value, but the actual frequency still cannot exceed the Boost mark. Overclocking video cards without an additional power connector is especially hopeless: GT 1030, GTX 1050 and 1050 Ti.
The GeForce 600, 700 and 900 series models have weaker auto overclocking, and the temperature and power consumption limits are less strict. Therefore, it makes sense to overclock these video cards, unlike the 1000 series.
Farewell words
In order to avoid possible overheating and subsequent breakdown of the video card during experiments with overclocking, it is necessary to strengthen the ventilation inside the PC. To do this, you can either increase the speed of the case fans or temporarily remove the side wall of the case. Once the balance between increased frequency and tolerable heating has been found, the wall can be returned to its place. Also, if your video card is more than three years old (that is, the warranty period has already expired), it is recommended to replace the thermal paste. And if more than five years old, then also thermal pads (for example, on the Arctic Thermal Pad).
General overview of the device
At the time of release, AMD announced the following characteristics for the RX 570:
- Core frequency – 1168 MHz with the possibility of overclocking to 1244 MHz.
- The memory has a clock speed of 7 Gbps.
- Memory capacity – 4 Gb, manufacturer – Hynix.
- The memory bus is 256 bits wide.
These are decent figures compared to its predecessor, the RX 470. However, the increased performance had to be paid for by an increase in base power consumption. It amounted to 150W, which is already a noticeable value.
Among miners, the release of the card aroused increased interest, which was also supported by a relatively affordable price. The unavailability of the RX 470 and RX 480 cards, generated by high demand, also played a role. The first results obtained with these devices cooled the ardor somewhat - at stock frequencies the card provided a hashrate slightly higher than 21 MH/s, which is a good result for the stated price, but not outstanding. However, stock settings never guaranteed full performance from the card. In addition, it was worth waiting for the cards to be released by the largest manufacturers.
How to overclock a video card for mining: results
The top card of the 500 line shows good results. However, the high cost of the device itself makes one think about its economic feasibility. Considering how much even a top-end nitro 580 video card brings in mining, it will not be possible to recoup the investment even in a year. Fluctuations in coin rates and card values make it difficult to predict for such a long period.
Therefore, the question of whether it is worth investing in expensive cards or whether you can find something cheaper, each of the miners must decide for himself in accordance with his preferences and the situation on the card market in his city. If it is possible to purchase the RX 580 at a reasonable price, buy it; if not, look for another option.
Power Limit is the maximum amount of power is allowed to consume. This is closely related to the card's TDP, also known as "How much heat it can generate."
Those. The GTX 1070's TDP is around 150W. So at 100% power the card consumes 150W.
The power limit can be adjusted safely. When it is set to lower values, the voltage regulator becomes less stressed, power consumption is reduced, and the board cools down. And vice versa.
How much can you earn
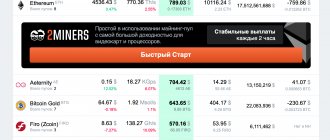
ASUS RX 570 STRIX Gaming OC mines Ethash and CryptoNightV7 algorithms best.
Next come the algorithms that bring slightly less profit per day, but they can also be considered for mining on this map. This is NeoScrypt, X16R, X16S
And finally, algorithms, the mining of which is generally unprofitable (by mining them, you will not make a profit, but will go into the red) or, at best, you will be able to pay for the consumed electricity. These are Equihash, CryptoNight and many others.
Note that there are coins even among profitable algorithms, the mining of which is unprofitable.
We will also add that if you want to receive coins of unprofitable algorithms, you can resort to the “pseudo mining” technique. In this case, you must mine any coin of a profitable algorithm and sell it on the exchange in exchange for a coin of an unfavorable algorithm.
In order not to be unfounded, we will give specific examples. All tests were performed on 10/08/2018, that is, the difficulties and prices for the given coins are current as of 10/08/2018.
Let's start with the most profitable algorithms, for example, Ethash, an Ethereum coin. Per day from 1 video card:
- Total coins – 0.0021 ETH.
- Amount in dollars equivalent to mined coins – $0.49
Quite a good indicator for 1 video card in this series.
Below is an example of mining the Ethash algorithm on an ASUS RX 570 STRIX Gaming OC video card:
Let’s immediately look at another profitable algorithm for comparison, for example, CryptoNightV7, Monero coin. Per day from 1 video card:
- Total coins – 0.0039 XMR.
- Amount in dollars equivalent to mined coins – $0.44
Below is an example of mining the CryptoNightV7 algorithm on an ASUS RX 570 STRIX Gaming OC video card:
As you can see, the profit per day is almost the same. From time to time it happens that 1 coin of one profitable algorithm becomes much more profitable than another coin of the same algorithm, but this is literally for a day (maximum a couple of days). This is due to the increase in the rate of this coin or the factor that miners have temporarily left this coin, which means you can get more coins if you mine it.
Therefore, in fact, which algorithm is profitable to mine is up to you to decide!
Next, we will consider less profitable algorithms, for example, X16R, Ravencoin coin. Per day from 1 video card:
- Total coins – 15 RVN.
- Amount in dollars equivalent to mined coins – $0.24
The profit per day is already noticeably less than that of profitable algorithms. However, it is usually a little larger. At the time of writing, Ravencoin has dropped slightly in price.
Other less profitable algorithms work on the same principle as the profitable ones. Today 1 coin of one algorithm may be profitable, and tomorrow it will be another. The factors influencing this are the same (rate and temporary departure of miners).
Well, in the end there are unprofitable algorithms, the mining of which is either, at best, a socket, or a minus.
As for unprofitable algorithms, as we said earlier, you can resort to the “pseudo mining” technique. In this case, you will be able to receive coins of an unfavorable algorithm.
This technique can also be applied to less profitable algorithms. You must start mining any coin of a profitable algorithm and sell it during the day in exchange for the coin you need from a less profitable algorithm.
You need to sell during the day for a reason: the profitable coin you are mining may fall in price, in which case you will receive the same number of coins as you would have received if you had mined a coin of a less profitable algorithm directly, or in the worst case, even less coins
Combination of price and quality: the best model to buy
The 570 series belongs to budget boards for mining; the most expensive model is the productive Gigabyte AORUS. It is recommended to invest in a GPU equipped with an 8GB RAM module to generate long-term income. The Gigabyte 570 Gaming model has the highest performance.
READ Cloud mining HashFlare: registration, tariffs, instructions
Models from ASUS are the optimal budget solution. The hashrate after firmware can reach 29 megahash, however, due to the imperfect built-in cooling system, the service life of the GPU is limited to two to three years.
A long-term investment for solo earnings or mining as part of a pool is the RX 570 ARMOR from MSI, the model lends itself well to manual tuning using Afterburner. If you have a limited budget, it is recommended to purchase used boards; it is optimal to buy used GPUs from gamers.
User reviews and opinions
Experienced miners note the low performance of the RX generation 570 relative to previous series. For example, a 470 generation board, with successful fine-tuning, can process blocks at speeds of up to 25 megahash per second, while the cost of the GPU does not exceed 13 thousand rubles.
Many users mention significant differences in the performance of RX 570 video cards with different memory modules. For example, owners of boards with RAM from Samsung can overclock the board to 31 megahash; owners of copies with memory from Hynix, after fine tuning, achieve a hashrate of a maximum of 25 megahash.
In general, purchasing a GPU 570 for mining will be of interest to experienced users who want to upgrade a working rig at minimal cost. Thanks to an effective cooling system and a manufacturer's warranty, the graphics adapter demonstrates the optimal balance between low cost and relatively good performance.