How to check a Bitcoin transaction
The chain payment system is designed in such a way that when transferring bitcoins, the transaction time constantly increases. This is due to attracting new users. Technical problems also reduce the speed of translation. In this case, you need to look at what stage of execution the transaction is at, and then make adjustments so that the payment goes through within an acceptable time frame. To do this you need to know the following information:
- the address to which bitcoins should be received;
- transfer amount;
- the outgoing address from which the crypto was sent.
There are several services that you can use to track transactions. You don’t need to register for them; you just need to enter information about the “stuck” payment.
Double spending
The most difficult method, available only to Bitcoin Core users. Recommended for advanced users as it requires command line skills and very careful handling of transaction inputs.
First you need to launch the wallet from the command line with the -zapwallettxes parameter. In addition, modern versions of Bitcoin Core require deleting the mempool.dat file from the program folder. After this, you can create a new transaction that will exactly repeat the old one, except for the increased commission.
With double spending, an important nuance arises: the old transfer at some point may also be confirmed, which is why the funds will be debited from the wallet twice. You can avoid this situation by specifying in the list of inputs for a new transaction at least one input that was used in the previous transaction.
Confirmed and unconfirmed transactions
When transferring bitcoins, all operations in the system can be divided into confirmed and unconfirmed. The first ones are those payments that were included in the system. Unconfirmed transactions include transactions that are not included in the blockchain block.
When transferring money to other users, you need to take into account that the period for completing the transaction may vary. It depends on the number of bitcoins that the user decided to transfer.
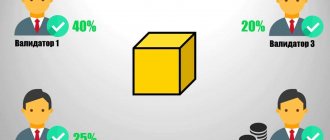
The system uses from 1 to 6 transaction confirmations or more. A one-time confirmation is a situation where inclusion in a blockchain block is performed once. The speed of funds transfer depends on the number of activations.
Using mining pool accelerators
Mining pools, which control a large share of the power in the Bitcoin system, can help users speed up transactions. At the moment, the services of two large pools are of interest:
- ViaBTC
- Antpool
First of all, you should use the ViaBTC accelerator: it does not require registration, and all the user needs to do is enter the transaction id and captcha.
If after several attempts the transaction is still not confirmed, you should proceed to using the Antpool accelerator. To register on the site you need to provide an email and password.
Transaction costs
The blockchain system differs from others in that the commission is calculated in a different way. Network participants choose its size independently, and miners process operations. The speed of miners depends on the “generosity” of users.
It is not profitable for miners to waste computer power on processing transactions with low commissions. If someone wants to transfer bitcoins faster, they should increase the reward.
Properties of hash functions
The hash ensures the security of the entire blockchain, this is its main function.
The cryptographic hash function used in mining operates on the basis of an extremely complex formula that only a few understand. It has several main properties, which we will list.
But first let's look at one more concept:
A collision is a situation where a hash function converts more than one input data array into the same summaries. Since the block is of a fixed length, it has a limited number of possible values, and therefore repetitions are possible.
Now let's look at the properties of hash functions:
- Determinism. It doesn't matter how many transformations are performed, the output is the same hash. This property makes it possible to track the original information.
- Operational computing. The hash function needs to return the original information as quickly as possible, otherwise the entire system will be ineffective.
- Collision resistance. This property ensures reliable security of digital coins.
Blockchain transaction time
Blockchain technology was created to ensure the anonymity of transactions and the security of their execution, but it is designed for fast payments. Blockchain works in such a way that transactions need to be confirmed every time.
The verification process may take up to 24 hours. This happens even if an increased commission is paid and the rules for conducting transactions are fully observed.
If one user transfers a large amount to another, the system must confirm the transactions. This requires more blocks than when making a small payment.
This leads to increased waiting, and the transfer may be delayed for several days. The following factors influence the timing of the operation:
- Transfer amount. If you need to send few bitcoins, the payment will be completed in 10-15 minutes. The market may be in a state of peak activity, in which case delays are possible, but they rarely exceed 1-2 hours.
- The state of the blockchain network, the stability of its operation. All transactions that the system must verify are in a general queue.
- Bitcoin transfers have become popular among a wide range of users. This has resulted in system load levels increasing 10-fold in recent times alone. Trillions of operations are performed every second. If the number of transactions increases greatly, the system may slow down.
- Change of course. When it changes dramatically, cryptocurrency traders and users who want to make an exchange and make money from it start working. If you need to quickly transfer bitcoins, it is better to make payments when there is a lull in the market.
- Commission size. This parameter affects the speed of the transaction. The higher the fee, the higher the chances that miners will verify the transaction.
If you need an urgent transfer, you need to either increase the reward, or simply wait until it’s time to process the transaction.
Everything you need to know about cryptocurrency. Glossary of terms
The field of digital money is full of words that are not always clear even to experienced traders. We talk about what a novice user needs to know in order to pass as one of their own in any conversation about cryptocurrency
To work in the field of digital money, you need to know and understand many terms. The editors of RBC-Crypto have prepared a list of the most important concepts and divided it into blocks: cryptocurrency, blockchain, mining and trading.
Cryptocurrency
Altcoin is a term that describes all digital assets that are alternatives to Bitcoin. The first altcoins appeared in 2011, they were Litecoin and Namecoin.
Bitcoin is the first cryptocurrency. It was released in 2009 by a person (or group of people) hiding under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. At the moment, Bitcoin is the leader of the crypto market with a share of 59%.
Cryptocurrency is a digital asset and at the same time a payment system that uses a cryptographic function to encrypt records. Cryptocurrencies are based on distributed ledger technology - blockchain. Cryptocurrency is considered an alternative to fiat money, which is issued by the government.
Stablecoin is a token with a fixed rate. Most often, quotes for such coins are tied to the dollar. There are other options. For example, the Tether company released the XAUT stablecoin, which costs the same as one troy ounce of gold.
A token is a digital asset that is related to a specific project and is issued on the basis of cryptocurrency. For example, based on the Ethereum blockchain platform, you can create tokens of the ERC20 standard, including the well-known stablecoin USDT.
Shitcoin is a coin that was released by scammers. This is also called unpromising cryptocurrencies.
Ether, Ethereum (Ethereum) is the leading altcoin by capitalization. It was released by developer Vitalik Buterin in 2015.
Blockchain
An address is a set of characters that is used in a cryptocurrency blockchain to designate a specific wallet or smart contract. You can transfer funds to the address within the coin network. Addresses can also be represented as a QR code.
A block is a list of transactions in the cryptocurrency network that were processed and confirmed by miners. Blocks are created once every certain period of time, which varies for most cryptocurrencies. For example, in the Bitcoin blockchain, a block is generated once every 10 minutes. The block, after formation, is added to the previously found blocks connected in a chain. This is how a blockchain is formed.
Blockchain (from English - chain of blocks) is a distributed registry consisting of a chain of blocks, within each of which transactions are recorded. Each subsequent block is connected to the previous one. This sequence cannot be broken or modified, otherwise the data on the cryptocurrency network will become invalid.
Wallet is an application for storing cryptocurrency. It allows users to access digital assets, transfer them to other addresses, use them for payment and other purposes.
There are several types of wallets. Cold or hardware wallets are in the form of a separate device, similar to a flash drive. They are considered the safest, since you can use cryptocurrency only with direct access to the wallet and knowing the password for it.
Browser wallets are wallets that are built into the browser as an extension.
Desktop wallets are special applications installed on a computer.
Exchange wallets are wallets that users receive when opening accounts on exchanges for trading cryptocurrency. This method of storing funds is considered the most unsafe.
Key is a set of characters that is needed to gain access to a wallet with cryptocurrency. There are two types of keys. A public address, also known as an address, allows anyone to view the contents of the wallet. Private - this key is required to spend funds from the wallet.
Pending is a transaction that has already entered the blockchain, but has not yet entered the block and is awaiting processing by miners.
A smart contract is a specific algorithm recorded in the blockchain. Smart contracts are used to carry out complex transactions, such as issuing tokens or exchanging assets through decentralized applications.
Transaction is an operation on the blockchain, such as transferring coins between wallets or using a smart contract.
Fork is the creation of an alternative blockchain from an existing one. When a soft fork is carried out, a modification is made to the previous block chain. During a hard fork, the original block chain is split into two independent ones. As a result, a new cryptocurrency is formed. For example, as a result of the Bitcoin hard fork, the Bitcoin Cash coin was obtained. It later split into two new forks: Bitcoin Cash and Bitcoin SV.
Halving is a mechanism that reduces the reward for mining cryptocurrency. For example, on the Bitcoin network, halving occurs approximately every four years. The last time this happened was in May 2020, after which the reward for finding one block decreased from 12.5 to 6.25 BTC.
Mining
Cryptocurrency mining (from English - mining) is the process of finding a block in the coin’s blockchain. Miners - people and their mining devices - receive a reward in cryptocurrency for finding a block, that is, they mine it.
A mining pool is an association of miners who collectively mine cryptocurrency. Many devices combine to find a block, and the reward is divided among all participants in the process.
A mining farm is several devices combined to mine cryptocurrency. Unlike mining pools, a farm is usually owned by one person
Cloud mining is a type of mining that does not involve the purchase of equipment. The company purchases devices for cryptocurrency mining and rents them out on a remote basis.
Mining difficulty is a parameter that determines how much computing power is required to find a block in the coin network. The difficulty of mining increases as the hashrate increases.
The hashrate or computing power of a cryptocurrency network is the computing power of all mining devices connected to the coin’s network. Measured in hashes per second. The more devices are connected to the network of a particular cryptocurrency, the higher the hashrate.
Trading
Bulls (the opposite of bears) are market participants who expect the price of an asset to rise and buy or hold it with the aim of locking in profits in the future. When a bull sells a cryptocurrency, he may go over to the side of the bears, who are shorting the price.
Volatility is the degree to which the price of a cryptocurrency fluctuates over a certain period of time. The higher this indicator, the more the coin became more expensive and cheaper, for example, over the course of a month. Assets with greater volatility carry more risks, but at the same time provide more opportunities to profit from strong price fluctuations.
A dump is the deliberate sale of a large amount of cryptocurrency in order to bring down its rate.
Keith is a major player with a large amount of funds. He may have enough capital to manipulate the price of the asset.
Long or long position is a transaction in which a trader or investor buys an asset and expects its value to increase.
Bears (the opposite of bulls) are market participants interested in falling asset prices. They can wait for the asset to fall in price in order to buy it at a better price, or they can play short, that is, hold a short position.
Pump is a deliberate increase in the price of cryptocurrency. Several users with large capital can team up to “pump” a coin and then sell it to other users at an inflated rate. Almost always, the pump ends in a sharp drop, and the profit is recorded mainly by the organizers of the scheme.
Rocket is a slang term for a sharp increase in the price of a cryptocurrency in a short period of time. On the chart, the asset looks like a large, green candle.
Snot is a slang term for a sharp decline in the price of a cryptocurrency in a short period of time. On the chart, the asset looks like a large, red candle.
Tuzemun - translated from English “to the Moon” means flying to the moon. This means a rapid increase in the price of cryptocurrency.
Flat or sideways movement is a situation when the market or the rate of a particular cryptocurrency does not rise or fall, but is clamped in a certain range. For example, if the Bitcoin rate fluctuated in the range from $9,000 to $10,000 over the course of a month, it means that it was in a flat all this time.
Hodl or Hodl is an abbreviation resulting from the distortion of the English word Hold - to hold. It involves buying a cryptocurrency and storing it for a long period of time due to the belief in a future increase in value. It stands for Hold On for Dear Life - to hold as if life depended on it.
Hamster is a novice trader who tends to make wrong decisions due to panic and emotions.
A short or short position is a transaction when a trader borrows cryptocurrency from an exchange using his assets as collateral, immediately sells it and waits for its price to decline. When the price falls, the trader will be able to buy the same number of coins that were borrowed, but cheaper, and repay the debt to the exchange.
Other terms
A 51% attack is manipulation of the cryptocurrency blockchain, which will make it possible to gain control over it. An attacker or group of attackers connects coin mining equipment to the coin network, the amount of which is sufficient to capture more than 50% of the computing power. This allows you to process transactions that are beneficial to the fraudster, for example, spending more money from the wallet than is available on it.
Airdrop is one of the ways a project can attract new users, implying free distribution of cryptocurrency. Tokens can be obtained for nothing or for completing simple tasks, for example, for registering on a platform conducting an airdrop, or for inviting other traders to register.
All Time High (ATH) is the historical maximum value of the cryptocurrency. For example, the Bitcoin rate set its ATH in December 2022 at $20,000.
Decentralized Application (Dapp) - decentralized applications and services that are open source, built on the blockchain and operate autonomously.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is a field of decentralized services, which include exchanges and platforms for opening deposits and processing loans secured by cryptocurrency.
Fear of missing out (FOMO) - fear of missing out. It is inherent in novice traders who are ready to invest in cryptocurrency, fearing that they have missed out on the growth in its value.
Initial Coin Offering (ICO) or initial coin offering is a way to raise initial capital using cryptocurrency, analogous to an IPO on the stock market. The project sells its tokens to investors and uses the proceeds for development. ICO participants hold the purchased tokens in the hope of future growth in their value.
Initial exchange offering (IEO) is an alternative to ICO. The principle is the same, but the project organizes the initial sale of tokens using a specific exchange.
— How not to lose all your bitcoins due to scammers. List of rules
— How to transfer cryptocurrency without risk and not lose all your money. 10 rules
— How to identify a promising cryptocurrency. List of rules
You will find more news about cryptocurrencies in our telegram channel RBC-Crypto.
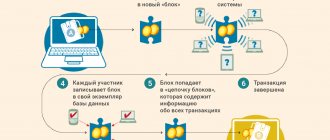
Where can I see the history of all transactions?
To track the transfer, you need to do the following:
- Go to blockchain.info. This is the official resource of the system, where you can see all the actions that have been performed by users since the creation of the network.
- In the field, enter the wallet address and other transaction data.
- Find out information about the crypto block and the operation performed.
From the information received, you can find out how many confirmations the system made for the transfer of funds. Information about the status of the operation will also be displayed here.
If you liked it, like and subscribe to the channel. We will write a lot about the world of blockchain and try to keep you up to date with current events.
If your miner is faster and sends shares more often than expected, NiceHash increases the difficulty. If your miner is slower and rarely sends shares, then Nicehash reduces the difficulty.
CPFP (Child pays for parents)
This method is intended primarily for the recipient of a stuck transaction, but in most cases it can also be used by the sender.
Without going into complex technical details, we can say that the method is based on the use of funds, the receipt of which has not yet been confirmed in the blockchain. Many mining pools are able to see the connection between an unconfirmed transfer and a new transaction that is associated with the previous address.
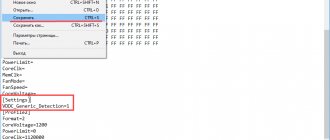
To use CPFP in Bitcoin Core, you need to go to the “Settings” - “Options” menu, select the “Wallet” tab and check the boxes, as shown in the screenshot.
After this, all that remains is to create a new transaction on the “Send” tab. By clicking on the “Inputs” button, you need to select the amount that was originally sent to the recipient’s account. If the sender performs the acceleration, the input must be the “change” that is left after sending the transaction. You can see the change amount when viewing the transaction on the blockchain.info website.
When using CPFP, you should set a fee that is sufficient to carry out two transactions at once. For example, with a recommended fee of 150 sat/B, the fee should be set to 300 sat/B or higher.
The downside of Nicehash or why it is unprofitable
Most novice miners consider Nicehash.
(read more…)
If you’re not afraid, you can study the indicators as you go, but for now, just throw 0.01 BTC on Nice, choose the most common Ether pool, say ethermine.org, and see how it works. Most likely you will find yourself in the “zero”, but you certainly won’t lose much. As all foreign video bloggers say: “This is not a financial advice”, in general, guys, we do not bear responsibility, everything is at your own peril and risk!
Nicehash.com is a service for buying and selling mining power for Bitcoins (and only for Bitcoins). Hashing power (in English “hashing power”) can be for any hashing algorithm: X11, Scrypt, DaggerHashimoto, etc. And, simply put, for mining Ether, Bitcoin, Litecoin, or whatever. Let's look at the job from a farmer's point of view.
If you want to buy hashing power on NiceHash, read our publications Ethereum Network Difficulty and Hashrate and How Pool Mining Works, and then spend a couple of weeks monitoring all the cryptocurrency indicators.
You need to understand that NiceHash is an auction. By connecting your farms or ASIC equipment, you rent out your capacity at a price unknown to you in advance.
If you want to buy hashing power on NiceHash, read our publications Ethereum Network Difficulty and Hashrate and How Pool Mining Works, and then spend a couple of weeks monitoring all the cryptocurrency indicators.
By the way, there is one more point that we missed when considering the operation of the service. When NiceHash switches between different coins and different orders of its clients, the miners lose profit... the switch takes N time and no one pays for it!
If the commission was set too low when sending, your transaction will receive the “Pending” status.
Understanding the Role of Peer-to-Peer Networks
To use the blockchain as a ledger to record transactions, you need to be able to check the blockchain to see if the transaction was made to your address or wallet.
If the blockchain was stored on only one computer and it suddenly turned out to be disconnected, then this would be very unpleasant, to say the least. In fact, the current state of the blockchain is downloaded, synchronized, and shared by many computers around the world.
These computers are called "nodes" or "nodes", and they work together in a peer-to-peer network to ensure that the blockchain is secure and up-to-date. Each of these nodes stores a complete, updated (current) version of the blockchain. Every time a new block is added, all nodes update their blockchain. Using a peer-to-peer network has certain advantages:
- You can always check the state of the blockchain using a blockchain explorer.
- You don't have to rely on just one party to know the true state of the blockchain.
- You don't have to rely on the security of a single server to know that the blockchain is secure.
- An attacker would have to simultaneously hack thousands of computers, rather than just one server.
- There is always confidence that the blockchain will never disappear, because for this to happen, all nodes will have to destroy it.
This is all very important, but the above does not mean that blockchain is now suddenly reliable enough to be used to store transactions.
For example, how do you know that all transactions on a blockchain are correct? How do you know that there are no invalid transactions in the blocks? And if there are different versions of the blockchain, how do we know which ones are true?
All these concerns are very creatively solved by the consensus mechanism , the use of which became possible primarily thanks to the peer-to-peer network.
Ethereum
The most common reason for freezing is making transactions with fees that are too low. If there are any transactions on the network with higher fees, then miners have no incentive to confirm those that pay them little. This is why transactions with low fees have to wait longer. Why is the transaction stuck?
What to do to prevent transactions from remaining unconfirmed
Mobile wallets often cannot predict future network load, so may not be suitable in the event of a very sudden increase in network activity.
There are other acceleration options, such as "RBF", which stands for Replace By Fee.
Actions on the part of the recipient when the transaction hangs
Of course, a transaction that is stuck is a problem, especially if the money does not come to you - time is running out, there is no way to cash out the crypto and spend fiat for your needs.
The cryptocurrency recipient can request the sender to use CPFP or Opt-In-RBF features
In case your wallet allows you to spend money from unconfirmed transactions, the problem can be solved using CPFP. You need to act in the way that was described earlier. Resend crypto with high fees. This transaction will jump the queue and be confirmed much earlier. If the new commission is sufficient, the transaction will be confirmed in the next blocks.
Another option is to ask the person who sent you the money whether they used Opt-In-RBF or not. In this situation, he can resend the funds with an increased processing fee if you ask him to do so.
Send and receive crypto via unloaded platforms
Use uncrowded cryptocurrency platforms to send and receive cryptocurrency. It is not necessary to use Bitcoin, the cost of transfers within which is tens of times higher than that of Dogecoin (DOGE). Young platforms and those that are already more or less well-known and at the top of the cryptocurrencies represent more valuable peer-to-peer networks than Bitcoin. Since we remembered about dogecoins, let's say that the commission in this system is only $0.007, while for bitcoin it is $1,152.
Incoming transaction
Copy your own Bitcoin receiving address.
Bitcoin
If you have sent an unconfirmed Bitcoin transaction, there are a number of services that claim to speed up confirmations, such as https://bitaccelerate.com and https://pushtx.btc.com. The effectiveness of these services is not guaranteed. It is impossible to find a completely reliable service that will best speed up a transaction.
§ If the commission was set too low when sending, then your transaction receives the “Pending” status. You can also check if there is an outgoing transaction in the blockchain explorer. If a transaction has 2 destinations, you can follow these steps to speed it up. This method is called child pays for parent (CPFP).
Bot accelerator in Telegram
Telegram bot @FastTXbot was created to automatically speed up transfers in the Bitcoin network. To use it, you need to send the number of the pending transaction and wait for the result. In fact, the bot uses one of the previous methods - acceleration through Antpool. In this case, the robot automatically does all the work for the user: just wait for the notification about the result of the procedure, which usually arrives within 10 minutes.
This method does not always work for transfers that use a very low commission.