What caused Overstock.com shares to rise by 400%
Shares of Overstock.com Inc are showing rapid growth amid the crisis.
Meanwhile, the online retailer has become embroiled in a bitter battle with Wall Street over controversial plans to issue a first-of-its-kind digital dividend.
The dispute stems from Overstock's attempt to impose requirements that would limit trading of new securities to a specific marketplace, rather than allowing investors to buy and sell them wherever they want. Earlier this month, the company sent a letter to a number of financial firms reminding them that all digital dividend trading must take place on a platform called tZERO, which is owned by Overstock.
The retailer's lawyers repeated that demand during a conference call with brokers that industry executives said quickly turned into threats of legal action, although Overstock denies such claims.
As we know, the digital dividend, which will provide investors with one preferred share for every ten common shares, will be issued on Tuesday. According to company representatives, some data will be stored in the form of a blockchain for security purposes. However, they claim that it is not a new virtual currency.
If Overstock's dividend plan is successful, the implications for US markets will be significant. More companies may decide to get into digital assets or add restrictions to their shares, especially if they find that it gives them more power over investors. On Wall Street, brokerage firms and exchanges are not willing to tolerate the launch of any security that could lead to a monopoly and cut them off from trading and listing fees.
What does the SEC think?
The issue of whether a company can determine where investors are allowed to sell their securities has caught the attention of the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), which has long focused on ensuring shareholders get better execution for their trades at low prices. While the regulator signed off on Overstock's digital dividend after careful analysis, it is aware of the tZERO controversy and is able to assess the pros and cons, people with knowledge of the matter said.
"This situation raises fundamental questions about shareholder rights," said James Angel, an associate professor at Georgetown University's business school. He owns shares of Overstock and follows the company closely.
In a statement, Salt Lake City-based Overstock said it is perfectly legal for the company to limit trading within its own platform. Its representatives also expressed the hope that
market participants will adhere to this requirement. “Otherwise, like any issuer of securities, we will take the necessary measures to ensure compliance with trading conditions,” the company said in a statement.
The SEC's scrutiny of Overstock's dividends is nothing new. The company reported that in October last year it received a subpoena from the regulator demanding that it provide plans for organizing the circulation of securities. In its official statement on May 7, the company said it fully agrees with this requirement.
An SEC spokesman declined to comment.
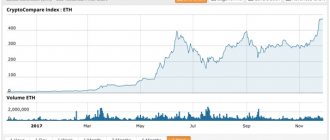
Jump 400%
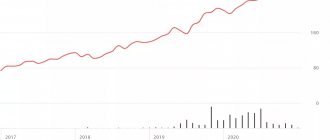
Overstock's dispute with Wall Street comes at a pivotal moment for the company as it benefits greatly from the fact that most people are forced to shop from home. Its shares have jumped more than 400% since mid-March, one of the best performances among U.S. companies. Recall that last year the price of Overstock securities fell by 48%, and in 2018 - by 79%.
The company's share price fell 11% to $15.19 on Monday, its biggest daily drop since April 22.
Complaints from brokers and exchanges about digital dividends are varied. For example, some believe that limiting trading to a single platform would harm liquidity and make selling securities difficult and costly for investors. Dinosaur Financial Group is the only broker doing business with tZERO. According to an April press release, he plans to charge a 1% commission. This solution is contrary to the usual rates that many retail brokers offer. Dinosaur Financial is led by Glenn Grossman, whose son is tZERO's chief executive.
Still, Overstock says it's not unusual for financial industry professionals to have family ties. A representative for Dinosaur declined to comment.
Overstock's dividend already has a trading ticker - OSTKO. Some buying and selling transactions have taken place in the lead up to the official issue, but these transactions will be executed after investors receive shares.
Bidding platform
GTS, which is the nation's largest market maker of over-the-counter securities, was trading the new digital dividend and was one of many companies that received a letter from Overstock's lawyers on May 7. This restriction, according to GTS Chief Executive Officer Ari Rubenstein, violates the principles of freedom and fairness in the market, and also complicates the task of obtaining the best price for customers.
“This is completely contrary to everything we believe in,” Rubenstein said. “The American market system does not involve anyone imposing a location and charging exorbitant fees.”
On Friday, GTS received permission from the Financial Services Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA), the main regulator for brokers, to trade dividends, a move that could potentially negatively impact Overstock.
TD Ameritrade recently told its clients who own Overstock shares that they cannot trade digital dividends through the firm. Clients wishing to buy or sell securities "will need to use other mechanisms," the letter said.
Burn's obsession
The online retailer's digital dividend plans have sparked controversy since they were first made public in mid-2019. The company said it created the security system in part to push Wall Street toward blockchain. As you know, the company's founder, Patrick Byrne, is obsessed with this technology. He left Overstock last year amid a scandal surrounding his romantic relationship with alleged Russian spy Maria Butina, who was jailed after failing to register as a foreign agent.
Overstock aims to expand tZERO's business by limiting trading to its platform. The new securities could attract tens of thousands of new investors to the digital token marketplace.
Critics also argue that this is the company's way of trying to deter short sellers, which it has been battling for years. This is because traders betting against the company will be required to provide digital dividends to the brokers from whom they borrowed the securities.
The potential difficulty of the process will prompt many to cover their short positions, according to some market participants. The company's share price soared within weeks of announcing a digital dividend last year.
In its statement, Overstock said the digital dividend would not have any impact on short selling.
Chesapeake Energy is currently experiencing the worst period in its 30-year history.
Falling oil and gas prices, coupled with rising costs of maintaining shale infrastructure, have driven the stock price down 94% since the start of this year. The company's total debt is $9 billion with a capitalization of just over $100 million. In its latest report to the US stock regulator SEC, the once legendary oil and gas corporation this week explicitly stated that it was no longer able to continue its business activities. The company has taken such unprecedented measures as transferring employees to quarterly instead of monthly payments, as well as paying an annual salary to all 20 directors in advance so that they do not start leaving en masse. Continuation
How the forecast method becomes a cause of Out-off-Stock/Overstock
The most common methodology included in the ordering policy is the construction of forecasts. For example, let's look at sales for some past period: a month, two, three. Based on these data, we will get the average daily sale, and then we will plan sales for some period in advance - say, two weeks.
The longer the lookback period, the less impact rising and falling sales have on average daily sales, slowing the speed at which replenishment responds to changes in demand. To calculate the order size, min-max criteria are most often used. The maximum is either a specific value or a period by which we multiply the average daily sale to calculate the quantity of goods to be replenished. The minimum is the quantity of a specific item (SKU) at which we decide on the need for replenishment. In other words, if the balance has not reached the minimum quantity, for example, for a package order, then it will not be replenished. Another confirmation of this is that very often companies react rather slowly to changes in demand.
On the one hand, a replenishment policy based on forecasts creates a long response time to changes in demand. On the other hand, demand at each retail outlet (PP) is subject to significant fluctuations.
If you respond slowly to changes in demand, then when it grows, the remaining stock is sold off, which leads to a lack of goods and lost sales. If the average daily sales calculation period includes a period of sales growth, an increased replenishment batch will arrive at the store. Typically, due to the same long response time, this will happen after a surge in demand and this stock will be excess. Plus, logisticians or category managers use protective coefficients, which are usually used if the stock of goods has dropped to zero. This further leads to excess inventory.
Long reaction times lead to long replenishment times. Consequently, each individual SKU is replenished less frequently because it is not contained in every delivery vehicle. You can easily verify this using the residual graph:
You can understand how this situation is typical for the entire assortment by comparing the average frequency of sales and replenishment (in days) over a short period of 2-3 months. The table below shows the result of this comparison: 85% of SKUs were replenished less than once every 2 weeks, but 84% of SKUs were sold much more often. This is only possible when each delivery does not replenish everything that was sold after the previous delivery. Consequently, the replenishment time for most SKUs is many times longer than the period between their sales. The task of an effective distribution function is to synchronize these values, otherwise Out-of-Stock will inevitably occur for some positions, and Overstock for others.
The central warehouse (CS) or distribution center (DC), which the network has, is designed to largely solve problems with distortions in the distribution of goods across TT. However, most chains use DCs to obtain discounts from suppliers and quickly send goods to TT themselves. As a result, excess inventory shipped to some stores depletes the DC's inventory and causes a "hunger" of the same goods for other stores. In this case, the same SKU is in excess in one store, and the same SKU is in zero supply in another (as shown in the graphs below).
In addition, for the entire assortment, regardless of the sales speed in each location, as a rule, the same approaches are used for replenishment. With a long response time, you can only count on the fact that good protection will be provided only to those SKUs with a slower sales speed.
One important element of the solution is the establishment of a buffer for each SKU (not to be confused with safety stock or physical stock at the storage location). Understanding the size of the buffer also allows us to more accurately evaluate excess inventory, as inventory that exceeds the buffer.
If you distribute the assortment into buffers, as shown in the table, you can see that there is excess inventory in each group.
Paradoxically, the forecast method provides the greatest protection for the slowest SKU. With the change in demand for fast SKUs, this policy works much less successfully. From this example in the table, it can be seen that SKUs with buffer 1 have 50% inventory protection in the overall inventory structure, and faster SKUs with buffer 3 or more are only 27% protected by inventory.
The greatest threat to the stability of the store is the lack of goods that its visitors are accustomed to buying. Using the buffer concept, you can simply determine the most popular products in this outlet (not to be confused with ABC analysis). The buffer is nothing more than a reflection of the SKU sales rate during the replenishment period. Occasional buyers cannot generate high sales, therefore, most of the SKUs that sell in above average quantities (need to be determined in each category and price range separately) are generated by your regular and loyal customers. If we check the reliability of availability according to SKU data, we will get the number of customers who are dissatisfied with the lack of a familiar product and the approximate size of the financial potential of the network.
To check the level of lack of goods or Out - off - Stock, data on daily balances for 1-2 months is sufficient. To do this, we daily look at the dynamics of the number of SKUs with a balance of zero.
If you build a graph based on daily balances, then in this example you can see the absence of 20% of the assortment on an ongoing basis.
But there is an important note. Not having SKUs that sell 10 per week for 1-3 days is not the same as not having SKUs that sell once a month for a week or two. In the first case, we risk upsetting many more of our regular customers. Therefore, to assess the magnitude of this effect, it is worth looking at daily balances.
Photo: Daily store balances (periods of SKU absence are highlighted with shading)
Current forecast-based replenishment systems create the risk of the customer not satisfying his primary need - finding and buying what he is used to every time he visits the store (we are talking about regular and/or frequent purchases). The higher the level of satisfaction of this need, the stronger the attachment of customers to this store and the network as a whole.
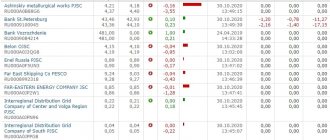
Five new shares on St. Petersburg with a potential of up to 150%
In our general review of upcoming new products, we deliberately avoided promotions with maximum targets, focusing on larger businesses. Now let's look at the top 5 small but promising companies - from those that will start in St. Petersburg on Tuesday. The list includes young and mature market players with a size of less than $5 billion.
The Beauty Health (SKIN)
This company is a candidate to revolutionize the cosmetology market, as the inventors of Botox from Allergan once did (now the patent belongs to Abbvie ). Beauty Health has been heading towards success since 1997, until it brought to the market a technology for skin rejuvenation without injections.
Today, its flagship product is HydraFacial (vacuum facial cleansing) treatments. To understand how quickly they become popular, just type this name into a search engine. Dozens of new sites on this topic have appeared on the RuNet in less than a couple of years.
Beauty Health's financial performance is impressive: sales growth in the last (second) quarter was 370%, gross margin exceeds 70%. The first profit appeared in the report at the end of June. 100% of house recommendations are worth buying. The average target for the promotion is +11%, maximum up to +22%.
Vista Outdoor (VSTO)
The largest of the big three American gunsmiths, along with Smith & Wesson and Sturm, Ruger & Co. Nominally it is a store of sporting and outdoor goods, but in fact the main revenue comes from the production and sale of firearms and ammunition for them.
Unlike the old-timers of the market, Vista Outdoor is steadily expanding its business. It has about 40 of its own brands, including 25 gun stores, factories and service centers in 11 states and sales centers in 30 locations across the country.
The company looks confident in terms of finances, while the shares are very cheap. Sales growth in the last quarter was +38%, profits +149%. P/E ratio is only 8, moderate debt of about 62% of assets. The stock is up 84% year to date. The consensus forecast is for another +26% over the next year.
Open Lending (LPRO)
The fastest growing SPAC of the last two years. The company has developed a platform for automatic risk assessment when issuing loans called Lenders Protection. Creates robotic models of borrower default for sale to banks and other financial institutions.
By the time it went public, the company was already profitable. There was a drop in performance at the height of the pandemic, but later revenue and profit volumes increased significantly. Thus, in the last quarter the company showed sales of $61.13 million (in pre-Covid 2022 it was 3.5 times less) and EPS of $0.6 per share (+200% over two years).
Shares are still lagging behind growth in fundamentals. After soaring by more than 200% last year, the stock has been fluctuating in a huge range of $32–44 per share in recent months. And, importantly, it is now right at the lower end of the range. The stock is slightly oversold according to RSI (=38). The house consensus gives a potential of +47% with 91% recommendations to buy.
Overstock.com (OSTK)
The company rose during the dot-com crisis by reselling inventory from bankrupt online stores. As a result, she began to specialize in home decor, toiletries and furniture. Her star rose for the second time during the COVID-19 pandemic, when demand for everyday items with delivery surged.
Today, the company has several businesses, including selling handmade gifts, which has become another strong trend in the US in recent months. Financial indicators are strong: profit growth of 135% this year, return on assets above 70%, no debt.
The stock is up nearly 70% year to date. Technically, the stock maintains an upward trend, holding above the 20-, 50- and 200-day moving average. The share of purchase recommendations from investment houses is 100%. Average forecast for the year +47%.
Danimer Scientific (DNMR)
The smallest (just $1.55 billion) of the companies listed, but probably the most valuable of them all. Belongs to the small capitalization class. It went public in December last year as part of a SPAC (reverse acquisition) at a valuation of over $5.5 billion, but has since gradually cooled until it has settled down around current levels.
The company's main interest is Nodax technology for the production of biopolymers. It allows the production of plastic fibers, films, adhesives and paint coatings from biomass (waste): straw, sawdust, edible fats and oils. This is a small but rapidly growing niche in the chemical industry.
Danimer Scientific is currently unprofitable, but revenue has grown by 62% over the past 1.5 years. The company has $417 million in accounts and annual outflows of less than $100 million, making it an interesting takeover target. 100% of investment houses recommend this stock for purchase with an average target of 147%.
Short
We looked at the top 5 companies out of more than 40 listed on the St. Petersburg Stock Exchange on Tuesday. They have the best potential for rapid growth in the medium term. Of these, three are of interest due to promising technology: SKIN , LPRO and DNMR . Two more are market old-timers who caught the growing trend due to the shift in demand for online shopping ( OSTK ), as well as tightening gun regulation in the United States (relevant for VSTO ).
The range of targets for the next year for them is from +11% to +147%, the share of purchase recommendations from leading investment houses is at least 90% for each of the shares.
BCS World of Investments