Delisting is the exclusion of securities from quotation lists or their complete withdrawal from the stock exchange. Delisting is carried out for various reasons. This may be a decision of the issuer, or the non-compliance of securities with the conditions necessary for participation in trading. From this article you will learn what listing and delisting of securities are, what grounds exist for it, and what the delisting mechanism is. We will also talk about what actions should be taken by a shareholder – the holder of securities for which delisting is being carried out, and we will look at examples.
What does delisting of shares mean?
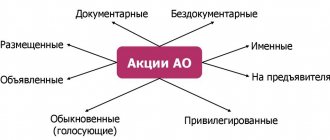
Listing is the addition of items to a list that meets certain requirements. When listing securities admitted to trading, the stock exchange is guided by certain rules designed to protect the interests of investors. Delisting, on the contrary, means exclusion from such lists.
In international and Russian legislation, the term “delisting” is interpreted differently. This is due to the difference in the structure of stock exchanges. For example, the New York Stock Exchange does not have levels; uniform rules apply to all securities. In European countries, on the contrary, there is a certain level listing structure. According to international financial terminology, delisting shares is their complete exclusion from trading. After leaving the exchange, the issuer can place its shares only on the over-the-counter market.
In Russia, delisting means that the securities of a given issuer will be transferred to a lower level. The Moscow Exchange has three levels of listing, which we will talk about below.
If shares leave the quotation lists (first and second levels), this means that they can continue to be traded on the stock exchange as securities.
The higher the listing level, the lower the investor's risk. The first level contains the most reliable securities with high liquidity. Conversely, the lower the level, the higher the risk.
For each level, certain conditions must be met, which are determined by the stock exchange based on stock market legislation. These include:
- "Age" of the issuing company. Newly registered companies cannot list their securities at the first level.
- Control features. There are certain requirements for the company's management and founders. This concerns the organizational structure, participation in the management of other companies, etc.
- Submission of annual reports. Financial statements must be made publicly available.
- Number of securities in free circulation, etc.
The listing position of the issuer helps the investor to navigate when compiling a portfolio of securities. The listing and delisting procedure is established by the stock exchange, whose activities are regulated by stock market legislation and supervised by the Central Bank.
What should an investor do in case of delisting?
Protecting one's own investment is the first concern of a shareholder during delisting. To this end, financial experts recommend paying attention to the following points:
- Clarification of all the circumstances. Even illiquid companies sometimes have reserves for a favorable forecast.
- Refrain from selling shares. Negative information about the issuer sharply reduces the value of its financial instruments. It would be wiser to buy time or keep the assets with you altogether.
- Studying the offer. During the consolidation of an organization, the terms of the offer are the most favorable. This is due to the fact that majority shareholders want to buy up to 95% of the total shares and the price for them is sometimes set above the market price.
- Consideration of over-the-counter offers. If the investor is not interested in the price of the exchange platform or offer, he has the right to sell assets on the over-the-counter market with the help of a broker.
- Clarification of dividend policy. Some organizations continue to pay dividends even after delisting. Holding unquoted shares along with regular interest payments is a good option for shareholders with a small holding.
- Obtaining information about plans for re-issuance of shares. During reorganization, some companies exchange unquoted securities for assets issued by a new legal entity.
Delisting is an option for the development of stock exchange events, for which it is important for every investor to prepare. In many ways, the issue can be resolved by preliminary diversification of the portfolio. With the right combination of securities, in the event of delisting and other risks, the income from some investments will compensate for the losses of other shares.
Reasons for delisting
Delisting in exchange trading can be carried out on the following grounds:
- Bankruptcy or unsatisfactory financial position of the issuer. This conclusion is drawn on the basis of the presented financial statements and additional documents on the financial position that are required to be submitted.
- Failure to submit financial statements on time.
- Non-compliance of financial instruments with established rules. An opinion on such discrepancies is made by the Exchange Expert Council.
- Company initiative. The decision to leave the exchange can be made by the management of the issuing company for several reasons, the most popular of which are the following:
- reorganization;
- consolidation of securities (purchase of the full value by one or more majority shareholders);
- reluctance to disclose information about financial position.
Pros and cons of delisting
Delisting of securities is a mechanism that has both advantages and disadvantages. The positive aspects include the following:
- No publicity costs. These are listing costs and some other costs associated with maintaining the company's image as a public company.
- Simplification of control over document flow and financial reporting indicators.
- Minimizing the risks of disclosing information about the financial condition of the company.
The main disadvantages include the following:
- reduction of credit limits provided by banks;
- falling stock prices;
- problems arising during the sale of the company;
- decrease in investment attractiveness.
What is it and why is it carried out?
Delisting of securities is the process of removing them from the list of shares admitted to trading. This is possible in two situations:
- The company ceases trading in its securities.
- Downgrading of listing level.
I will note 3 reasons for this procedure:
- Inconsistency with the requirements of the exchange. This also includes the refusal of the issuing company to provide reporting documents.
- Dire financial situation or bankruptcy.
- The wish of the company itself.
Delisting procedure and levels
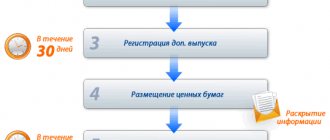
The standard delisting procedure includes several stages:
- The stock exchange or issuer prepares an application and sends it to the Delisting Department.
- Trading in shares is suspended for 15 days, but not earlier than 14 days and no later than 3 months before the conclusion is made.
- The application is reviewed within a month.
- An expert opinion is issued.
- If the decision is positive, the majority holders of the securities send a notice of delisting to the remaining investors.
- An offer to repurchase securities is published. Holders of more than 30% of the package can submit an offer.
Majority shareholders are the owners of shares of at least 20-25%. This size of the package allows you to participate in the management of the joint stock company. Minority owners are considered to be holders of smaller blocks of shares.
Above we looked at what delisting on a stock exchange is. Below we list the listing levels assigned by the exchange:
- The first level is securities characterized by high liquidity and low risk. These are OFZs, as well as shares and bonds of large companies.
- The second level is reliable securities that do not meet the requirements for First Level instruments. There are no government securities in the second level.
- The third level is high-risk instruments, the so-called shares of the third and fourth echelons. These include securities of new issuers, as well as companies that do not meet the requirements for inclusion in quotation lists.
Benefits for the issuer
The listing process can be lengthy and expensive. In addition, in order to remain on the list, the issuing company is required to submit its reports every six months. Why does any developing company go to all this in order to get listed on the stock exchange? There are two main reasons for this.
The more trust, the higher the demand. The company's weight and influence in the market is growing. In the eyes of investors, partners and even competitors, the appearance of a company among participants in stock trading means its entry to a qualitatively new level.
The higher the demand, the greater the capital. Once included in stock exchange lists, investment attractiveness increases significantly. Now, for the development of the organization, a loan will not be required, because if necessary, the company can simply sell part of its shares.
That is, for the issuer, the approval of his application and the inclusion of shares in the quotation list of the exchange in any case brings a significant increase in capital.
Forced delisting
Delisting of shares can be initiated by both the issuer and the stock exchange. Forced delisting of shares is the exclusion of securities from the quotation lists by decision of the exchange. Such a decision may be made because the shares do not meet certain requirements. These reasons include:
- Bankruptcy of the issuer.
- Reorganization or liquidation of the company.
- Failure to submit financial statements or provision of inaccurate data.
- Violation of the rules for issuing securities.
- Failure to pay listing fees.
Delisting: the legislative framework of the Russian Federation and its differences with the databases of other countries
Both procedures, both listing and delisting, have rules clearly defined in the legislation of a particular region that are necessary for execution by both shareholders and representatives of the exchange. The main regulatory framework governing the rules for inclusion in the register in the Russian Federation is the federal laws “On the Securities Market” and “On Joint-Stock Companies”. The procedure for the admission and disposal of shares from organized trading is regulated by Order No. 10/98 of 2010, which was finalized and improved in 2013.
The concept of delisting procedure is the exclusion of shares from the quotation register of the exchange. In Western countries, this means that the issuer withdraws all its securities from public circulation, and the company becomes private. In the Russian Federation, delisting does not mean the cessation of trading, but only implies the inability to participate in the trading of listed shares; these securities can easily circulate on the organized market in the “unlisted” category. At the same time, the issuing company can remain public.
The delisting of shares in the Russian Federation is not yet a fully corrected procedure; the legislative framework relating to it needs significant improvement. This is due to the long period of time during which there were no stock exchanges in Russia (from 1917 to 1992). In this regard, different Russian exchanges may have their own requirements for listing shares. Since 2013, active work has begun to improve the legislative framework of the securities market in Russia.
The reform affected the simplification of the admission system to the register, which became more understandable and transparent, providing the exchange organizers with the opportunity to determine part of the requirements for listing/delisting of shares and much more. Regardless of the location of the delisting procedure, all securities removed from the stock exchange can be traded on the over-the-counter market. Another nuance of regulatory aspects in the Russian Federation regarding the delisting of securities concerns the possibility of a decision being made solely by the director of the company (chairman of the board of directors) without the participation of other shareholders. For reference, in European Union countries at least 70% of participants must sign the application.
↑ to contents
Delisting at the initiative of the issuer
One of the most common reasons why an issuer decides to delist shares is the consolidation of a controlling stake in one or more shareholders. Most often, these are founders who have decided to manage a narrow circle of people or individually.
Another reason is the reorganization of the joint stock company. In this case, the majority owners decide that the shares will be delisted, and then, after the reorganization, other securities will be issued, which can also be traded on the exchange.
The third common reason is reluctance to disclose information about one's financial situation. It should be noted here that the stock exchange requires not only standard financial statements, which are already publicly available, but also some other data. Information about debtors and creditors, income of founders, movement on current accounts, tax returns, etc. may be required.
Mechanism for excluding an issuer from the quotation list
The delisting mechanism is regulated at the legislative level, and, as is known, the laws in each country have their own nuances. Trading platforms in Western countries have already developed a general mechanism that allows minimizing all the negative consequences of this procedure. First, the delisting must be approved by at least 75 percent of shareholders. The issuer is required to notify about the procedure twenty days before the upcoming cancellation of the listing. On the NYSE, voluntary delisting can occur if the procedure is approved by the board of directors.
In our country, until recently, there was no time limit between the decision to cancel a listing and the cessation of circulation of securities on the stock exchange. The right to make a decision to exclude securities from listing is vested in the head of the issuing company or the board of directors. The law also does not provide for mandatory publication of information about this decision.
Currently, the rules of the procedure have become a little more complicated due to changes made by the Moscow Interbank Currency Exchange.
The application for delisting shares is now considered within a month by the exchange commission. The decision to cancel the listing is made within 15 business days, after which trading in shares ceases for a certain period, ranging from 2 weeks to 3 months. The decision may be not only positive, but also a refusal to delist.
Protection of the interests of minority shareholders by law
The rights of minority shareholders (owners of less than 20% of the issuer's shares) are directly proportional to their shares in the authorized capital.
The main risks of minority shareholders include:
- Forced repurchase of shares.
- Forcing to sell securities at reduced prices. In this case, not entirely legal methods may be used.
How does legislation protect the interests of minority shareholders? Firstly, in any type of reorganization - be it a merger or accession - a minority shareholder has the right to demand the redemption of its shares. If such a requirement was not made, then the shares are converted into securities of the company created as a result of the reorganization. At the same time, the size of the share in the authorized capital remains unchanged.
Separately, it should be noted that when the nominal value of shares changes, shares in the authorized capital are also retained. The procedure by which the total number of securities is reduced and the value of one share is increased is called consolidation. The reverse operation, when the number of shares increases and the cost per security becomes less, is called a split.
Example. Shareholder Petrov I.I. is the owner of 10 ordinary shares of Rubin LLC, with a par value of 1000 rubles. for each, which is 5% of the authorized capital. Consequently, the authorized capital of the company consists of 200 shares with a total value of 200,000 rubles.
The majority shareholders decided to split the shares in the proportion of ½. Thus, the authorized capital will consist of 400 shares with a par value of 500 rubles. for each. At the same time, the share of Petrov I.I. will not change and will be the same 5%, only now he will be the owner of 20 securities.
Biorevitalization
Biorevitalization (BRV) is a basic aesthetic medicine procedure that can significantly improve the condition of the skin, moisturize it, and achieve visual rejuvenation for 5–15 years. This manipulation accounts for about 30% of the total number of cosmetic interventions. The high effectiveness of biorevitalizing products is due to the presence of hyaluronic acid in their composition - a powerful regenerative factor that affects the biochemical composition of the skin. Preparations based on HA are recognized as the most effective way to combat age-related changes.
What is the biorevitalization procedure?
Biorevitalization with hyaluronic acid is performed using the transdermal or injection method. In the first case, the skin is treated with creams containing this drug. This method is not as effective as injections. In addition, it requires daily treatment for several months, which is not always convenient for the patient. The use of local forms of GC is justified if there are contraindications to injections or a pathological fear of them.
There is a laser method for biorevitalization of facial skin. In this case, a restorative gel is applied to the skin, which is carried into the tissue using laser radiation. This method does not create pain, but does not allow the product to be delivered to the desired depth. At least 3-4 procedures are required, which entails additional costs for the patient.
The essence of biorevitalization is to activate the reparative and regenerative mechanisms of the skin. The long molecular chains of the drug promote the formation of the skin framework, suppress the activity of macrophages and fibroblasts, and have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Short chains enhance cell migration and proliferation. In addition, they trigger a chain reaction, during which the formation of its own hyaluronic acid increases. Oligosaccharides included in the molecules promote the proliferation of stem cells, have an immunomodulatory effect, and help restore the capillary network.
Biorevitalization of facial skin leads to the fact that the tissues begin to function as they did in youth. They actively produce type 3 and 7 collagen, heal minor injuries, and restore the ratio of liquid to solid structures. It is important that the running processes continue to work even when the initially administered drug is absorbed and excreted from the body. Thanks to this feature, the clinical effect lasts 3–6 months. Next, a repeat maintenance procedure is required.
What effects can be achieved with biorevitalization?
The effect of the revitalizing drug begins almost immediately after administration. However, it becomes noticeable after 2-3 days, when the swelling caused by the injections has completely subsided. In the absence of reactive phenomena (swelling or hyperemia), the first positive transformations are visible within 12–24 hours from the moment of the procedure. Over time, the condition of the skin continues to improve. Final changes are achieved after a few months.
If you have deep wrinkles, dryness and sagging skin, one session may not be enough to achieve the desired result. Requires 2-5 visits to a beauty salon at two-week intervals. The list of effects of biorevitalization with hyaluronic acid includes:
- Hydration . HA promotes fluid retention, which helps increase skin moisture. Due to this, the skin becomes more delicate, pleasant to the touch, does not peel or crack.
- Lifting . Biorevitalization of facial skin increases the tone of the dermis, and proteins responsible for its elasticity are produced. Visible sagging disappears, the skin takes its normal anatomical position, looks fresher and more toned.
- Slowing down aging . Many age-related changes are caused by free radicals—oxygen atoms with one missing electron that can damage the cell wall. HA has an antioxidant effect, binds and neutralizes such formations.
- Improved skin color and texture . Due to the normalization of blood circulation and humidity levels, the integument acquires a normal physiological color.
- Recovery . The injection allows for rapid healing of microtraumas and sunburns. This makes the procedure indispensable for people returning from vacation in hot regions.
You need to understand that drugs that improve skin condition act only in the area in which they were introduced. There is no systemic influence. Therefore, biorevitalization of facial skin does not lead to rejuvenation of other areas of the body, as some people mistakenly believe.
How is it different from mesotherapy?
Mesotherapy and biorevitalization techniques are generally similar to each other. The main difference is that with mesotherapy a cocktail of active ingredients is injected under the skin. The composition of the mixture may vary depending on your goals. The choice of one or another combination is made by a cosmetologist. BRB involves using only hyaluronic acid-based products. This approach allows you to avoid some complications, including those associated with individual intolerance to certain medications and allergic reactions.
MT is used both as a cosmetic and therapeutic method. For skin diseases, drugs can be injected directly into the pathology site in small doses. BRV is used for aesthetic purposes only. Medicinal cocktails for mesotherapy are usually liquid. Biorevitalization of the face and other areas is carried out with gel-like preparations, which are distributed more evenly in the skin and remain in it longer.
Indications and contraindications
Like any other procedure involving the introduction of medications under the skin, biorevitalization has a number of indications and contraindications.
The procedure is prescribed in the following cases:
- photo- and chronoaging of the skin;
- dry skin, regardless of cause;
- presence of scars, age spots;
- preparation for plastic surgery and recovery period after it;
- correction of deficiencies associated with insufficient volume of subcutaneous tissue;
- disruption of the sebaceous glands.
Biorevitalization with hyaluronic acid is not recommended for the following diseases and conditions:
- acute infectious and somatic diseases;
- exacerbation of chronic pathology;
- active herpes;
- uncontrolled hypertension;
- cancer, especially in the injection area;
- inflammatory processes on the skin;
- moles and papillomas at the site of intended injections;
- lactation and pregnancy.
Preparation for biorevitalization
Despite the minimal invasiveness, the procedure requires some preparation. This is especially important if the face is subjected to biorevitalization. A few days before your visit to the clinic, you must stop drinking alcohol. With the permission of the attending physician, it is permissible to stop taking medications that reduce blood clotting. Otherwise, there is a possibility of hematomas (bruises) forming at the injection sites. This will lead to certain aesthetic inconveniences and reduce the effectiveness of the revitalizing agent.
According to a number of experts, you should not be exposed to intense ultraviolet radiation immediately before BRV. Between returning from vacation and visiting a cosmetologist, 7–14 days should pass. It is better if at this time a person follows a diet and refuses excessively fatty, spicy and salty foods. All this contributes to the formation of edema, which can complicate biorevitalization.
Injection technique
Injections of restorative agents are carried out in a cosmetic center. They are performed by a specialist who has completed the necessary training courses. The work is carried out in several stages:
- Inspection and planning . At the first contact with the visitor, the center employee finds out which parts of the body he wants to undergo correction. Most often, biorevitalization is performed on the face, neck, décolleté, and hands. After this, an inspection of the area of the proposed intervention is carried out. Together with the client, the doctor develops a plan for the procedure and explains to the client how the manipulation will take place.
- Anesthesia . The application method of pain relief is used. A patch soaked in an anesthetic is applied to the skin or treated with a freezing gel. The time to achieve the effect varies from 10 to 20 minutes. Biorevitalization of facial skin is not accompanied by severe pain, therefore, at the client’s request, it can be carried out without anesthesia.
- Antiseptic treatment . The surface of the body in the area of the intended punctures is treated with antiseptic agents. This makes the procedure safe and prevents infectious complications.
- Biorevitalization . A cosmetologist infiltrates the skin with a restorative preparation. Punctures are made using a thin needle that leaves no visible marks. The needling technique can be papular, point or linear. Its choice depends on the goals set and the size of the area being treated.
- Completing the procedure . After administration of the product, repeated antimicrobial treatment of the skin is carried out, followed by application of a soothing cream. It allows you to reduce swelling and hyperemia, which occurs immediately after injections and lasts 1-2 days.
To achieve optimal effect, it is not recommended to visit baths and saunas or drink alcohol for two weeks after injection. In addition, prolonged exposure to the open sun and other sources of ultraviolet radiation is contraindicated. It is necessary to take measures to normalize night sleep, if possible, reduce the number of cigarettes smoked or completely abandon them. If these conditions are violated, the visible effect of therapy can be reduced by 20–40%. The influence of these factors is especially noticeable if the face has been subjected to biorevitalization.
Types of drugs
BR can be produced using several drugs that differ in molecular size, degree of purification and concentration. Each of them has its own characteristics. The most common rejuvenation products are:
1. Hyaluronic acid . It is the basis for creating revitalizing gels. Produced by bacterial synthesis. Streptococcus equi strains that have not been subjected to genetic modification are used as producers. Next, the product goes through several stages of cleaning, during which all foreign matter is removed from it. This ensures the safety of biorevitalization with hyaluronic acid.
It exists in the form of high molecular weight, medium molecular weight and low molecular weight substances. Medium and low molecular weight preparations make it possible to quickly moisturize the skin, but do not have a significant effect on its structure and weakly stimulate cellular activity. Used primarily for recovery after long-term exposure to the sun.
High molecular weight formulations attract enough moisture to maintain a moisturizing effect comparable to that described above. In addition, they act on the skin matrix, restoring and maintaining it. Allows you to achieve prolonged biorevitalization of the face, décolleté, neck and other areas of the body.
2. Ial system . One of the most common drugs based on unstabilized and unmodified HA. It is manufactured by the international concern Fidia Farmaceutici SpA in two forms - Ial system and Ial system ACP. The first type of product is distributed in branded syringes with a volume of 1.1 ml. The consistency is a viscous gel. The concentration of the active component is 18 mg/ml. It is injected to a depth of 2–3 mm into the papillary layer of the skin. Has a short action. The clinical effect lasts for an average of 2–3 months. Suitable for restoring skin after damaging effects and protecting it during trips to hot countries.
Biorevitalization Ial system ACP is used to achieve a prolonged effect. The product is produced using hyaluronic acid ester obtained by biofermentation. The concentration of the active component is 20 mg/ml. The drug has a slow onset of action. The synthesis of own HA begins only from the 10th–14th day. Moreover, the achieved results last for 4–6 months. The duration of the morphological effect reaches 18 months. The effectiveness depends on the level of hydration of the dermis.
The most common is the combined use of both products for facial biorevitalization. At the initial stage, a short-acting Ial system is introduced, which works well in conditions of hypohydration. After the skin moisture increases, Ial system ACP is injected, which could not be used at the initial stage due to insufficient water content in the tissues. The interval between procedures is two weeks.
3. Viscoderm. The product is produced in two forms - Viscoderm skinko and Viscoderm skinko E. The concentration of hyaluronic acid in the first of them is 2 mg, in the second - 32 mg. In addition, the composition includes vitamins, amino acids and other components that help maintain healthy skin. Both drugs are gels for subcutaneous and intradermal administration.
Biorevitalization with the drug "Viscaderm Skinko" is carried out during initial age-related changes. It is also used in the treatment of seborrhea, to get rid of “smoker’s skin” and increase its tone. "Skinko E" is necessary to achieve a prolonged effect and long-term stimulation of the body's own regenerative systems. Recommended for use when working with patients over 35 years of age.
Intradermal injection of hyaluronic acid is a modern, low-traumatic way to improve skin health. It is comparable in effectiveness to a surgical facelift. At the same time, biorevitalization is practically not accompanied by risk and does not lead to the development of life-threatening complications. The cost of tt is significantly lower than that of surgical rejuvenation techniques. 95% of people who have used this procedure are satisfied with the results of BRV.
Purpose of the offer
As already mentioned, the right to make an offer during delisting has the majority shareholder, who is the owner of at least 30% of the securities.
An offer is an offer to repurchase securities that is sent to small shareholders before or after a decision to delist is made. Holders who agree to the terms of the offer must apply to sell their securities. There are two conditions that are mandatory:
- the public offer must be sent to minority shareholders no later than 35 days before the date of the proposed redemption;
- the redemption price of shares should not be lower than the average for the last six months.
What to do if your shares are planned to be delisted
So now you know what delisting of shares is in simple words. Suppose you are a minority shareholder and you find out that your shares are planned to be delisted, that is, they will not be freely sold on the stock exchange or purchased to the desired quantity. What's the best way to proceed?
If the delisting is carried out by the exchange forcibly due to the bankruptcy of the issuer, then there is no way out - you lose your investments, like other shareholders. In all other cases, you have three options, which we will consider further.
Sell shares before exclusion from trading
Many shareholders resort to this method in order to preserve at least part of their investments. The stock market reacts quite sensitively to any changes, so the massive sale of securities leads to a decrease in quotes, and you risk losing some of your funds. If you were one of the first to receive information about the upcoming delisting, then there is every chance to save your funds in full by selling securities and investing the money in another financial instrument.
Kinds
There are and are used by issuing companies such types of listing as
- Primary listing. The issuer submits an application for inclusion of its assets in the exchange list only to the exchange of its country.
- Double listing. A situation in which the issuer submits several applications at once to different domestic exchanges.
- Secondary listing. In this case, the issuer submits an application to a foreign exchange.
A secondary listing is impossible without a primary one and, in order to enter international trading, you must be an active player, first of all, from the issuer’s native country.
- Cross listing. The issuer submits several applications at a time to exchanges in different countries. This approach can significantly save time and money, since if the application is approved by at least one exchange, the issuer can count on a simplified listing procedure on all others.
Listing of securities of a Russian issuer
Examples of delisting
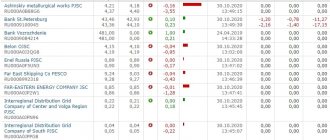
In March 2022, the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) decided to delist the American coal mining company Cloud Peak Energy Inc., a subsidiary of Rio Tinto Corporation. The reason for this decision was the drop in stock prices to a record low of 12 rubles. ($0.16 or 5 UAH) per security. The company's management stated that the company will continue to operate as usual, and the shares will be traded on the over-the-counter market.
Another example is that the Kazakh company ENRC left the London Stock Exchange in 2013 for the same reason – falling stock prices. According to British media reports, ENRC shares turned out to be one of the most unprofitable among mining companies that were part of the FTSE100 index. Since 2007, investors have suffered losses of about 54%. In addition, the delisting was preceded by allegations of corruption among the company's top managers.
As an example of delisting shares at the initiative of the issuer, we can cite the management of which decided to withdraw shares from circulation on the Moscow Exchange in September 2022. By the end of the year, the delisting procedure was completed. The reasons why this decision was made include the following:
- Recapitalization is the repurchase of shares by the Alliance Rostec Auto corporation (a joint venture of Rostec and Renault).
- Reduction of PJSC AvtoVAZ costs for managing a public company.
Dates
The timing of all stages of listing may vary on exchanges in different countries.
For example, the procedure for listing an issuer on the Moscow Stock Exchange can take on average about 2 months. Only the application review stage takes place within 10 days. It takes about 41-45 days to conduct an expert assessment, meet a commission, and add a company to the list.
At the same time, the London Stock Exchange allows consideration of applicants within a period of 4 to 6 months.