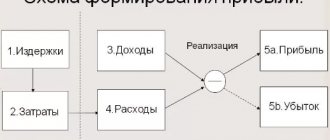
There is nothing complicated about the concept of income. Everyone will be able to answer the question “what does income mean?” But we need to determine what types of income exist, because this is an important concept not only for any entrepreneur, but also for every person.
Income can be considered both money and material assets.
Individuals, legal entities and the state can receive income.
We will not speak in complex and dry economic concepts, so we will try to translate everything into the language of mere mortals.
In economics, income will be considered what remains after a person’s activity, which consists of certain labor and the costs of its implementation.
We can also say that income is those funds that a person can spend and this will not in any way affect his economic condition.
From the point of view of accounting science, income will be the increase in profits after certain actions with assets. Again for a specific time.
What is income?
The term “income” refers not only to cash, but also to material assets that, for example, a company receives over a certain period of time. In other words, this is the total amount of all income, which includes even fines collected, interest received on deposits, etc., and not just the result of the enterprise’s activities.
REFERENCE!
Income can be received by individuals and legal entities, as well as the state.
There are cases when income does not require investment of funds (receiving a pension, subsidy, etc.).
It is also important to know that income can be unplanned, for example, when the counterparty violated the terms of the contract and paid a penalty for this.
When to take into account income of the simplified tax system
It's important to record earnings on the correct date because it determines when you pay tax on that money.
Earnings are recorded on the day you receive them. This is called the cash method of revenue recognition. If the income is cash, take it into account on the day the money arrives in your bank account or cash register. Prepayment must also be taken into account on the day of receipt.
In some situations, income must be taken into account before you receive the money. For example, you sell through a courier who receives payment and transfers it to you. In this situation, income is taken into account on the day the client paid the courier, despite the fact that you have not yet received the money.
If the income is non-monetary, for example, offsetting mutual obligations with a client, take it into account on the day when you signed the act of offset or other document.
For example, you developed a website for a furniture showroom, and he supplied you with office furniture. The counterparty must pay 100,000 rubles for the website, and you must pay him the same amount for the furniture. In order not to transfer money from account to account, you agreed on a mutual settlement, after which no one owes anyone. To formalize the agreement, you sign an act of offset. On the same day, you need to take into account 100,000 rubles in the income of the simplified tax system.
What is the difference between income and profit?
Unlike income, it is profit that reflects the efficiency of commercial activities, due to which the value of this indicator will always be less than income. Therefore, the term “profit” can be characterized as follows: the difference between total cash receipts and expenses for a certain reporting period. Shareholders are interested in this particular indicator, since dividends are paid from profits.
When calculating profit, both main and additional activities are taken into account.
REFERENCE!
Profit can be not only positive, but also zero and even negative. In the last two cases, the result of the activity is a loss.
Profit is divided into several categories:
- accounting;
- economic;
- arithmetic;
- normal;
- economic
Income code 2000 with decoding
The next most common code is 2000. According to Order No. ММВ-7-11 / [email protected] , this code corresponds to “remuneration received by the taxpayer for the performance of labor or other duties.”
Typically, the use of this code does not cause difficulties - everything that is reflected in the employer’s accounting as a salary accrued under an employment contract for the daily performance of job duties “passes” under code 2000. The same value is assigned to the average earnings saved for the period of a business trip, since it also is a salary (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated November 12, 2007 No. 03-04-06-01/383).
Automatically calculate the salary of a posted worker according to current rules Calculate for free
How are revenue, income and expenses determined?
There are two methods that help determine revenue, income and expenses:
- By shipment. All indicators are calculated at the time of provision of a specific service or several services at once, as well as when performing work or transferring inventory items (inventory).
- Upon payment. The most commonly used method. The indicator is determined after all calculations have been made. Most suitable for small and medium-sized businesses, such as retail stores. The only drawback of this method is the lack of ability to control accounts receivable and payable, and all because only received funds are taken into account, without data on goods sold, services provided and work performed.
Special points on BDR
By determining your sales budget and projecting it onto your income and expense budget, you can determine how much profit you can make each month as you move into the budget period. Drawing up a BDR consists of the following stages:
1. Understanding your business
. They say that a journey of a thousand miles begins with one step. The first step before you begin your journey to profitability is to understand your business. Involving key personnel directly executing your strategic plans increases your chances of success. This will also ensure that your budget aligns with your goals and ensures that it is compiled and reviewed by the appropriate people.
2. Documenting the process.
Be sure to document your annual budget process to set standards and ensure the process is correct. Processes may include the following steps:
- review monthly profit and loss statements for the previous year;
- if necessary, modify monthly data to reflect changes under the new plan, such as transactions, costs, and quantities;
- identify and correctly record assumptions made for the budget period;
- Enter and prepare your income and expense budget using templates. Various financial templates are available online for use. Choose the one that is most convenient for you.
3. Monitoring and managing the budget of income and expenses.
After preparing a budget of income and expenses, it is important to track the budget against actual results, which should give you information about how your business is performing and whether it is going to achieve the expected goals in your strategic plan.
- monthly results from your income statement should be compared with the results of your budget;
- any deviation, positive or negative, must be taken into account and action plans must be developed to resolve the problems;
- various information can greatly help you in revising your plan at critical moments so that strategic goals can be achieved.
4. Determination of cost of sales.
The calculation of how much you earn is determined by taking your total sales revenue minus your total sales cost. When determining your cost of sales, you need to follow the following process:
- determine the cost of producing your product. Will include your labor and material costs. Your cost to produce a product is the cost per unit. Unit cost is the gross cost you pay to obtain or produce a product. You can then calculate the price per unit, which again includes bills for utilities, equipment, repairs and maintenance, storage, packaging, shipping costs and staff commissions.
- Costs per unit, such as utility bills, can be calculated as the average monthly cost divided by the number of units expected to be sold per month. You now have an average estimated cost per unit.
- Breaking down your costs by budget month should help you determine your total sales cost for the month.
- Again, from your sales budget, get your projected number of units per month and divide your sales expenses by the number of sales. This gives you the selling price per unit.
- Adding the price per unit to your selling cost per unit gives you your total selling cost per unit.
5. Determination of gross profit.
Gross profit is the amount of money after subtracting costs. When calculating gross profit you must:
- get annual sales from your budget. Selling value is also called turnover;
- get the sales value from the previous section;
- subtract the cost of sales from your turnover to get your gross profit.
6. Receiving net profit.
Your gross profit is not your actual profit. To get what you actually make, subtract other costs indirectly associated with sales and unit production, such as:
- staff salaries, which include government contributions such as pensions and other insurance;
- office and property operating costs, including cleaning;
- marketing, public relations, media, advertising and exhibition expenses;
- professional fees such as legal, accounting or consulting fees;
- financial expenses, which include bank interest and fees
Indirect costs are also called overhead or fixed costs. These costs tend to change over time, so your budget should be realistic about the rising costs that may arise.
7. Calculate your cash flow.
Another factor that is largely underestimated when calculating your P&L budget is your cash flow.
Cash flow refers to the amount of money coming in and out of your company at the beginning of a period of time or the opening balance in relation to the final amount at the end of that period or the closing balance at the end of the period. Cash flow is considered either negative or positive.
Positive cash flow occurs when the closing balance is higher than the opening balance, which means your company's assets are growing or increasing. They say you can't make money if you don't spend money. Companies that post good profits but have negative cash flow may face problems in the long run.
Cash flow is the ability to pay out cash before doing anything in return. Therefore, when planning your budget, it is vital to include or list all of your business's cash inflows and outflows and the expected timing for each. The ability to control how cash flows in and out of your business affects your business's ability to pay off any debt at any time.
Types of income - gross and net
Gross - the total amount of revenue for a certain reporting period, which takes into account absolutely all types of income. The size of the gross indicator is mainly influenced by the following factors:
- volume and range of goods produced or services provided;
- trade price premium and its economic justification;
- the quality of additional services provided and their quantity;
- selection of counterparties and the cost of purchased goods/services, as well as methods of payment.
To calculate the gross indicator, several methods are usually used:
- by trade turnover and its assortment;
- according to the assortment of the remainder of a certain type of product;
- by average percentage.
Net income is the amount that remains at your disposal after making all necessary payments (for example, paying taxes, interest on a loan, paying employees, etc.).
What happens if you don't pay income tax?
Since the tax payer is an individual, responsibility for non-payment falls mainly on him. An employer may be fined under the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Article 123, for performing the duties of a tax agent in bad faith. In some cases, the additional accrued tax of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation Article 226 will be taken from him - if he previously withheld it not in full.
But in most cases, it is the individual who will be forced to pay the tax. Additional sanctions are also possible.
Fines
For tax evasion, you can be fined 20% of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation Article 122 of the unpaid amount. And if you can prove that you did it intentionally, the sanctions will be 40%.
For failure to file a tax return, you will be charged 5% of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation Article 119 of the unpaid tax amount for each month of delay, but not less than 1 thousand rubles and no more than 30% of the amount owed.
Penalty
For each day of delay in tax payments, you will have to pay a penalty - 1/300 of the Central Bank refinancing rate. Now it is 0.02%.
Criminal liability
A person who owes more than 900 thousand in three years can face a fine of 100–300 thousand rubles (sometimes income for a period of 18 months to three years), or up to a year of forced labor, or up to six months of arrest, under the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation Article 198, or up to a year in prison.
Other types and sources
In addition, you can also identify several types of income and sources of their receipt.
simplified tax system income
STS income is a special type of profit to which a simplified taxation system (or a special procedure for paying taxes) is applied. This scheme is mainly aimed at small and medium-sized businesses. Income from the simplified tax system is determined in accordance with articles 346.15 and 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; this can be revenue from the sale of services, goods, rights, etc.
Income tax
According to the legislation of the Russian Federation, any income must be taxed, no matter who receives it, an individual or a legal entity. The only difference is that in some cases, the tax is paid for an individual by an organization from which it receives officially and documented funds (for example, wages or dividends).
Each category of taxpayer and type of funds received has its own tax rates; most often in Russia they range from 13% to 15%. The size of such a payment can be obtained by multiplying the tax base by the rate.
Budget revenues
Budget revenues are funds whose sources are:
- Taxes.
- Fees.
- Foreign loans.
- Foreign economic activity.
- Sale of land.
- Sales of government reserves, etc.
This type is used exclusively for government activities:
- legal;
- political;
- organizational;
- social;
- economic;
- cultural;
- educational;
- environmental.
The material basis of all budget revenues is national income. The structure of the type in question may be subject to changes that depend on the current economic situation in the country.
OBD report form
Your business will benefit from budgeting if you update your budget monthly using your expenses and income from the previous month as a guide, and consider your company's financial goals or objectives for the year.
Also, work with your senior employees to see if they have information about upcoming issues that could impact planned sales and expenses, either positively or negatively. This allows you to adjust your budget and financial expectations as needed.
A monthly review of your company's budget can indicate where efforts to achieve business goals have been successful. For example, if you switch health insurance providers to get cheaper coverage, you'll see how that change affects your bottom line month after month and year after year.
A monthly review of your business budget can also help you identify potential problems. For example, if you own a retail business, you may realize that you need to increase your advertising spend in the fall to take advantage of the holiday shopping season. Or, if you have made changes that may have tax implications for your company, you may need to increase your budget for accountant fees in anticipation of the additional accounting work needed to overcome the implications.
The following worksheet provides income statement line items that you can use to set up a basic business budget. Depending on your specific type of business, you may have to include additional types of income or expenses, but this worksheet should give you a general idea of the types of items you should include in your business budget.
| Basic Business Budget Worksheet | |||
| CATEGORY | BUDGET AMOUNT | ACTUAL AMOUNT | DIFFERENCE |
| Sales income | |||
| Interest income | |||
| Income from investments | |||
| Other income | |||
| TOTAL PROFIT | |||
| EXPENSES | |||
| Accounting services | |||
| Bank service fee | |||
| Credit card fee | |||
| Shipping costs | |||
| Deposits for utilities | |||
| Estimated taxes | |||
| Medical insurance | |||
| Hiring costs | |||
| Equipment Installation/Repair | |||
| Interest on debts | |||
| Inventory of purchases | |||
| Legal expenses | |||
| Licenses/Permits | |||
| Loan payments | |||
| Office tools | |||
| Payment statement | |||
| Payroll taxes | |||
| seal | |||
| Professional fees | |||
| Rent/leasing payments | |||
| Pension contributions | |||
| Subscriptions and fees | |||
| Utilities and telephone | |||
| Fare | |||
| Another | |||
| TOTAL COSTS | |||
| TOTAL INCOME MINUS TOTAL EXPENSES |
Income accounting
Accounting for the profit of each organization is carried out on the basis of Order No. 32n of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation. 86n and 25 chapters of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. For each company, depending on its activities and the type of funds received, there is its own calculation and accounting procedure. So, for example, individual entrepreneurs must keep a special book, and enterprises keep such records on accounting accounts 90 and 91. For any violations in accounting, legal entities are subject to fines.
Income book
The Income Book is the most important tax register for individual entrepreneurs. Its maintenance is carried out on the basis of the rules prescribed in Order No. 135n of the Ministry of Finance of Russia. It indicates all cash receipts and expenses of individual entrepreneurs who use the simplified tax system or the patent system. Each taxpayer must ensure continuity, reliability and, of course, completeness of the data provided. Each transaction entered consists of the date of the transaction, the transaction itself, the total amount and other information.
The book is maintained according to the following rules:
- For each new tax period, a new book is opened.
- The book can be kept either electronically or in paper form, but when using the first method, it must be transferred to paper at the end of the tax period.
- Each entry must have documentary evidence.
- Entries must be reflected in full ruble equivalent.
- The absence of activity or operations does not exempt from the formation of a document; in this case, the individual entrepreneur must have a zero book.
- You do not need to submit the book to the tax authority every time, but you should definitely have it in case of unplanned audits.
REFERENCE!
If during the inspection the individual entrepreneur does not have a book, then he will be fined. The book must be stored for four years.
Expenses: you can’t do without them
This article is the most unpleasant for an entrepreneur. But if you do not take it into account, the company will not be able to exist for long. The funds that an entrepreneur needs to spend to make a profit differ depending on their direction.
- Operating expenses are the money that will have to be invested so that the enterprise can function: produce products, provide services, sell goods, etc. Amenable to relatively precise planning.
- Additional expenses are all costs that “pop up” in the process of entrepreneurial activity. Not all of them can be predicted and calculated in advance.
We invest in production and sales
The first item of expenditure consists of several elements, each of which provides its own aspect of the functioning of the company.
The most extensive is the economic component .
- Material resources:
- purchase of raw materials;
- provision of tools, materials, inventory, equipment;
- various expenses on property;
- purchase of special clothing, personal protective equipment, etc.;
- payment for fuel, water, electricity;
- payments to third-party organizations performing part of the work.
- The wage fund is remuneration for the work of hired employees.
- Contributions to social funds.
- Expenses for depreciation of property.
- Miscellaneous:
- taxes and fees;
- duties;
- safety costs;
- compensation for hazardous work;
- rental payments;
- expenses for official transport;
- business trips;
- finances for training and recertification of personnel;
- entertainment expenses;
- fees for outsourcing and consulting services;
- advertising costs;
- costs of communication services, including Internet, etc.
For all these indicators, it is impossible to calculate the cost of the goods produced or services provided. To do this, you need to take into account the intended purpose of the expenses .
- Fixed and variable expenses : depending on the frequency of deductions or changes in sales volume, it is possible to determine unprofitability or break-even at each specific stage.
- Direct and indirect : in relation to expenses to the cost of a product or service.
- Basic and invoices . The first are inevitable, since they are related to production technology (these are raw materials costs, wages to workers, bills for electricity and fuel, wear and tear of equipment, etc.). Invoices are associated with the process of managing the company, with how the sale of products is organized (administrative and commercial expenses).
“Other expenses” is a loose concept
Financial and investment expenses are not directly related to the product or service being produced, however, they cannot be overlooked when planning the company's budget. Not all of them are required, but many should be taken into account. These include:
- participation in the authorized capital of other legal entities;
- payment for the use of someone else's intellectual property (patents, industrial designs, etc.);
- temporary use of assets of other organizations (leasing, rent);
- write-off of intangible assets;
- interest on loans, credits;
- penalties in favor of counterparties;
- past losses recognized in the reporting period;
- debts that are unrealistic to collect;
- charity;
- expenses for corporate events (sports, entertainment, health, cultural, etc.);
- costs due to force majeure (accidents, natural disasters, catastrophes, etc.).
Declaration of income
According to Federal Law No. 118, all citizens of the country must annually submit a tax return to the relevant authorities at their place of residence. A declaration is understood as a statement drawn up in the form of the tax authority, which indicates all income and expenses, tax benefits and the calculated amount of tax. But there are also exceptions that exempt the following categories of the population from this procedure:
- persons who do not have a permanent place of residence in the Russian Federation;
- persons who receive money during a certain reporting period only at the place of employment;
- persons receiving funds, the total amount of which does not exceed the taxable amount.
What income does not need to be taken into account in the simplified tax system?
Not all money received is your income. When calculating the simplified tax system, you do not need to take into account:
- loan repayment;
- obtaining a loan;
- replenishing your account with personal money;
- security deposit or pledge;
- refund from the supplier;
- erroneous receipts from a counterparty or bank - Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 7, 2006 N 03-11-04/2/231;
- money received by an agent under an agency agreement, except for agency fees;
- grants;
- income from business on a different taxation system, if you combine the simplified tax system with UTII or a patent;
- other income from Art. 251 NK.
Individual entrepreneurs have income that is not taken into account in the simplified tax system, but personal income tax is withheld from them at a rate of 35%:
- The cost of winnings and prizes from participation in incentive competitions that are held to advertise products. Personal income tax must be paid on that part of the winnings whose value is above 4,000 rubles. Personal income tax is transferred not by the individual entrepreneur himself, but by the organizer of the competition.
- Saving on interest when receiving a loan at a rate below ⅔ of the refinancing rate. The bank itself will calculate and pay personal income tax to the tax office.
Per capita income
The concept of “per capita income” implies the economic well-being of the state and its citizens. It measures the average income an individual earns in one calendar year. This indicator is calculated by dividing national income by population.
Using this value, the economic development of the state is judged, thanks to which the place in various ratings is determined. But this indicator has a weak point, because its characteristics do not take into account imbalances in the distribution of funds among different segments of the population.
IMPORTANT!
For cross-national comparisons, this indicator is converted into dollars, and the purchasing power of citizens is used to obtain an accurate assessment of the economic situation of a particular state.
Income codes 2002 and 2003 with decoding
But bonuses for the purpose of coding income as wages are not recognized, although they are named in Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation as part of remuneration. Moreover, bonuses are reflected in tax registers and in 2-NDFL certificates in three different codes.
The main code is 2002. It is used for awards that simultaneously satisfy three conditions:
- the payment is not made at the expense of profits, earmarked proceeds or special-purpose funds;
- the payment is provided for by law, labor or collective agreement;
- the basis for payment is certain production results or other similar indicators (i.e. indicators related to the employee’s performance of his or her job duties). This circumstance must be confirmed by an order for payment of the bonus.
Code 2003 reflects bonuses (regardless of the criteria for their assignment) and other remunerations (including additional payments for complexity, intensity, secrecy, etc., which are not bonuses), which are paid from special-purpose funds, targeted revenues or profits organizations.
For other bonuses, code 4800 must be used.
Also see: “We reward employees correctly: how to register bonuses in an organization” and “Taxes on bonuses: we calculate personal income tax and contributions, take them into account in expenses, and reflect them in reporting.”
Passive income
Passive income is funds the receipt of which is not related to work activity, that is, you can receive money of this type regardless of age, health and activity. Moreover, it is also subject to tax, paid once a year. The main sources of passive income can be:
- Renting out any type of property (buildings, equipment, vehicles, etc.).
- Non-state pension. It is formed by concluding an additional pension agreement. That is, an individual, before the deadline for assigning a pension, makes regular contributions to the fund (NPF), and after reaching a certain age, which will be specified in the contract, he will gradually begin to receive them along with the official pension.
- An open deposit in a bank that can generate profit both monthly and only after the end of the period specified in the agreement.
- Investments in securities (for example, stocks, bonds, etc.). This method can be a good source of additional profit. But in this case, it is necessary to take into account that the possibility of obtaining additional funds is directly proportional to the risk, that is, the greater the profit, the higher the risk. Therefore, it is always recommended for beginners to start with proven and more predictable tools.
- Investment life insurance. In this case, the investment will be handled by an insurance company, with which an agreement is concluded for a period of 3 to 5 years. During this time, it is necessary to make one or more contributions, the amount of which will be returned along with the accumulated investment income after the end of the agreement. Insurance companies can also offer more or less risky strategies, which will determine the amount of profit.
- Crowdfunding. This method is less common, but is still sometimes used. It involves investing money in someone else’s business, if it is fast-growing, then you can get a considerable amount out of it, but at the same time you can lose everything in one moment. Therefore, it is not recommended to invest all your money in such projects.
- Intellectual property. Suitable for creative people who, thanks to their talent (writing a book, song, patenting an ingenious device, etc.) will be able to make a profit of various sizes.
Revenue
Revenue (Sales Revenue or simply Sales) is income from the company’s normal activities. It is income, not the flow of money. Last time I talked in detail about how these categories differ.
What is considered normal activities is determined by the company itself. The main rule here is systematic income generation. If a product, product, work or service is sold regularly, its sale is a normal activity.
Here's what brings in revenue in different businesses:
- store - sales of purchased goods;
- plant - sales of its own products;
- broker - sales of securities;
- hairdresser - hairdressing services;
- leasing company - renting out property.
In this case, a company may have several normal activities. A grocery store can start producing salads that will be sold along with purchased goods. And the plant sells not only its products, but also purchased spare parts for them. Such sales will also generate revenue.
Once again, I would like to focus on the moment of revenue recognition. Revenue arises in accounting at the moment of transfer of ownership of a product or product from the seller to the buyer. For works and services, the moment of revenue recognition is the date of signing the act of their completion.
The amount of revenue is equal to the amount of the buyer's receivables arising. If the purchase is paid for at the time of purchase, the proceeds coincide with the amount of cash received. If the purchase is partially paid, the proceeds consist of the payment amount and the balance of receivables. This is the so-called “dirty” revenue or gross revenue. It may contain VAT and excise taxes, which will need to be returned to the state. The financial statements reflect net revenue from which these taxes are excluded so that the real income of the company can be understood.
Example 1. A car dealership sold a new Gelendvagen for 12 million rubles. According to the terms of the contract, the client pays half of the cost immediately, and the second half within a year from the date of purchase. Gross revenue consists of 6 million rubles. paid money and 6 million rubles. debtors. Net revenue - 10 million rubles. The remaining 2 million rubles. VAT is the income of the state, not the car dealership.
Income code 2720 with explanation
Code 2720 is used in personal income tax reporting to include the cost of gifts for employees. In particular, it should be used for gifts for the New Year, birthday, etc.
Attention
According to paragraph 28 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, gifts worth no more than 4,000 rubles are exempt from personal income tax. in a year. This income must be reflected in the tax registers, regardless of the amount of the gift. But in the 2-NDFL certificates the cost of gifts does not exceed 4,000 rubles. for a year, you don’t have to show it (letters from the Federal Tax Service dated 07/02/15 No. BS-4-11/ [email protected] and dated 01/19/17 No. BS-4-11/ [email protected] ).
Also see: “Tax accounting for gifts and bonuses, or what an accountant should do after February 23 and March 8.”
Revenue codes 2762 and 2760 with decoding
Using code 2762 in tax registers and 2-NDFL certificates, you must indicate the entire amount of financial assistance issued to the employee at the birth of a child. Let us remind you that such financial assistance is not subject to personal income tax up to 50,000 rubles. for each child, provided that the payment is transferred no later than one year after his birth (clause 8 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When paying employees of other types of financial assistance, the code 2760 is used. In this case, the basis for the transfer of money does not matter. So, if the company decides to issue financial aid for vacation, then this amount must be separated from the main vacation pay and reflected with code 2760. This code must also be assigned to financial aid paid to former retired employees. Let us remind you that such income is not subject to personal income tax up to 4,000 rubles. per year (clause 28 of article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Income codes 2012 and 2013 with explanation
The 2012 code corresponds to the amount of vacation pay, that is, the average earnings retained by the employee during the vacation period. This code is used to make payments both for regular vacations and for additional ones, including educational ones.
Code 2012 can only be applied to vacation pay that is paid to existing employees. If the employer transfers compensation to the dismissed employee for unused vacation, this income must be assigned code 2013.
Attention
The Labor Code allows for the provision of leave followed by dismissal (Part 2 of Article 127 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In this case, the employee receives the final payment and work book before the vacation, and does not return to the previous employer after the vacation. However, from the point of view of labor legislation, the transferred amounts are vacation pay, and not compensation for unused vacation. Therefore, the code 2012 must be applied to such a payment. Also see “An employee is ill or recalled from vacation: what to do with personal income tax, contributions and reporting?”
Revenue code 2001 with decoding
Code 2001 is used for remuneration paid to directors on the board of directors and other members of the organization's collegial governing body.
At the same time, the salary of the manager according to code 2001 is not “posted”, even if the corresponding position is called “director”. However, if the manager is a member of the board of directors (board, other collegial body) and receives additional remuneration for this, then this payment must be separated from the salary and reflected for personal income tax purposes using code 2001.
Income code 2300 with decoding
Using code 2300 in personal income tax reporting, temporary disability benefits are indicated. This code must be assigned not only to the benefit that is paid in case of illness of the employee himself, but also to those amounts that are transferred in the case of caring for sick children or other family members.
Reference
Formally, maternity benefits also fall under this code, since the basis for its accrual is sick leave.
But since maternity benefits are not subject to personal income tax (clause 1 of article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), this payment may not be recorded at all in the registers and certificate 2-NDFL (clause 1 of article 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Ministry of Finance dated April 2, 2019 No. 03- 04-05/22860). Create electronic registers and submit them to the Social Insurance Fund via the Internet Submit for free