Trading on the stock market, especially on the stock exchange, is carried out according to clear regulated standards. These standards provide for the trading of assets, property rights and debt obligations in set lots, called lots.
The volume of a transaction between counterparties is determined by the number of lots sold by one party and purchased by the other. The use of such regulation significantly simplifies exchange trading, increases turnover, and increases the liquidity of securities. This article provides a description, types, sizes of lots, features of their use on different trading platforms and markets.
What is "lot"?
In exchange trading, a lot denotes the minimum quantity of shares, goods, bonds and other financial instruments that can be sold or bought on the exchange. This is a standard unit determined by the rules of the exchange; it has a fixed size for a particular asset.
A trader will not be able to sell 19 or buy 8 shares if the lot size does not allow this. The size depends on the market value of the security and its liquidity. If a company's share costs a few kopecks with high liquidity, then the size of a standard unit can reach 10 thousand. On the world's leading exchanges, securities are traded in batches of 100, 1000 or more units.
The word " lot" translated from English means: "batch", "series", "unit".
The volume of the transaction is the quantity specified in the agreement for the purchase and sale of securities or currency. It can be calculated in lots or number of securities. In stock exchange applications, orders, and broker notes, the first option prevails. This is due to the goal of simplifying settlements for brokers, dealers and investors, as well as in connection with trading using modern software.
ETFs are exchange-traded funds. Issuers FinEx Funds ICAV and FinEx Physically Backed Funds ICAV, hereinafter referred to as the Funds. Management company FinEx Investment Management LLP (registration number OS407513, registered office: 2nd floor 4 Hill Street, London, W1J 5NE). The Fund is the entity committed to shares of the ETF. Information is disclosed on finexetf.com.
The information presented on this website is for informational purposes only, does not contain guarantees of the reliability of possible investments and the stability of the amounts of possible income or costs associated with these investments, and is not a statement of possible benefits associated with asset management methods; is not a promise of payment of income, is not a forecast of an increase in the market value of securities; is not an offer of any kind, including an inducement to purchase ETF shares; does not constitute individual investment advice and the securities or transactions referred to therein may not be suitable for an investor's investment objectives. Determining whether a security or transaction suits the interests and investment objectives of the investor is the responsibility of the investor. Investments in the securities market involve risk. The value of assets can go up and down. Past investment performance does not determine future returns. The FinEx Group of Companies, its subsidiaries and affiliates do not make guarantees or representations and do not accept any liability, including for any possible losses (direct or indirect, foreseen and unforeseen in relation to the financial results obtained based on the use of the information posted on this website and does not recommend using the information provided as the sole source of information when making an investment decision.
This information does not constitute an offer of financial services and/or individual investment advice. The financial instruments or transactions mentioned therein may not meet your investment objectives (expectations). Determining the suitability of a financial instrument or transaction for your personal circumstances, investment objectives, investment timing and the level of risk you are willing to accept in implementing your investment decisions is solely the responsibility of the investor. The FinEx Group of Companies, its subsidiaries and affiliates are not responsible for possible losses in the event of transactions or investments in the financial instruments mentioned here, and does not recommend using the information provided as the sole source of information when making an investment decision.
The information presented is of a public nature, is not intended for a specific target audience and/or individual, does not take into account the personal circumstances of each investor (is not based on information about him) and cannot be considered as suitable for investment by a particular person who has access to it.
Any information provided by a user of the site is not used for the purpose of determining that person's investment profile. The information provided is used solely to generate a set of data on the basis of which the task designated as a target in the corresponding section can be solved.
FinEx Group Disclaimer
Development - Internet agency Future
Kinds
Property rights in the form of shares or debt obligations in the form of bonds are traded in a number established on the stock exchange, for example, it could be 100 shares of a certain company ( 1 lot = 100 shares ). In this case, such a lot is called full or round . Most transactions in the stock market are concluded on the basis of such parties.
In addition to full lots, there are the following types of lots on the exchange:
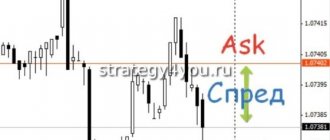
- Incomplete (non-circular) – formed if the seller has a quantity of securities that is not a multiple of 10. There are often cases when the owner cannot sell his assets in full lots. For example, after the formation of an incomplete lot, the owner of 34 bonds can easily sell 30 securities in three lots, and the remaining four are registered on the exchange as an incomplete lot. Partial lots are traded on the exchange at a designated time, usually towards the end of the trading session. At this time, there are significantly fewer sellers and buyers, which affects quotes and spreads.
- Unpacked is a fractional lot, the size of which exceeds a full one. Determined by the smallest established number of securities of a certain denomination.
- Packaged – determined by the number of securities based on their face value. The face value of securities in the vast majority of cases is not a fractional number, so it is convenient to form lots on its basis.
The concept of a divisible lot is more typical for auctions and tenders than for an exchange. From literature and cinema, the most famous example is the auction from the work “12 Chairs”, when a lot of furniture was “broken” into smaller ones after the first unsuccessful auction.
Lot of shares
A lot of shares is a unit of purchase and sale during trading on stock exchanges. The predetermined size of the product in physical terms corresponds to the lot size.
What is a stock lot and its types?
It is known that a lot of securities is the current number of shares that are purchased in one transaction. The lot concept provides an opportunity for financial markets to standardize and unify price quotes. For example, shares that give its holder the right to buy and sell a certain number of securities at a specific price in a limited time are valued in such a way that each lot (contract) allows the purchase of 100 shares of the total capital at once. That is, investors always know exactly how many units they are purchasing each time they enter into a contract. Therefore, they can easily estimate the cost of one unit. Experts note that trading securities without such standardization would be time-consuming and unreasonably burdensome.
On the stock exchange, other names are used to refer to the term “lot”:
- full (round) lot - consists of a package of 10, 100, 50 or another number of shares;
- non-standard (incomplete, non-round) lot;
- bulk (fractional) lot - the number of securities is determined depending on the smallest established number of shares of a particular denomination;
- prepackaged lot - depending on the denomination of securities, their quantity is determined.
Non-standard lot
Blocks of shares that are smaller than a standard trading unit were handled by two and DeCoppet s Doremus until the 70s. The merger of these companies did not solve their problem: the profitability of this business was steadily declining. Therefore, in 1976, a decision by the New York Exchange provided the opportunity for Merillinch to begin executing orders for its clients in non-standard lots. This led to the liquidation of the united.
After 1970, there was a consistent trend in the sale of partial lots compared to purchases.
Trading of non-standard lots is always carried out according to special rules. For example, the Moscow Exchange has established a “partial lot mode” for trading. Trading is carried out exclusively only from 16:00 to 18:45.
It should be noted that in the non-standard lot mode, the volume of transactions that are concluded will be smaller than in the main mode, since at this time there are fewer sellers and buyers. Therefore, the spread between the best sell quote and the best buy quote in the “non-standard lots” mode will be larger.
Lots of shares on the Russian stock exchange
The number of securities included in one lot is determined by the exchange. For example, the standards of the Moscow trading platform establish that:
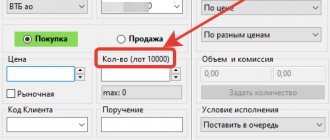
- 1 lot of the VTB banking institution consists of 1000 VTB Bank securities;
- 1 Rosneft lot contains 1 Rosneft share;
- 1 lot of Surgutneftegaz has 100 Surgutneftegaz securities.
Experts note that recently there has been a tendency for the trading platform to reduce the number of assets in one lot. This is done in order to reduce its cost. In this way, purchasing one lot becomes correspondingly more accessible. Thus, new small investors are attracted to the exchange.
Securities of the Russian market, which have only one share in the lot, belong to such large Russian companies as:
- Aeroflot;
- Gazprom;
- Sberbank;
- Gazprom Neft;
- VTB;
- Lukoil.
Lots of shares on the American stock exchange
On the NYSE, NASDAQ, and AMEX exchanges, the standard number of shares in one lot is 100. Only a few shares of the American stock market have one share in a lot, for example, such giants as Warren Buffett's Berkshire Hatway and the Washington Post.
Trading with fractional lots, when transactions are carried out in a number of shares less than 100, is also possible, but it is rare that a broker provides it.
What are partial lots in Quik?
Domestic traders in trading on stock exchanges use the popular software product QUIK, with the help of which they access goods, submit orders, and carry out settlements. It is used by both small traders and large players such as Sberbank. In fact, it is a trading terminal for the exchange.
Incomplete lots in the Quik terminal
The Quik terminal has a special mode for buying or selling incomplete lots of shares in the “Incomplete Lots” section. They are traded on the Moscow Exchange from 17:00 to 18:40 Moscow time. The liquidity of such lots of assets is noticeably lower than full lots, even if blue chips are traded. Large players prefer purchasing or selling in fixed quantities, and in large quantities.
It is the large players who are market makers, since they set trends, plan and carry out large speculative operations.
What is a lot on the stock exchange in simple words
A lot or exchange lot (from the English “lot” - a set of something) is the minimum amount of a unit of a financial asset that can be purchased during the main trading session.
On the stock exchange, all financial assets are sold not individually, but in lots. That is, one lot can contain several units of an asset.
The Moscow Stock Exchange accepts standard lots that are multiples of 1, 10, 100, 1000, 10,000 units (they are also called full). Traders can purchase assets only in lots during the general trading session.
Why combine assets into lots?
The reason for combining stocks, bonds, futures, commodities and other assets is primarily due to the need to standardize transactions on the exchange. This creates order and consistency in trading for brokers, dealers and other professional participants in the securities market. In addition, the feasibility of such a merger is determined by the following factors:
- Low par value of some securities. So, if the par value of a liquid share is 10 kopecks , then trading 1 or even 100 shares will result in large transaction costs. That is why such securities are combined into large lots for trading on the stock market - up to 1000 pieces and more. For example, 1 lot of VTB shares contains 10,000 shares , because one share costs a few kopecks.
- High transaction costs in case of trading without combining assets into lots. You can compare over-the-counter and exchange trading. In the former, there is no standardization, so counterparties and intermediaries spend more time agreeing on quantitative indicators of assets. On the stock exchange this happens extremely quickly.
- Visibility for bidders, which allows you to quickly make a decision on a purchase or sale operation.
The minimum lot size is equal to one unit of an asset - this can be 1 share or 1 ton (kilogram, ounce, barrel) of an exchange commodity.
The maximum amount is set by exchanges individually for each asset or debt obligation.
Looking for a good broker? Check out these:
How to buy paper shares of Sberbank?
Shares of Sberbank PJSC are in free circulation on the stock market. On the united Moscow exchange MICEX-RTS shares have the ticker SBER. The easiest way is to buy securities on the stock exchange. To purchase shares, you need the services of a broker - an intermediary between the exchange and investors.
Interesting materials:
What is 1 kn equal to in tons? What is the charge of an atomic nucleus? What is the rate constant of a chemical reaction? What is the mass of an electron? What is the median of the series? What is the speed of propagation of electromagnetic waves? What is the speed of rotation of the Earth around the Sun? What is the angular velocity? What is the size of the angle between the intersecting lines? What is the mass number of the nucleus of a calcium atom 40 20 CA?
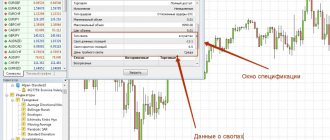
Where can I see how much of an asset is included in a lot?
To assess the situation in order to calculate his position when trading a particular asset, a trader (investor) needs to quickly obtain information about the lot sizes of various securities.
Expert opinion
Dmitry Dunyashev
Blogger, private investor, project manager real-investment.net
The main task of a trader on the stock exchange is to maximize his own income, for which he can change (depending on quotes, incoming information from markets, emerging trends) the quantitative and qualitative composition of financial instruments in the basket. When trading on the MICEX, information about lot sizes can be obtained using the methods described below.
Asset passport on the Moscow Exchange
On the Moscow Exchange website, any registered user can find information in the appropriate section. So, on the right side of the site on the main page there is a widget with a list of “blue chips”.
Share passport using the example of Sberbank
Having found the required share, you should click on it, after which the passport of this asset opens. It indicates, among other things, the number of shares included in a full lot. Based on this information, your own financial capabilities and the leverage provided by the broker, you can plan your further actions.
Quik terminal
In the Quik program interface, on the right side is the current table, which contains the assets available for the operation. Just below there is a list according to which the trader’s work is configured: short name of the security, price step, previous profitability, price of the last transaction, turnover, seller’s guarantee. There is also a “lot” line here, with which you can find out its quantitative characteristics.
View the number of assets in one lot through the Quik terminal
In Quik terminal orders
The easiest and fastest way is to view information in buy or sell orders in the Quik terminal. When filling out an application for certain shares or goods, the full lot size established by the exchange rules is automatically filled in.
Viewing data in buy or sell orders in the Quik terminal
Methodology for calculating a trading lot for trading futures on FORTS
Below I will show you step by step how you can calculate a trading lot using simple mathematical operations and give specific examples.
As an example, let's calculate the trading lot for a futures contract on the RTS index. We decide on the input parameters:
- Deposit size = 120,000 rubles.
- Risk per trade = 2% of the deposit.
- Price step - 10.
- Price step cost = 10,065 rubles.
- Entry price is 99,000 points.
- The stop price is 98,200 points.
Step 1. Calculate the acceptable risk per transaction in rubles, depending on the specified risk percentage
Risk per transaction in rub. = (deposit size * percentage of acceptable risk per transaction) / 100%
Example:
Risk per transaction in rub. = (120,000 * 2%) / 100% = 2400 rub.
Or:
Risk per transaction in rub. = 120,000 * 0.02% = 2400 rub.
Step 2. Calculate stop loss in points
Stop loss in points = (entry price - stop price)
Example:
Stop loss in points = (99.000 - 98.200) = 800 points
Step 3. Calculate stop loss in rubles
Stop loss in rubles = (stop loss in points / price step) * point value
Example:
Stop loss in rubles = (800 / 10) * 10.065 = 805 rubles.
Step 4. Calculate the trading lot (number of contracts) per transaction
Number of contracts = acceptable risk per trade in rubles / stop loss in rubles
Example:
Number of contracts = 2400 / 805 = 2.9 (rounded to 3) contracts
It only took us 4 simple steps to correctly calculate the trading lot for RTS index futures. For example, I deliberately took the RTS index futures, since the value of its point directly depends on the dollar exchange rate, although I already wrote about this above.
As you may have noticed, the “Guarantee” parameter was not included in my calculations. In fact, to calculate a trading lot, we absolutely do not need this parameter. But with its help, we can calculate the maximum possible number of contracts that can be traded, based on the amount on deposit.
Let's remember what “Warranty Security” (GS) is. This is a kind of collateral that the exchange takes when we open a transaction. So for each contract the exchange will block funds in the amount of GO. Now we will return to our example and I will show how GO will affect the trading lot.
Let's reduce the stop loss from 800 to 100 points. After recalculating, we get a result that allows us to open a deal with a volume of 24 contracts. But, unfortunately, the size of the guarantee will not allow us to open a deal with a volume of more than 6 contracts.
Let's count the maximum number of contracts and make sure of this. And our formula will be as follows:
Maximum number of contracts for trading = deposit size / GO
Example:
Max. number of contracts = 120,000 / 19,438 = 6 contracts
Well, that's all, friends! Now you have a calculation method that allows you to correctly calculate the lot for futures trading on FORTS.
By the way, this process can be automated using Excel by making a simple but effective calculator. For example, this one:
If you liked my solution, you can use it by downloading the calculator from this link. Or you can make a similar calculator to calculate the lot yourself.
And that's all for me. Thank you very much for your attention. Don't forget to subscribe to blog updates and share your opinion about this article in the comments.
Good luck in trading!
Best regards, Vadim Atroshchenko
How to determine how many shares are in one lot?
You can view the information in the table in which data is entered based on information from the Moscow Exchange.
Table 1. Number of shares in one standard lot
| No. | Name of the companies whose shares are being considered | How many shares in one lot |
| 1 | Gazprom | 10 |
| 2 | Sberbank | 10 |
| 3 | VTB | 10000 |
| 4 | Aeroflot | 10 |
| 5 | Tatneft | 1 |
| 6 | Rosneft | 10 |
| 7 | Surgutneftegaz | 100 |
| 8 | NOVATEK | 1 |
| 9 | Lukoil | 1 |
| 10 | MTS | 10 |
| 11 | Unipro | 1000 |
| 12 | Yandex | 1 |
| 13 | Alrosa | 10 |
| 14 | RusHydro | 1000 |
| 15 | NLMK | 10 |
| 16 | Gazpromneft | 10 |
| 17 | FGC UES | 10000 |
| 18 | MMK | 100 |
| 19 | System | 1 |
| 20 | Child's world | 10 |
| 21 | Severstal | 1 |
| 22 | Nizhnekamskneftekhim | 10 |
| 23 | NCSP | 100 |
See the rest of the information on the Moscow Exchange website
What is one lot equal to in Forex?
Lot in Forex means the minimum amount of currency that can be traded. The standard size in Forex is 100,000 units in the base currency. For example, in the RUB/USD pair, the base is the ruble, since it comes first, which means the lot size is 100,000 rubles . To admit a larger number of participants with different financial capabilities, minilots and microlots with sizes of 10,000 and 1,000 units of the base currency, respectively, are used.
In Forex trading, in addition to the lot size, the size of the deposit, the direction of the opened transaction, the market entry price, the leverage provided by the broker and other factors are important. If the broker's leverage is 1:100 , then with a deposit of $1,000 a trader can trade $100,000 .
Lot on Forex using the example of the EUR/USD pair
Simple calculations such as leverage size or margin amount can be calculated manually. However, trading on the Forex currency market is quite a risky activity, so special calculators are used here, which are provided by the Forex broker to its clients.
Calculating the lot size in Forex is required to manage trading risks. Initially, the trader determines the risk percentage for himself. A value not exceeding 5% . It is optimal if the risk value does not exceed 2% . That is, if the deposit is $1000 , the risk of losing will be 20% .
Calculating lot size using an online calculator
Independent calculation of risks, margin and other factors is unproductive and even harmful when trading on Forex, when special accuracy and speed of calculations are required. Some resources offer an online calculator that accurately determines the optimal lot size for trading in the foreign exchange market and when trading metals.
It also works with cross rates. To make the calculation, fill in the main fields in the calculator: deposit amount, acceptable risk in percentage or in money, stop loss size (loss limit). Next, the calculator itself will do all the calculations based on the current exchange rate.
The procedure for calculating the volume of open currency positions
The foreign exchange position of a trader, broker or bank is the relationship between requirements for receiving currency and obligations for its delivery. These liabilities and requirements are calculated either at the reporting date or at the completion of certain future transactions.
There are two types of currency positions: closed and open .
Types of currency positions
Closed type is a position when the volume of obligations and claims are identical, that is, there are no receivables or payables for the transaction. With an open currency position (OCP), the size of the trader’s requirements does not coincide with his obligations. The higher the discrepancy, the greater the risk, other things being equal.
Open positions can be short or long . The former are indicated by a (-) sign and indicate an excess of obligations over receipt requirements. A long position (+) means exactly the opposite.
Calculation of an open currency position is a legal and arithmetic procedure, which is described in Bank of Russia instruction No. 124-I.