The issue of securities is the issue by the issuer of shares, bonds and other types of financial instruments for circulation on the stock exchange, in accordance with the norms of the current legislation and the requirements of the financial regulator.
Objectives of the issue
The purpose of any issue is to attract third-party capital:
- if the issuer wants to raise borrowed funds without transferring voting or ownership rights to the buyer, he issues bonds - debt securities or preferred shares;
- if you are ready to give up part of the company - ordinary shares. They are listed on the stock exchange.
Analysts transformed the two listed points into 5 , which were included in all textbooks in the world in special courses on securities. This
- raising capital (shares, warrants);
- raising borrowed funds (bonds, preferred shares);
- transformation of the company into a joint stock company;
- formation of the initial authorized capital or its increase;
- splitting securities, changing the scope of rights through additional issue.
Emission policy in Russia
The basic principles of the emission policy in our country are as follows:
- Monopoly. Only the Central Bank regulates the volume of money supply; it injects money supply, and it also withdraws it depending on current tasks.
- The absence of the obligation to provide the gold reserve that we have in our country today is not enough for the ruble to be fully backed by gold. The situation is the same in most other countries.
- The principle of par. The ruble is the monetary unit of Russia; the manufacture of analogues or the introduction of other units is prohibited by law.
- Rubles are accepted for payment throughout the country. Banknotes are interchangeable - a 5 thousand ruble bill is always 5 1 thousand ruble bills or 10 500 ruble bills.
Circulation of securities after issue
After the issue, the issuer launches the securities into listing on the stock exchange , after which they are fully traded on the stock exchange and are available to thousands of investors.
The issuer can issue the issue of its shares, bonds, etc. at once on several of the world's leading stock exchanges - NYSE, NASDAQ, Swiss, London, etc. There is only one limiting factor: for the issue of its shares you need to pay an impressive entrance fee and annual subscription fee, so even large corporations (Gazprom, Sberbank, Rosneft, Lukoil, Novotek, MTS, etc.) place their emission products on a maximum of only a few stock exchanges in the world.
Subjects of securities issue and their circulation on the stock exchange
Subjects of the securities market can be divided into 6 categories:
- Issuers – issue securities. The issuer of securities can be the government, various government agencies, municipalities, or commercial enterprises.
- Investors and traders – buy and sell equity securities . Investors and traders can be individuals and legal entities. The difference between them is conditional: - investors are LONG-TERM traders who buy securities for a period of 1 year or more; — traders trade on both sides of the market, opening Buy or Sell in order to take Profit on changes in prices of financial instruments. Scalpers and Day Traders open several trades a day, a Position Trader carries out several trades over several months, “taking profit” from medium-term trends in the market.
- Brokers - provide technical trading support for private traders and investors and act as intermediaries, transferring client orders to the exchange, incl. through the provision of Margin and Leverage (these are brokers, brokers, market makers, dealers, forex dealers, etc.).
- companies that maintain an electronic “register of securities owners” and depository storage of securities certificates and accounting for changes in ownership of securities. These are two independent guarantors of documentary confirmation of the owners of each valuable book on the exchange;
- trading organizer - operators of the St. Petersburg and Moscow MOEX exchanges;
- Financial regulators develop rules, issue permits and licenses, exercise control and supervision, and combat financial crimes. In the Russian Federation this is the Bank of Russia, in the USA - NFA, CFTC and SEC, in Switzerland - FINMA, in Germany - BaFin, etc. Read more in the materials Financial regulators and their licenses.
Algorithm for placing shares
The purpose of this procedure may be to reorganize the structure, change the nominal value, increase the authorized capital, consolidate or split previously issued options. The investment process is supported by underwriters. Professional stock market participants provide services at all stages.
The underwriter has the opportunity to take responsibility for the implementation of issued certificates. When purchasing documents from the issuer at a fixed price and selling them to investors at market value, the reseller is responsible for the negative consequences. The risk is limited if he commits to repurchase the actual portion of the options.
Documentation of the decision
The initiative to issue is confirmed by the founders of the company at a general meeting after conducting a detailed analysis of the activities and justifying the feasibility of the procedure. The agreement reached specifies the decision on the chosen type of shares, their volume and method of distribution on the market.
The law provides for the issuer's right to include in the decision made additional conditions for sale and restrictions for holders.
Drawing up a draft issue
This document is drawn up according to the model established by law. The project contains data on the financial condition of the company, previous issues of shares, and other information. Drawing up a document is mandatory when planning to sell shares to more than 500 investors.
State registration
The issuing company prepares a package of documents, which includes a drafted decision, share forms, and an issue draft. State registration is carried out after approval of the request. The appeal is reviewed within 30 days.
During the initial procedure, information is provided 1 month from the date the company is assigned a state number. In case of repeated issue, the deadline for submitting information is 3 months.
Issue cost
Registration is carried out by the department of the Bank of Russia, to which the powers of the Federal Financial Markets Service have been transferred. Consultation can be provided by legal companies that study and monitor the procedure and contact the registration authority of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
The cost of registering a primary issue is 22.5 thousand rubles, a securities prospectus, an additional issue is 45 thousand rubles.
Information disclosure
After state registration, the company places the information contained in the project in sources with public access to information. This allows potential investors to familiarize themselves with information about the planned event in advance.
Placement of securities
Sales of shares are carried out in accordance with stock exchange quotations. The lower limit for the placement of securities is limited by the nominal value. The final stage can begin 2 weeks after the announcement in information sources.
The company can carry out the sale of shares independently or use the services of a specialized trader - an underwriter. Based on the final results of the event, the joint-stock company draws up a report, which is submitted to the state registration authorities.
The document reflects:
- information about deadlines,
- information about the price and number of options;
- amount of revenue;
- information about citizens and legal entities owning 2% of the issue.
The placement of options involves the alienation of certificates based on transactions concluded between the investor and the issuer. The procedure can begin only after state registration and provision of public access to information about the issue to acquirers.
The period is set by the decision, but cannot exceed 1 year from the date of approval of the decision on release. During the process of alienation of securities, their value may change without the right to provide individual investors with an advantage in the acquisition. The main method of placement is purchase and sale with the drawing up of an agreement.
The most popular stock exchanges in the world for placing securities issues
The modern securities market is formed through a network of stock exchanges around the world, the largest of which are the 60 largest stock exchanges with a capitalization of $84 trillion as of April 1, 2019.
24 securities exchanges have a capitalization of over $0.5 trillion. This is “real money” for which all previous issues of securities were purchased. Among them
- New York Stock Exchange - capitalization $23.211 trillion.
- NASDAQ: No. 2 exchange in the world - capitalization $11.218 trillion.
- Tokyo Stock Exchange – $5.608 trillion.
- Shanghai Stock Exchange SSE – $5.013 trillion.
- Hong Kong Stock Exchange HKE – $4.307 trillion.
- Euronext (Paris, Amsterdam, Brussels, Lisbon, Dublin) – $4.268 trillion.
- London Stock Exchange LSE – $3.965 trillion.
- Shenzhen Stock Exchange SZSE – $3.355 trillion.
- Toronto Stock Exchange – $2.216 trillion.
- Bombay Stock Exchange BSE – $2.179 trillion.
- National Stock Exchange of India - $2.156 trillion.
- Frankfurt Stock Exchange - $1.867 trillion.
- Swiss Stock Exchange - $1.603 trillion;
- Korea Exchange (KRX) - $1.468 trillion;
- OMX Group Nasdaq Nordic Exchange (Vilnius, Iceland, Copenhagen, Riga, Stockholm, Tallinn, Helsinki, Armenian stock exchanges) - $$1.432 trillion.
- Australian Stock Exchange ASX - $1.384 trillion.
- Taiwan TWSE - $1.041 trillion.
7 securities exchange markets have capitalizations ranging from $500 billion to $1 trillion. This
- Johannesburg Stock Exchange (South Africa) - $950 billion;
- Sao Paulo Stock Exchange (Brazil) - $820 billion;
- Madrid Stock Exchange - $770 billion;
- Singapore Stock Exchange - $715 billion;
- Moscow Exchange MOEX - $636 billion.
- Saudi Stock Exchange (Tadawul) - $557 billion.
- Stock Exchange of Thailand (SET) - $535 billion.
A complete list of the 60 largest stock exchanges of securities can be found at the link of the author's research of the Masterforex-V Academy. Of course, the company that issued the issue independently decides to place its securities on one or another exchange in the world.
Issue of shares and bonds by commercial entities
Commercial structures (banks, large holdings, corporations) have the right to issue securities subject to a number of rules , compliance with which is mandatory. In different countries, the rules may differ in detail, but the main points are similar, otherwise issuers will have problems attracting foreign investment. So,
- the right to issue is granted only after registration of the issue with the relevant government bodies;
- forms of securities are produced in protected state printing houses that have the appropriate license;
- the issue of shares should not be intended to cover financial losses. This is how the state, represented by the regulator, protects investors from purchasing securities of potentially risky companies. However, companies suffering long-term losses have virtually no chance of being listed on reputable exchanges.
Issue of government securities
Government bonds are loans that the government takes from investors. Short-term bonds are designed to patch budget holes, while long-term bonds are issued to finance certain projects or for the purpose of profitable investment.
The main difference between government securities and corporate securities is that the obligation for them is borne by the entire state (the obligation for municipal securities is borne by the municipality, but in some cases the state acts as a guarantor).
Government bonds are in high demand among investors . Bonds of countries with high credit ratings - the USA, Switzerland, Germany, Great Britain ... - have a low interest rate - you won’t earn much, but they have the highest reliability.
Debt securities of countries with low or low credit ratings - Ukraine, Serbia, Greece , Uzbekistan ... - have a high interest rate. You can earn a lot from them, but... only if the bonds are repaid on time, and do not declare a default or do not agree on restructuring. Investors face risks in the form of postponement of payment terms, cancellation of interest accruals, reduction of interest and other “delights”.
Government bonds are denominated in national or foreign currency (usually USD, EUR, GBP, CHF, CAD, NZD, etc.) In countries with high inflation and significant devaluation, bonds denominated in national currency have a noticeably higher interest rate.
Non-cash funds
This is a replenishment of bank accounts with resources. This money is put into circulation at the time when banks issue loans and credits.
At the same time, borrowers pay back their debts and bring cash to the banks. This type of emission is necessary to meet the needs of enterprises and individuals. persons in additional finance.
*click on the picture to open it full size in a new window
The deposit-check form (non-cash) is much larger in volume than the size of the cash issue described above.
Organization and procedure of issue
The issue of securities is a responsible step; such decisions are not made rashly. This simultaneous change in the legal profile of the company (transformation into a joint stock company) , the free sale of its shares (shares), disclosure of information, etc. - have serious consequences, so it is necessary to carefully weigh the pros and cons and approach the issue of implementation responsibly.
Briefly, the emission can be divided into 4 stages:
- Adoption and approval of an official decision.
- State registration.
- Placing securities on the stock exchange.
- State registration of a report on its results.
Proper organization of business - everyone should mind their own business, in which they are a professional . Having decided to issue, organizations involve stock market professionals or underwriters in the process. Yes, they need to pay and incur additional expenses, but it is better to pay a professional once than to deal with the consequences of mistakes made due to an illiterate approach to the issue and placement of securities.
Underwriters are not just consultants; they take on the entire process of selling the issue , greatly simplifying the issuer's task. Depending on the agreements, the conditions for working with them are as follows:
- The underwriter can buy the entire issue at an agreed price, and then put the securities up for auction on your own behalf.
- a plus for the issuer - a guarantee of sale of the entire block of shares at the agreed price;
minus – lost profit if the securities are in high demand.
- The underwriter does not purchase the entire issue, but accepts obligations to purchase securities that were not sold. The purchase price may be pre-agreed or market price at the time of purchase.
- a plus for the issuer - a guarantee of sale of the entire block of shares;
- minus - loss in case of insufficient demand in the market and, as a result, a lower price than the opportunity to sell to the underwriter on full buyout terms.
- The underwriter acts only as an intermediary. It qualitatively accompanies the entire procedure for placing securities, but does not buy back either immediately or unsold balances.
- a plus for the issuer - obtaining maximum benefits when there is high demand for securities;
- minus – risks in case of weak interest in them (low price, unsold packages).
Who makes the decision to issue:
- issue of shares – general meeting of shareholders;
- issue of bonds – board of directors, executive body.
Classification of issuing securities
Emission securities are divided depending on the form of issue into:
- documentary;
- undocumented.
In addition, they can be:
- to bearer;
- nominal.
Personalized and bearer
Securities are called registered securities, which by law are required to contain in their description identification information about a specific holder.
Bearer securities, in turn, do not require identification of their owner, but provide rights assigned to them upon presentation of a certificate confirming ownership of the financial instrument.
Documentary and non-documentary forms
The documentary form implies the presence of a physical paper certificate certifying ownership.
Non-documentary form means an electronic record of owners recorded in the register of holders. Such registers are maintained in specialized depositories, which are controlled by the Central Bank.
However, there is an important point that from January 1, 2022, the issue of issue-grade securities can be made exclusively in book-entry form!
By type of income
Based on the type of formation of the income base, the following groups are distinguished:
- Interest. Bonds whose income is set as a percentage; they can be constant or tied to some calculation formula.
- Winning. Bonds with a touch of excitement. The meaning of such financial instruments is that coupon income is not accrued to each owner every moment, but is consolidated on a common account, but after the reporting period it is played out randomly among all participants.
- Dividends. Ordinary or preferred shares, where part of the company's profit is distributed among holders through dividend payments. Such accruals may be regulated by the approved dividend policy or proposed for distribution according to other principles, if the current financial position of the issuer allows it.
- Coupons. Corporate or government bonds with a predetermined size, quantity and currency of regular coupon payments.
- Discount. Bonds that are initially placed below their face value, thus generating future income for the investor.
By terms of application
Depending on the circulation period there may be:
| TYPE | Period | Tools |
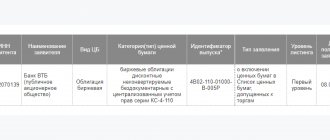
| Short term | Up to one year | This generally includes bonds or derivative contracts on securities such as options. Often such bonds are issued for a month/quarter/half-year/year, but in some cases banks can even use one-day instruments to maintain an optimal level of liquidity, so-called Overnight transactions. The main borrower of this type is VTB Bank, which issues discount bonds every day. For example: “VTB Bank-KS-3-293-bob”. |
| Medium term | From one to five years | This group includes some state, municipal and corporate bonds. For example, building bonds of the large retailer Magnit: “Magnit-003R-01”, with issue in February 2022 and maturity in February 2022 or municipal issue “Mordovia 34003 region.” with a maturity of 5 years. |
| Long-term | From five years and longer, but with a limited circulation period | This group includes most government bonds and some corporate and municipal bonds. For example, government OFZ 26230 with issue in June 2022 and maturity in March 2039. |
| Indefinite | No limitation on circulation period | Basically, there are shares that do not have a maturity date. But in some cases, organizations can issue perpetual bonds or, as they are also called, “perpetual bonds.” |
By stages of circulation
Regarding the stage of circulation, they take the following form:
- primary market;
- secondary.
Types of emissions
So, the organization decided to issue securities. How to understand what is needed and best suited? The following are the main 5 types of securities issues:
- Primary issue refers to the very first issue of securities. The initial public offering of shares on the stock exchange is called IPO (Initial Public Offering);
- secondary issue is securities of the same type re-offered for sale in the form of a new issue;
- subscription is the placement of securities by concluding a purchase and sale agreement. It can be open or closed. With an open subscription, the circle of buyers is not limited; with a closed subscription, securities are sold to a narrow, pre-approved circle of investors.;
- the distribution of securities is similar to a closed subscription - they go to a limited, pre-known circle of investors. However, in this case, no purchase and sale agreement is concluded. Distribution is used when changing the form of a company to a joint stock company without the intention of a public offering of shares or during an additional issue with the subsequent transfer of shares to existing shareholders. This type of issue is not used for bonds.;
- Conversion in its essence is a replacement: some securities are exchanged for others (of the same issuer) on agreed terms. The securities being replaced are redeemed.
Development of a prospectus
To register an issue of shares, a prospectus must be developed. A prospectus is a document containing information about the issuing company, its financial position and the future issue of shares. Registration of a prospectus is required when:
- securities are issued and placed by open subscription;
- more than 500 buyers via closed subscription;
- more than 500 shareholders exercising preemptive rights;
- more than 200 million rubles. raised by issue during the year.
Prospectus is an information bulletin intended for investors, which reflects information about the issuing company and the securities being issued. The form of the prospectus is approved at the legislative level. The data it contains must be complete and reliable. The issuer is responsible for this. The document contains 5 sections:
| Chapter | Content | Description |
| A | Information about the issuing company | The name of the issuer is included, the legal address, complete data on branches (if any), founders, management bodies, specialization, and products are indicated. Large shareholders owning more than 5% of shares are also indicated. |
| B | Information on the financial position of the issuer | This section includes annual financial statements (in accordance with the requirements of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation) for 3 financial years or less if the issuer has been operating for less than 3 years. Indicators characterizing the reserve fund and authorized capital are given, the state's share in the authorized capital is indicated, the presence of a “golden share” (if any), etc. When creating a JSC, this section may be absent, but during reorganization it is mandatory |
| IN | Information on past issues | Information about previous issues is indicated and fully decrypted. This data must coincide with the information specified in the decision to issue securities. In addition, the start and end date of the placement of shares is indicated, and the state body that carries out the registration is designated |
| G | Information about placed shares | Information about the re-issued share is reflected. The information specified in the decision to issue shares is repeated, information on restrictions is entered (if insufficient distribution, the issue is considered invalid). The rights granted by the security are indicated. With the participation of the underwriter, it is necessary to indicate his data and information about the agreement with him. Data on the method of distribution of shares and taxation of profits is also indicated. |
| D | Additional Information | Additional information is included that the issuer wants to convey to potential shareholders. For example, restrictions, special conditions, implementation parameters, etc. are indicated. |
Issue timing
The timing of the issue of securities is influenced by various factors:
- how quickly the decision on the issue will be made;
- how soon will they find an intermediary and conclude an agreement with him;
- deadlines for state registration of the issue.
Deadlines for registering shares in Russia:
- issue upon establishment of a joint stock company – up to 20 days;
- additional issue – up to 20 days;
- issue during reorganization – up to 30 days;
- report on the results of the issue – up to 14 days.
According to Russian legislation, no more than 1-3 months should pass from the moment the decision on the issue is made to the registration of securities.
- no later than 1 month, it is necessary to register the issue when distributing securities among the founders, when issuing bonds or convertible shares;
- up to 3 months in other cases.
Reference materials (download)
| # | File | file size |
| 1 | Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Article 277 Peculiarities of determining the tax base for income received upon transfer of property to the authorized (share) capital (fund, fund property) | 857 KB |
| 2 | Regulations on bills of exchange and promissory notes | 140 KB |
| 3 | Regulation of the Bank of Russia dated December 19, 2019 N 706-P “On standards for issuing securities” (Registered with the Ministry of Justice of Russia on April 21, 2020 N 58158) | 2 MB |
| 4 | Federal Law of April 22, 1996 N 39-FZ (as amended on December 27, 2019) “On the Securities Market” | 2 MB |
| 5 | Budget Code of the Russian Federation | 1,011 KB |
| 6 | Civil Code of the Russian Federation (part one) | 4 MB |
| 7 | “Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Part One)” dated July 31, 1998 N 146-FZ (as amended on August 2, 2019) | 6 MB |
| 8 | “Regulations on the disclosure of information by issuers of equity securities” (approved by the Bank of Russia on December 30, 2014 N 454-P) | 3 MB |
Production of securities
The production of securities is fundamentally different from many documents.
- A security cannot simply be printed on a printer or ordered from any, even the most high-tech printing house. Why? It’s simple - otherwise the market will be flooded with tons of fakes.
- The security must be printed on paper with anti-counterfeit elements, in a printing house licensed to produce security forms. For each printed form of a security, the printing house is responsible and reports to the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation.
- Securities are produced according to a specific government template. Printing of securities from a layout provided by the customer is excluded.
State registration of the issue prospectus
The prospectus for the issue of securities is a kind of extended passport of the issuer . It contains thorough information about both the security being prepared for issue and the issuer. The prospectus is necessary so that both registrars and buyers have the broadest possible understanding of the company whose securities they are registering (going to buy).
The following information is included in the securities prospectus:
- type of securities, issue amount, purpose of the issue, issuer contacts;
- business plan, business features, entry into foreign markets, prospects, etc.;
- disclosure of financial information (income, profit, financial statements, etc.);
- risk factors: stock splits, information about competitors, main contracts, availability of licenses, business development plans, presence of financial risks, influence of politics, etc.;
- information about intermediaries of the issue, type of agreement with the underwriter;
- information about personnel, main shareholders.
Regulators carefully check issuers to assess their reliability and to prevent the introduction of shell securities to the market. For example, the SEC (US Securities Commission) requires a report after the IPO on where the funds received from the placement were invested.
If it turns out that the money was used to pay off debts, problems will arise, since the main purpose of the issue is considered to be business expansion and investment (acquisitions, mergers, etc.), and not patching financial holes.
Central Bank classification
Regarding the nature of the issue or issue, securities are divided into two types:
- emission;
- non-emission.
Read more about each type and their differences below.
Emission
The main difference between emission securities is a combination of factors, which includes:
- mass issue of securities;
- securing equal rights throughout the entire period of circulation of Central Bank data;
- a clear release procedure and mandatory state registration. registration;
- regulation by a unified legislative framework.
Among the issuing financial instruments, the most common types are shares and bonds.
Non-emission
The subject of placement may also be non-issue securities.
The main features characterizing their release are:
- lack of mass placement;
- lack of special state registration of the issue;
- regulation by various legislative acts;
- property or liability rights under such securities are fixed on an individual basis.
There are many types of non-issued securities, for example, certificates, checks, bills, certificates.
What is the difference
For clarity, I have summarized the main differences between emission and non-emission securities and reflected them in the following table:
| Emission | Non-emission |
| Regulated by the Law on the Securities Market or the Law on the State. papers | Regulated by special legislative acts (law on bills of exchange, investment funds, mortgages) |
| Mandatory registration for all types of securities | Registration is required only for investment units of mutual funds |
| Mandatory Standardized Disclosure | Disclosure is required only in relation to investment units of mutual funds |
| From 2022 can be issued only in undocumented form with centralized storage | Can be issued in both documentary and electronic form |
Information disclosure
Issuers of securities must be open to regulators and investors , therefore their responsibilities include periodic (at least once a quarter) disclosure of information:
- informing about the current financial and economic situation (quarterly, annual reports, etc.);
- measures taken, plans;
- upcoming issues;
- other.
The need to regularly inform investors and regulators may be contractual or mandatory. However, in any case, even if this is not an obligation, failure to provide timely information or withholding some important information can lead to an investigation by the financial regulator and will result in a decrease in investor confidence, which will lead to a fall in the price of securities. The longer an issuer deceives investors by concealing financial or other problems, the more avalanche-like the collapse of its securities will be when the truth is revealed.
Information disclosure occurs:
- through publications on the official website, traditional media (Wall Street Journal, Financial Times, Economist, etc.), online publications;
- notifications to government agencies in the approved manner;
- personal notification to security holders.
What does emission lead to?
It stimulates the economy , and theoretically should always lead to economic growth, because its result is more money.
However, the process also has negative consequences. The more money in circulation, the lower its value . When emissions are high, inflation occurs.
Prices begin to rise, and the purchasing power of citizens even decreases, since with a fixed salary for the same amount of money over time, fewer and fewer goods and services can be purchased.
The incomes of some entrepreneurs, primarily those who sell essential goods, begin to grow unreasonably, and this leads to imbalances in the balance of payments.