What is BMI and how to calculate the Big Mac index? Why was this particular McDonald's product taken as the basis for certain economic calculations? Is the Big Mac Index applicable to Forex market analysis? I wrote an article that answers all these and some other important questions.
To assess the economy as a whole, states use many complex indicators and terms: inflation, denomination, GDP, employment level and many others. Using all this data, economists determine the quality of life of ordinary citizens. The listed terms are difficult for ordinary people to understand. Is there an easier way to determine purchasing power? Yes, and it was presented in The Economist back in 1986.
What is the Big Mac Index?
Big Mac Index (BMI) is a special parameter used to determine PPP (purchasing power parity). BMI is based on the theory that the value of a basket of similar goods in two countries is compared to calculate the real exchange rate. For example, in a Russian supermarket they spent 500 rubles on bread, milk and meat. It costs $25 to buy identical products (in the same quantities) in a US supermarket. The fair exchange rate between the dollar and the Russian ruble is equal to the quotient of the amount spent in the Russian Federation divided by the amount spent in the United States. That is, the desired value: 500/25 = 20 rubles.
PPP theory states that identical goods in different countries should cost approximately the same. Based on this equality, a “fair” exchange rate is calculated. Additional parameters (income level of state citizens, costs of transporting products, etc.) are not taken into account.
The economists who came up with the Big Mac index replaced a basket of goods with a single product that is most popular around the world. Why was Big Mac used as the basis for calculations?
There are two reasons. Firstly, restaurants of the famous fast food chain are located in almost every country in the world. You can buy a Big Mac at any of them. Secondly, this product contains such a quantity of food components that is sufficient to consider it a so-called national economy model. The Big Mac contains meat, bread, cheese, and vegetables. The Big Mac Index is a convenient way to determine the discrepancy between the values of currencies of countries with similar income indicators (especially during crisis events). It clearly demonstrates how unprofitable an expensive currency is for the country’s economy.
It is noteworthy that for a long time many economists did not know how to calculate the Big Mac index to estimate the “fair” value of the Indian rupee, since in this country, for obvious reasons, it is impossible to buy a burger with a beef patty. A compromise was made in 2011: the index was calculated based on Maharaja Mac, a product containing a chicken cutlet instead of a beef cutlet.
Formula for calculating the Big Mac index
The McDonald's restaurant chain and their signature product (Big Mac) appeared in the United States. For this reason, the US dollar is used as the reference currency when calculating the index. The formula for calculating BMI contains only two parameters and has the following form:
BMI = Plc/Pusd , where Plc is the cost of one Big Mac in local currency (lc – local currency), Pusd is the cost of a Big Mac in the USA.
Let’s say that 1 Big Mac in the Russian Federation can be bought for 150 rubles, and in the USA - for 6 dollars (prices are taken arbitrarily for ease of calculation). BMI is 150/6= 25 rubles. This is how much one US dollar should cost. The actual rate (at the time of writing this article) was about 76 rubles per 1 US dollar. The difference of 51 rubles indicates how undervalued the national currency of the Russian Federation is.
The calculation is so simple because it makes several assumptions, including that the shipping cost of any Big Mac ingredient is zero, to ensure that the product is priced equivalently in any country. This is how the degree of undervaluation or overvaluation of a particular currency is determined (based on the theory of purchasing power parity). The above example clearly demonstrates that the Russian ruble is undervalued by more than 200% against the US dollar.
Historical information
The Big Mac index first calculated in 1986 as a joke. The idea belongs to representatives of the British magazine “The Economist”. Its essence was to clearly demonstrate the unfairness of the exchange rates of some countries, which, from the point of view of PPP theory, are overvalued or undervalued. The McDonald's network in 1986 was not very developed, so the list initially included only 15 states. McDonald's most popular product at that time in the United States cost $1.60.
The first McDonald's restaurant in the Russian Federation was opened in 1990. Since then, BMI has also been determined for the Russian ruble. It is noteworthy that for 1 Big Mac you had to pay 3.75 rubles (about 6.2 dollars at the then exchange rate). The price of this product in the US managed to rise to 2.1 dollars. From this we can conclude that in 1990 the Russian ruble was greatly overvalued. In subsequent years, the difference between the value of the ruble and the dollar decreased. In 2022, the Russian ruble (based on the same calculations) was recognized as the most undervalued currency.
Myth #3. The ruble is artificially undervalued
According to the Big Mac index, the ruble is undervalued by 60% relative to the dollar exchange rate. The media usually do not specify by whom and how it is underestimated, but sometimes they increase the intrigue with the phrase “artificially underestimated.”
Among the main culprits of such underestimation, participants in economic discussions name the Central Bank and the government, large exporters, speculative bankers and financiers of the “world behind the scenes.”
If you don’t want to become a victim of such fast food in analytics, watch our video. We will teach you to press the “close” button in time when dubious forecasts appear on the screen.
If we turn to the theory of exchange rates, then the intrigue with “artificial undervaluation” comes to naught.
Fundamentally, an exchange rate can be overvalued or undervalued if the inflation-adjusted nominal exchange rate deviates from the calculated level. The only question is which year to choose as the base year for calculations.
Let's calculate changes in exchange rates taking into account accumulated inflation over 25 years, since 1995. During this time, the ruble depreciated 25 times, and the dollar by 75%.
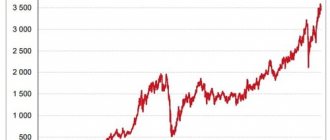
The chart below shows that the real ruble exchange rate, adjusted for inflation, fluctuated greatly under the influence of oil prices. During the period of high prices in 2005-2014, the ruble exchange rate strengthened and was higher than the base year.
However, for the last five years the rate has been near the level it was in 2004-2005.
Schedule 4
Real exchange rate of the ruble to the US dollar in 1995 prices
Change in the average annual exchange rate adjusted for inflation in Russia and the USA, %
Source: The Economist, International Monetary Fund, World Bank, Bank of Russia Calculations: Yango.Pro
Economists have two views on the main reasons for the devaluation of the ruble in 1998, 2008 and 2014. Some believe that the collapse in oil prices, and later also sanctions, were to blame for everything.
Others believe that this is only a consequence, and the main reason is in fact the previous excessive strengthening of the ruble against the backdrop of rising oil prices: it leads to the accumulation of imbalances and an increase in external debt of the private sector, which ends in a crisis.
Be that as it may, now the stability of the real effective exchange rate of the ruble is one of the goals of economic policy. And that’s why the ruble has been consistently weak in recent years.
In essence, this is the official policy supported by the President. It is based on a floating exchange rate and a new budget rule aimed at removing oil and gas windfalls (above $43.3 per barrel in 2022). This rule neutralizes the impact of commodity prices on the exchange rate and prevents excessive strengthening of the ruble.
A weak ruble at current levels is beneficial to non-resource producers with a low share of foreign exchange costs, exporters, as well as the government, which receives ruble revenues to the budget from foreign currency exports.
When budget expenses increase due to a crisis, additional income from exporters also increases due to the weakening of the national currency.
For example, in 2022, the index of the real exchange rate of the ruble against the dollar decreased by 7.8%, and against the currencies of the main partner countries by 8.5%. This largely covers additional anti-crisis budget expenditures in the amount of 12.5% of total expenditures (2.86 trillion rubles).
In order not to get confused about which exchange rate is overvalued or undervalued, see the cheat sheet below (inset “Types of exchange rates”).
Types of exchange rates
- Nominal (exchange) exchange rate. It is used to exchange one currency for another and can have several varieties. For example, the rate may be exchange (market) or special (non-commercial). Depending on the method of regulation, a distinction is also made between fixed and floating nominal exchange rates. Read more >>
- PPP course. Shows the currency ratio by which the purchasing power of one currency is relative to another. It is calculated through the currency value of the consumer basket or specific goods and services. Essentially, this is an alternative rate for comparing the volume of goods per monetary unit in different countries.
- Real exchange rate. Reflects the price ratio at which goods from one country can be sold in another country. In general, it is calculated as the nominal exchange rate multiplied by the ratio of local prices. Essentially, it is a price index (without the influence of inflation).
- Real effective exchange rate. Shows the real dynamics of the national currency in relation to the currencies of other countries, taking into account the weight of each of these countries in foreign trade turnover. In 2021, the Central Bank of the Russian Federation calculates it based on changes in exchange rates of leading trading partners in 41 countries.
- Equilibrium exchange rate. An exchange rate that ensures a balance between supply and demand for a currency based on the balance of macroeconomic factors. That is, when domestic production provides maximum employment at a low level of inflation, and the country spends and invests abroad as much as foreign countries spend within it.
- Floating exchange rate. The mode of formation of the nominal exchange rate under the influence of market forces - supply and demand. Their balance is affected by changes in import and export prices, the level of inflation and interest rates in Russia and abroad, the rate of economic growth, investor sentiment in Russia and the world, as well as the monetary policy of the central banks of Russia and other countries. In Russia it has been in effect since November 2014.
Estimation of the cost of an hour of work in "Big Macs"
Another way to use BMI is to compare the cost of a popular burger with the minimum hourly rate adopted by the state at the legislative level. Having studied the available data, we can conclude that the average French or German earns about 2.5 Big Macs per hour of work. At the same time, a Spaniard or Pole earns almost 2 times less - about 1.3 Big Macs. Based on these values, it is possible to estimate the difference in the purchasing power of citizens of the above countries.
Sources
- Wikipedia: Big Mac Index
- economist.com: The Big Mac index
- fincult.info: Big Mac index and other unusual economic indicators
- Big Mac Index for July 2022
What other methods of calculating purchasing power can you suggest? You can share them in the comments.
Recommended for you
- How to calculate loan interest yourself
- How bank card payment systems work and how to choose the right one
- Why do Russian banks collect biometrics, is it worth submitting it and how to do it
Vitalina Slepukhova One of the leading journalists of the project. In the credit sector since 2008. Has a higher education with a degree in Banking. Published in the online edition of the Kommersant newspaper. Extensive experience in the financial sector helps to navigate the microfinance and banking services market and see the most important events.
(17 ratings, average: 4.9 out of 5)
How to Use the Big Mac Index to Trade Forex
The main goal of creating BMI is to simplify the understanding of complex economic processes occurring in various countries and to provide an objective assessment of what is happening in the global economy. However, this indicator is successfully used to forecast exchange rates. Most often, BMI is used to calculate the number of Big Macs that can be purchased in a particular country for a certain amount of money, for example, $100. This number can either increase or decrease. In the latter case, this indicates two possible phenomena:
- The exchange rate of the national currency increases. Without a lead on the exchange rate, BMI is difficult to use as an indicator for making forecasts.
- The price of the Big Mac is increasing. Significant changes in BMI with relatively stable exchange rates indicate internal economic problems. Most often they are expressed in inflationary processes occurring in certain sectors of the economy, an increase in the cost of rent, wages or raw materials used to produce a burger. If these factors have a significant impact on a state's economy, exchange rate fluctuations should eventually be expected.
There is a hypothesis according to which the significant difference between the real exchange rate and the one calculated on the basis of BMI will be smoothed out over time. But in practice, this hypothesis does not always work.
From the traders' point of view, the Big Mac index has the following features:
- Calculated using a formula that is too simple;
- Includes many assumptions that may not be true in practice;
- Suitable for assessing the market situation only when concluding long-term transactions;
- Serves only as an additional indicator.
Try to calculate the Big Mac index yourself for the currencies you are interested in and draw conclusions about whether they are undervalued or overvalued. You can track changes in BMI using special tables and graphs, which I will discuss below.
Myth #5. It is impossible to forecast the dollar exchange rate
If forecasting exchange rates was impossible, then George Soros would not have made his billion on the famous foreign exchange bet against the Bank of England. True, skeptics will note that since then such stories have not been heard on the foreign exchange market (see the “Black Wednesday” sidebar).
The thing is that economics does not have a reliable method for determining the exact value on a specific date. However, there are indicators that help determine whether a currency is significantly undervalued or overvalued.
Black Wednesday
In 1990, the UK, under the government of John Major, joined the European Exchange Rate Mechanism (ERM). As part of European integration, participating countries have pledged to keep their currencies within a band against the German mark. For the British pound the range was 2.95 +/-6. Read more >>
It soon became clear that the British pound was fundamentally overvalued and the recession in the economy worsened the situation. By August 1992, currency speculators realized that, due to the limited resources of the British government, the pound had little chance of avoiding devaluation.
The trigger was the words of the President of the German Bundesbank, Helmut Schlesinger, that a certain currency was under pressure and the measures taken could not solve the problem.
Within a month, George Soros's Quantum Fund opened short positions on the GBP/DEM currency pair for the equivalent of $10 billion. The fund began selling borrowed pounds on the morning of Wednesday, September 16, and other market participants joined the sale.
In total, on that day, the British authorities spent $27 billion of reserves to maintain the exchange rate, which led to trading losses of $3.3 billion. By Wednesday evening, they announced their withdrawal from the agreement on the currency corridor. Over the coming weeks, the pound fell by 14%. Quantum Fund made a profit of more than $1 billion.
The devastating day for the Bank of England went down in history as Black Wednesday.
IMF economist Louis Catan
believes that the main indicator for assessing the overvaluation or undervaluation of a currency is the real effective exchange rate. It signals significant exchange rate overvaluations before the onset of many crises.
In practice, it is difficult for market participants to use real rates for short-term forecasting because they can fluctuate significantly in response to market signals and prices do not change as quickly.
Nevertheless, Katan notes, a fairly large amount of data has been accumulated on real exchange rates, which reflects fundamental trends and qualitative changes in the foreign exchange market.
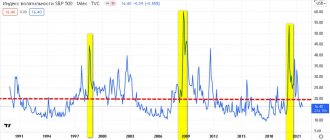
To check this, let's look at the real effective exchange rate of the ruble not only to the dollar, but also to other currencies with which Russia has foreign trade settlements. Taking into account the previous graphs, we will choose 2005 as the base year.
Schedule 6
Real effective* ruble exchange rate in 2005 prices
Change in the average annual rate adjusted for inflation, %
* Effective rate relative to the currencies of the main partners in the total foreign trade turnover of Russia (41 countries in 2022).
Source: Bank of Russia Calculations: Yango.Pro
The chart above shows a market trend: when the ruble strengthens, its growth against the dollar can outpace growth against other currencies. And vice versa: weakening against the dollar may occur faster than against other currencies. As a result, the real effective exchange rate of the ruble is now at the 2005 level, and the real exchange rate to the dollar is lower - at the 2004 level.
To evaluate the trend, let's look at the moving average line, calculated as a simple average of the two previous periods. This line smoothes out fluctuations and shows the existing trend - now it is downward (the effective rate is below the moving average and is declining).
Table 1
Trend in the real exchange rate of the ruble to the US dollar
Change in the average annual rate adjusted for inflation, %
Source: Bank of Russia Calculations: Yango.Pro
Several conclusions can be drawn from the graph above:
- Over the coming months, the ruble may weaken by another few percent, which would mean an increase in the nominal dollar exchange rate to 80 rubles. However, the fundamental potential of this weakening is limited - the real exchange rate of the ruble is already at its lowest levels over the past 15 years.
- Next year, in the absence of new shocks and geopolitical risks, the ruble may even strengthen in real terms. Provided that the Central Bank keeps inflation within the forecast of 4-4.5% by the end of 2022, and the US Federal Reserve returns it to 2%.
- At the moment, the exchange rate can be very volatile: it is influenced by the inflow/outflow of capital, the state of the balance of payments and other factors. But if the real exchange rate is relatively stable, then in the long term the nominal dollar exchange rate will increase, on average, by the difference between “domestic” and “external” inflation.
The constant growth of the nominal dollar exchange rate fuels devaluation expectations of the population and the habit of keeping savings in foreign currency. Although in the current conditions, when there are no serious imbalances and the Bank of Russia is targeting inflation, savings in bonds may be a good alternative.
It remains to find out what is considered the main signal that can warn private investors about a possible devaluation of the ruble.
To be precise, devaluation is the official reduction of a fixed exchange rate. In conditions of a floating exchange rate, they talk about the depreciation of the ruble, as this occurs under the influence of market mechanisms.
And yet, a strong weakening of the ruble is quite possible under different currency regimes. Therefore, it is useful for any investor to monitor the dynamics of the real ruble exchange rate. The graph below shows that it directly correlates with the undervaluation of the PPP course.
Table of rates for the Big Mac index in 2022
The website of The Economist publishing house provides all the information about the “real” value of the national currencies of many countries around the world, taking into account current prices for a Big Mac. The Big Mac index (table by country) is presented below.
As you can see, the last calculations were carried out in July 2022. At that time, the cost of a burger in the Russian Federation was 135 rubles, and in the USA – $5.71. The results show that the "real" exchange rate should be 23.64 rubles per 1 US dollar (the actual rate at that time was 70.58 rubles per 1 dollar). As a result, we have: the Russian ruble is undervalued by 66.5%.
In the world
According to statistics for 2022, according to this index, almost all world currencies are undervalued against the US dollar, except for the Swiss franc, Norwegian and Swedish krona.
Table 1. Countries with the highest cost of a burger in 2021
| State | Big Mac Index, % | Big Mac price, $ |
| Switzerland | 28,8 | 7,29 |
| Sweden | 12,6 | 6,37 |
| Norway | 7,5 | 6,08 |
| USA | Base | 5,66 |
| Israel | -5,5 | 5,35 |
| Canada | -6,6 | 5,29 |
Source: economist.com
As you can see, burgers are the most expensive in Switzerland – $7.29. That is, in Russia such a Bic Mac would cost 544 rubles. Sweden is not far behind with a price of $6.37, or 475 rubles. and Norway – $6.08, or 454 rubles.
Russia in the overall ranking. Source: screenshot from economist.com
Table 2. Countries with the lowest burger prices in 2022
| State | Big Mac Index, % | Big Mac price, $ |
| Lebanon | -68,7 | 1,77 |
| Russia | -68 | 1,81 |
| Türkiye | -64,5 | 2 |
| South Africa | -61,9 | 2,16 |
| Ukraine | -61,1 | 2,2 |
| Azerbaijan | -58,9 | 2,33 |
Source: economist.com
Why does the cost of a burger at McDonald's differ so much in different countries? Is it possible that in Switzerland they add some special ingredients to this dish? No, this is a very expensive state to live in general. High wages in Switzerland and taxes provoke an increase in prices for many goods and services, including burgers.
Indices similar to the Big Mac index
Purchasing power parity is determined based on other popular products produced by other companies. However, the Big Mac index remains the most popular.
Here are several indices that compete with BMI:
- The Starbucks index is calculated based on the cost of a cup of coffee (latte) in this chain. However, the Starbucks chain is significantly inferior to McDonald's in popularity throughout the world.
- The dating index is an indicator that takes into account the costs of a date with a girl, including the cost of dinner, a movie and a taxi ride.
- Olivier index. This salad, popular in many CIS countries, contains many ingredients (like the Big Mac). But, for known reasons, the Olivier index is not widespread throughout the world.
- Red lipstick index. This index is based on the theory that a woman will in any case spend money on buying lipstick, even if the state’s economy is going through hard times. When making calculations, the cost of a specific brand of lipstick is taken into account.
- Index of iPhone, one of the most popular smartphones in the world. Initially, the iPod player was chosen as a standard. But over time, it became less popular than the smartphone from the same Apple company. For calculations, a specific model with exactly matching characteristics is used.
In addition to those listed above, there are many different indices that allow you to assess the economic situation without resorting to complex calculations. However, due to its popularity and prevalence, the Big Mac is taken as the basis for calculations.
Criticism of the Big Mac Index
The Big Mac Index cannot be considered an accurate indicator for various reasons:
- Some countries do not produce beef patties (India, where the cow is considered a sacred animal, is a great example).
- Some countries are world leaders in beef exports, which should also be taken into account in the calculations.
- The composition of a Big Mac varies depending on taste preferences and local cuisine.
- The status of the Big Mac varies from country to country: in the United States it is a common food product, while in Asian countries it is considered an exotic dish. This affects both demand and pricing.
- On the African continent, the McDonald's restaurant chain is very poorly developed. You can only buy a Big Mac in South Africa, Morocco and Egypt.
For African countries, an index was introduced for KFC, the main competitor of McDonald's, which is more popular among local residents. KFC restaurants are open in more than 20 countries on the black continent. Therefore, to compare the purchasing power of the black population with the residents of Europe and America, they use the cost of a KFC bucket. This index is also not highly accurate for the reasons listed above.
Cons of burgernomics
McDonald's in different countries uses different commercial strategies to sell its products. In general, the price of a Big Mac will reflect its local production and delivery costs, as well as advertising costs.
In some markets, they use an approach aimed at increasing sales volume, while setting low margins; in others, it is the opposite. Thus, the numbers are relative, for example, a hamburger in France costs only 1 euro, in Belgium - 1.50 euros, but in general it is cheaper to dine at a Belgian McDonald's restaurant.
Prices can also vary greatly across regions of the country. For example, a Big Mac purchased in New York will be more expensive than in rural areas. Another example: in Russia, burgers are inexpensive, while Moscow is usually at the top of the ranking in terms of spending by both Russians and foreign visitors.
Source: freepik.com/alex9500
In other countries, on the contrary, food in McDonald's restaurants is relatively expensive compared to local cafes, therefore, the demand for burgers is not so great. An example is India with low wages and living standards.
Another limitation of the Big Mac Index was its geographic coverage. Not all countries have McDonald's franchises. For example, in Africa this network is present only in Morocco, Egypt and South Africa.
Thus, many factors, including the cultural preferences of citizens, are not taken into account in this indicator. But due to the non-standard approach to analyzing the economic situation, it remains popular.
Some analysts have gone further and included the Big Mac index in their research programs, for example:
- Gold-Mac-Index shows the ratio of purchasing power per 1 gram of gold, while at the same time experts calculate how many burgers can be obtained for such a gram.
- The Swiss bank has expanded its idea of using the Big Mac index. Experts now calculate the amount of time a person in a given country must work to earn enough to buy a burger.
The Economist itself made an adjustment in 2022 for the level of the country's GDP per capita. According to the new methodology, the ruble exchange rate is still 47.3% lower. That is, if we assume that in poor countries a burger should cost less than in rich countries, then the Russian currency turns out to be the most undervalued in the world.
Experts disagree on whether such conclusions can be trusted. For example, Oleg Shibanov, director of the Skolkovo-NES Financial Center, in an interview with Forbes, calls the Big Mac index “a good economic joke.”
“If the founders of modern economics, Adam Smith and David Ricardo, had known about this, they would have turned over in their graves.
In Zambia, a Big Mac costs even less, but can you really say that the Zambian kwacha is more undervalued than the Russian ruble?” Georgy Ostapkovich, director of the Center for Market Monitoring, National Research University Higher School of Economics. Source: Finam
However, many analysts continue to make forecasts based on the prices of burgers in different countries and even predict an increase in the ruble exchange rate, based on information about its undervaluation.
This is interesting! The most expensive products in the world: mushrooms for $200 thousand and tea for $700 thousand
The most expensive burger in the world:
Author: Viktor Sukhov, editor-in-chief. April 5, 2022.
Conclusion
Although the Big Mac Index demonstrates the economic situation in the world with some degree of accuracy, it is not recommended to take it seriously. It neglects many factors that influence both purchasing power and the real value of national currencies, including GDP, the political situation and much more. Some countries artificially lower the cost of certain imported goods, including those used as burger ingredients.
On the other hand, BMI provides a unique opportunity not only to look at “real” exchange rates, but also to predict their possible changes in the future. This feature of the index is more useful to people who are far from economics. In addition, by correctly comparing BMI with other economic indicators, it is possible to estimate with a certain degree of accuracy the difference in the cost of goods and services in different markets and determine global changes that affect pricing.
More visual information about the Big Mac index can be obtained by watching the video: