(aka Dow 30, Dow Jones Transportation Average, DJIA or US30) is the oldest in the United States, along with the S&P 500 it is popular among investors and traders. When compiling its basket, the authors focused on “blue chips”; Dow Jones quotes are influenced only by the largest companies in the world, the capitalization of some of them exceeds $1 trillion.
From this article you will learn:
- General information about the Dow Jones index
- Composition of the Dow Jones basket
- Dow Jones Index Calculation
- Stock selection criteria
- Dow Jones family of subindices
- How to make money on the Dow 30
- Criticism of the index, its comparison with its main competitor
- Factors influencing DJIA
- Conclusion
BUY SELL
General information about the Dow Jones index
- The provider’s website reports that the official launch date is May 26, 1896 , at which time it received the “industrial” prefix. But calculations were carried out earlier, already in 1884. Charles Dow calculated quotes, but then they were not published anywhere and were used as an internal analytical tool.
- In 1884, the emphasis was on transport companies (the basket consisted of 9 railway companies and 2 representatives of the industrial sector). At launch, 12 companies representing American industry were included.
- The next significant change in composition occurred in 1916, when the basket expanded to 20 components. And since October 1928, the calculation was carried out taking into account the 30 largest American companies.
Unlike the S&P 500, the Dow Jones index does not take into account capitalization ; US30 quotes are affected only by stock prices; this issue is discussed in more detail below. As for the prefix “industrial” in the name, this is rather a tribute to history; now the compilers of the basket do not focus only on the industrial sector.
As for the role of the DJIA, it is not suitable for assessing the state of the entire US stock market. The basket is quite narrow and characterizes only the state of blue chips.
The provider is S&P Dow Jones Indices. It provides basket adjustments and is directly responsible for calculating Dow Jones quotes.
Forecast, analytics and prospects
China and the US are negotiating new tariffs. Countries suffer losses by competing on the size of sanctions. This has a negative impact on quotes, and the value of the Dow Jones index shows this. The more positive the information on the trade war in the news feed, the higher the index.
The US Federal Reserve changes global financial markets with its speeches. Three state economic bubbles were recently exposed. All three of these bubbles keep the Dow at 25-24 thousand points, but are at risk of bursting:
- Unemployment in the US is low, it's true. But the unemployment rate does not take into account those who simply gave up looking for work. There are a lot of them now.
- The shares are expensive, but this price is unreasonably high compared to the yield of the securities.
Useful articles
What are portfolio investments Asset Allocation and why are they so popular?
What ETFs can you buy in Russia and how to do it?
Where should you keep your stash for a rainy day so you can look forward to it?
Why do some people make a million by the age of 30, while others are doomed to poverty?
So it turns out that the USA is a colossus with feet of clay. It doesn't matter for now: the Fed is raising rates, issuing attractive bonds, and the Dow Jones is rising.
Composition of the Dow Jones basket
Businesses representing the transport sector and housing and public utilities sector have been excluded from Dow Jones. Although US30 is called industrial, it includes IT companies, representatives of the financial sector, and healthcare.
As of the end of March 2022, the top five in the Dow are as follows:
- IT – 21.4%.
- Industry – 17.1%.
- Healthcare – 16.8%.
- Financial sector – 15.9%.
- Secondary consumer goods – 12.7%.
Complete list of companies from the Dow Jones index
Some of the companies have been in the basket for decades. For example, Proctor & Gamble was added to the Dow Jones Industrial Average in 1932.
Revolutionary changes in composition rarely occur; usually, when the basket is revised, no more than 1-2 components change; other shares of the Dow Jones index remain unchanged. Of the original 12 companies, only General Electric remained in the lineup.
The exception is crisis periods , when even a previously stable business may face a significant deterioration in performance. For example, in the middle of the summer of 1930, 7 companies immediately “fell out” of the DJIA, and 8 after 2 years, this is explained by the Great Depression. After the American economy stabilized, there were long-term periods (2 to 17 years) when the composition of the basket remained unchanged.
I also recommend reading:
Coca-Cola shares - company overview. How to buy shares and make money?
The name Coca-Cola is associated with the drink of the same name, but in addition to it, the company’s arsenal includes a whole range of drinks, syrups and concentrates of various […]
Which companies are included in the index?
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, or Dow Jones Industrial Average, includes a list of 30 companies.
| Company | Ticker | Year included in the index |
| 3M | MMM | 1976 |
| American Express | AXP | 1982 |
| Apple | AAPL | 2015 |
| Boeing | B.A. | 1987 |
| Caterpillar | CAT | 1991 |
| Chevron | CVX | 2008 |
| Cisco | CSCO | 2009 |
| Coca-Cola | K.O. | 1987 |
| The Walt Disney Company | DIS | 1991 |
| DowDuPont | DWDP | 2017 |
| ExxonMobil | XOM | 1928 |
| General Electric | G.E. | 1907 |
| Goldman Sachs | G.S. | 2013 |
| The Home Depot | HD | 1999 |
| IBM | IBM | 1979 |
| Intel | INTC | 1999 |
| Johnson & Johnson | JNJ | 1997 |
| JPMorgan Chase | J.P.M. | 1991 |
| McDonald's | MCD | 1985 |
| Merck | MRK | 1979 |
| Microsoft | MSFT | 1999 |
| Nike | NKE | 2013 |
| Pfizer | PFE | 2004 |
| Procter & Gamble | PG | 1932 |
| Travelers Companies, Inc. | TRV | 2009 |
| United Technologies | UTX | 1939 |
| UnitedHealth | UNH | 2012 |
| Verizon | VZ | 2004 |
| Visa | V | 2013 |
| Wal-Mart | WMT | 1997 |
Dow Jones Index Calculation
Quotes are calculated in real time. Uses standard formula for price-weighted stock indices
in this dependence the following notations are used:
- P – prices of shares included in the basket, with a total of 30 terms in the numerator.
- Divisor is a special correction factor (divisor) used in all indexes of this type.
The divisor is recalculated for any actions by business management that affect the number of shares in circulation, for example, during splits or buyback programs, decisions on the payment of dividends; these events are called corporate actions. At the initial stage of development, the divisor was determined taking into account capitalization; later this practice was abandoned. The calculation is carried out in 4 currencies - USD, CAD, EUR and JPY.
After corporate actions, the numerator of the fraction changes as the amount of the value of the shares changes sharply. Moreover, the index value before and after corporate actions is the same, from the proportion
you can derive a formula for the new value of the divisor
Calculations are carried out automatically. Knowledge of the calculation methodology is needed rather to understand the features of the US30 and its shortcomings.
The value of the divisor does not change regularly, it depends on the corporate actions of the companies included in the basket. Since 2018, Divisor is equal to 0.14748071991788, which means that a change in the price of any stock by just $1 leads to a change in the Dow Jones index quotes by $1/0.14748071991788 = 6.78 points . This is one of the reasons for criticizing the calculation methodology; stocks with greater volatility have a stronger influence on quotes, while the capitalization of such a business can be relatively small.
Depending on the accounting for reinvestment of income accumulated over time, DJIA subtypes are distinguished:
- Price Return – only changes in the price of shares included in the basket are taken into account. Dividends are not taken into account.
- Total Return – income distributed over time in the form of dividend payments is taken into account. This is a good indicator for investors; it shows potential investment growth.
- Net Total Return – taxes are taken into account. That is, dividends are first “cleaned” (the amount of tax is subtracted), and then the remainder is reinvested.
There is always a 100% direct correlation between the listed subtypes of indices. Only the numerical values differ.
Calculation method
At the end of the 19th century, Charles Dow calculated the index manually using a simple mathematical formula of the arithmetic average: the numerator is the sum of the market prices of the companies included in the indicator, and the denominator is the number of these companies. The resulting value was compared with previous indicators, which showed the growth or decline of the American economy.
As a result of numerous mergers, divisions (splits), acquisitions and other procedures natural for the development of the stock market, the DJIA ceased to give the correct value.
Let's look at an example. Let’s say there are 5 shares worth $10, $20, $30, $40 and $50. According to the old method:
DJIA = (10 + 20 + 30 + 40 + 50) / 5 = 30
The most valuable company decided to split its shares 1:2. The number of its shares doubled, the price dropped to $25. But the company's capitalization has not changed. According to the old method:
DJIA = (10 + 20 + 30 + 40 + 25) / 5 = 25
The index fell 5 percentage points. But in reality, nothing has changed in the economy. The companies still worked and are still working, it’s just that one of them carried out a split. In this form, the DJIA cannot serve as a market indicator. Therefore, we changed the method of calculating the indicator. The denominator is now not the number of companies, but a certain coefficient. Today it is equal to 0.15198707565833 and changes every time there are changes in the share structure.
The calculation method is often criticized because the index is not influenced in any way by the company's capitalization, but only by its share price. As a result, giants such as Coca-Cola with a price of $50.63 per share or Intel with a price of $60.71 per share influence the DJIA less than the issuers that are located at the bottom of the list. It is the expensive companies that will put strong pressure on the value of the indicator in the event of a collapse in their quotes, as happened, for example, with Boeing.
Stock selection criteria
The approach is somewhat non-standard. There are no clear criteria for selecting securities; a special committee (Averages Comittee) takes into account such factors as:
- Business reputation
- Sustainability of business growth at a distance
- Belonging to a specific sector of the economy
- Attractiveness from an investor's point of view
The committee takes into account these quality criteria and makes decisions based on this. For example, over the past 15-20 years, more than 10 technology companies have been included in the Dow Jones Industrial Average. Thus, the committee took into account the growing role of the IT segment. At the same time, representatives of the transport sector are not added to the DJIA, since they are included in another index from the Dow family.
As for the composition of the committee, it includes 5 people. Three of them are representatives of S&P Dow Jones Indices, and two more are from The Wall Street Journal.
The committee solves 2 problems. The listed 5 people not only review the composition of the basket, but also monitor the adequacy of the methodology for compiling US30 as a whole. At least once a year, the committee decides on the advisability of changing the calculation methodology as a whole.
I also recommend reading:
Interest-bearing investments - TOP 9 best options
Investments with interest involve investments with a known income in advance, the amount of income is indicated as a percentage of the invested capital. Of course, guarantee […]
How and where to make money on the index
You can invest in the Dow by purchasing all the shares individually. But it will be quite expensive. An alternative would be to buy or sell shares of investment funds (mutual funds or ETFs). They help investors protect themselves from the volatility of individual corporations or economic sectors by closely following the Dow Jones rate. Here are some of them:
- Dow Jones Select Dividend from iShares (DVY). Invests in all Dow-indexed companies.
- First Trust Dow Jones Industrial Index (FDN). Focuses on Dow companies that generate profits through the Internet.
- Dow Jones Islamic Fund (IMANX). Islamic Dow. Invests in corporations that comply with Islamic doctrine.
- SPDR Dow Jones Industrial Average (DIA). Mutual investment trust. Pays monthly dividends on underlying shares.
A Caution About Forex and Binary Options
I would like to remind investors that all Russian platforms that offer trading in currencies or binary options have nothing to do with securities exchanges. This is betting. Offices offer you a bet: they will fall, they will rise; up down; will win, will lose.
Best brokers
To trade financial instruments on an American stock exchange, you must enter into an agreement with a broker. Below is a table of the best brokers.
Verified foreign brokers
| Name | Rating | pros | Minuses |
| Interactive Brokers | 8/10 | They speak Russian | Subscription fee 10$\month |
| CapTrader | 8/10 | No monthly fee | They only speak English |
| Lightspeed | 7/10 | Low minimum deposit | Imposing services |
| TD Ameritrade | 6.5/10 | Low commissions | Not everyone gets an account |
Dow Jones family of subindices
There is the so-called Dow family of indices, which includes:
- The Global Dow . The prefix “global” indicates a global nature; the basket includes 150 shares of companies from all over the world.
- Transportation Average . Calculated on shares of 20 companies operating in the transport sector.
- Utility Average . Based on the stock prices of 15 utility companies.
- Composite Average . Composite index, calculated taking into account quotes from the Dow 30, Utility Average and Composite Average baskets.
- Global Titans 50 . The index is dedicated to the 50 largest companies in the world, whose shares are traded on the NYSE and the largest foreign trading platforms.
- Total Stock Market . The so-called broad index, which includes more than 3,500 companies, tracks the health of the US market as a whole.
- Sustainability . Evaluates business sustainability, a relatively young index, created in 1999.
In general, the provider calculates a lot of indices, the Dow Jones being one of the main ones.
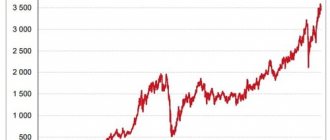
Cost and dynamics for all time
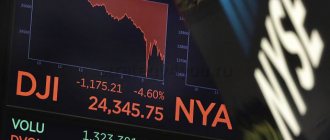
In February 2022, the stock exchange, if not fell, then sank to one knee: for the first time in 7 years, the Dow Jones index lost 1000 points. Then the Asian stock exchange caught up, having weakened so much for the first time in 15 years. Of course, the global economy as a whole suffered. Why?
This indicator is American, and half of all stock exchange transactions are concluded in the States. The Dow Jones is simple and straightforward, including only market leaders. He is sensitive to political and social events. That is why its fluctuations have such an impact on financial markets.
Criticism of the Dow Jones index, its comparison with its main competitor
DJIA is not perfect, and at least several of its features deserve criticism. These include:
- Weighting by price, not by capitalization . The calculation methodology itself ignores such an indicator as business capitalization. In the section on studying the Dow Jones calculation methodology, this issue was examined in more detail. Regardless of capitalization, a $1 change in the price of any share in the basket leads to the same change in DJ US quotes.
- Lack of clear criteria for adjusting the cart . The requirements are not formalized; in the end, everything is left to the discretion of the committee.
- Due to the too narrow basket, various sectors of the economy are represented by a small number of companies . An entire industry can be represented by 1-2 companies.
It is precisely because of these features that the DJIA is not suitable for the role of a universal barometer of the entire US stock market. A basket of 30 components cannot characterize such a large-scale market as the American one.
If we compare it with its direct competitor, the S&P 500, the latter is more suitable as an indicator characterizing the US economy. It includes 500 companies, different sectors of the economy are more adequately represented, there are clear criteria for revising the composition, and free-float capitalization is taken into account in the calculation.
This comparison does not mean that the DJIA is worse or better than the S&P 500. Both instruments are suitable for both investing and active trading.
Bulls and bears
Initially, these terms applied only to traders trading in the stock market, but then they spread to other trading platforms. Bulls are players who buy an asset with the expectation that its value will rise. In the optimal case, such a speculator buys a stock (bond, futures) at the bottom and sells at the peak, when demand for the asset reaches its maximum.
Bears are the exact opposite of bulls. These are speculators who sell a financial instrument in the hope that its quotes will fall. In professional language, such an operation is called short selling without covering.
It is easy to imagine stock exchange animals using a figurative picture: a bull raises the enemy (price) on its horns from the bottom up, and a bear, on the contrary, nails the victim (quotes) with its paw down.
Similar terminology applies to trends dominating the market. If demand on trading platforms exceeds supply and financial assets rise in price, then a bullish trend is observed. A bearish trend prevails when the economy deteriorates and stock prices fall. If there is an equilibrium between buyers and sellers, a sideways trend occurs in the market.
In many ways, stock exchange slang was formed in New York, where the first stock exchange was born. That's why the most popular bull sculpture stands on Wall Street, at the entrance to the New York Stock Exchange building. The bronze sculpture weighs more than 3 tons, its length is almost 5 m and its width is 4.7 m. It is believed that if you rub the horns of a bull, it will bring good luck in business and financial matters.
Factors influencing DJIA
When working with US 30, consider the influence from:
- Oil prices . Quotes of “black gold” greatly influence the index’s performance despite the fact that the IT sector is in the lead in the basket.
- Sudden changes in the cost of individual components. Due to ignoring the capitalization factor, a collapse or sharp increase in any of the components of the basket can provoke the same behavior of the entire DJIA. A good example is the 3,000 point drop in 2008, the main reason for this was the collapse of AIG's stock. In the S&P 500, such a scenario is excluded - the basket is an order of magnitude larger, and the capitalization factor would soften the impact of the price of AIG securities.
- The general state of the world economy . The same pandemic provoked a fall in all stock indices without exception, and the DJIA was no exception.
- High correlation with other major US indices.
- Dependence on US foreign policy.
This is a standard set of influencing factors for indexes of this size. These should be taken into account for long-term work; intraday work will require more emphasis on technique.