2/5 — (1 vote)
Translated from French, emission means release. Most often, this term is associated with the release of banknotes into circulation in order to increase the state's money supply. This is a complex term that has several interpretations. If you need to complete coursework or dissertation work, you can find help here. Any civilized state monitors the needs of its own market, which needs a constant and uniform increase in the money supply. It is the issue of money that plays a key role in this regard. At the same time, it should be gradual (uniform), since deviation from the norm will lead to an increase in the level of inflation in the country.
Types of emissions
Emission is a complex economic term that has several directions. Regardless of its type, the issue is somehow associated with the release of payment instruments into circulation. This term is also used in physics. Therefore, it is necessary to distinguish between concepts, since the meaning is not always the same. In financial and economic terms, emissions are divided into the following types and directions:
- Money emission is the issue of cash/non-cash funds.
- Issue of bank cards - issue of bank cards.
- Issue of bonds and securities - issuance of payment bonds and securities into circulation.
- Issue of electronic money.
You need to know these terms and concepts to improve your own financial literacy. For any state they are important, since the position of the country’s economy depends on the correctness of emissions.
They directly influence the internal factors of development of the economic sphere of society, forms of realization of private property, the level of development of economic individuals and the motives of their activity, the depth of the division of labor and freedom of competition, the nature of the exchange of results of activities, and methods of coordination of activities. What is the emission of each of these directions will be described below.
Types of issuers and their purposes
The emission instruments listed above can be issued by different issuers. Let's consider their main types and goals that are pursued by releasing assets into circulation.
The state represented by the Ministry of Finance and the Bank of Russia
The state is the largest and most reliable issuer. Issues federal loan bonds (OFZ) and Eurobonds through the Ministry of Finance. Such securities are considered low-risk and are often used by conservative investors to protect against stock market fluctuations.
The yield on OFZs is always slightly higher than inflation. If the Ministry of Finance cannot repay them on time, a default is declared. This is an extreme step that will permanently undermine confidence in the country both on the part of its own population and business, and on the part of foreign investors, and will also deprive it of the possibility of further large borrowings.
The goals pursued by the state through the procedure for issuing OFZs:
- replenishment of the state budget;
- the need to implement large infrastructure projects;
- the need to fulfill increased social obligations;
- curbing inflation.
Another major player in the market is the Central Bank. Its main issuing instrument is banknotes and coins. No one except him has the right to issue banknotes. The goals are clear - providing a convenient means of payment to everyone, as well as maintaining an acceptable level of prices and inflation by injecting money into the economy.
Municipal authorities
A riskier option, but still considered a reliable option, is municipal governments. They issue bonds with a yield slightly higher than OFZ.
The expectation of minimal risk is based on the fact that the government is unlikely to allow any region to default. She will always support you and help you pay off your debts. In addition, any municipal entity has property. In the event of a catastrophe, it can be sold and the debt to the bondholders can be repaid. But a technical default is possible - when the redemption of a security at par occurs not at the time indicated in the prospectus, but later.
The main goals of issuing municipal bonds are to obtain additional funds for the development of the region and fulfill social obligations.
Banks
Banks have a wide range of issuing instruments. These are bank cards, bills of exchange, traveler's checks, certificates of deposit, as well as stocks and bonds. On the one hand, bank issue allows banks to obtain capital for their development. On the other hand, to provide the economy with modern and efficient means of payment.
Do not forget that most banks are commercial organizations, so their main goal is to make a profit. Keep this in mind when you see great deals on credit or debit cards. The rules for trading securities (stocks and bonds) are the same for all issuers.
Commercial enterprises
Commercial enterprises issue securities on the stock and derivatives markets in order to finance their investment projects and increase their authorized capital.
The risk of investing in such instruments is higher than in government ones. However, the degree of risk has wide limits. For example, blue-chip stocks and bonds are considered the least risky, while third-tier securities have the highest degree of risk. Defaults among the latter occur with regular frequency, but the yield on such instruments is noticeably higher. The investor must independently decide for himself whether or not it is worth investing in securities of issuers offering high returns.
The list of blue chips consists of 15 largest companies from different industries. The top 10 includes Gazprom, Sberbank, Lukoil, Norilsk Nickel, etc. The full list can be viewed on the Moscow Exchange website.
Objectives of the issue
The main task is to regulate turnover and attract additional investments. If we are talking about the issue of cash, they are sent into circulation as banknotes and coins. Cash is exchanged between businesses and individuals. persons until they become physically dilapidated , or the Central Bank confiscates them.
Intensive emissions contribute to rising prices and increased inflation. Non-cash money does not deteriorate materially, but represents entries in an account.
The issue of shares and bonds is a calculation to attract additional capital. Securities are sent to the stock market, where they can be traded at market prices determined by the financial state of the issuer.
The state does not often engage in this type of issue: it occurs when solving a major problem that requires serious monetary support.
Money emission is sometimes incorrectly called simply its additional issue; it occurs constantly, but unlike emission, regular issue does not lead to an increase in the money supply.
If a decision is made on the need for an issue, the Central Bank collects data on the passage of the money supply through banks, determines the areas in which a monetary injection is required, and its required volume. Only after this the mechanism starts.
Banknotes are printed in specialized printing houses, where technical measures are taken to protect them from counterfeiting. New coins are minted at mints; they are in Moscow and St. Petersburg.
Should we pay attention to the issue of cryptocurrency?
A competent investor who really makes money on digital currencies knows that the emission rate makes it clear the stage at which the Blockchian project is currently located. And this, in turn, allows us to assess the prospects of a given cryptoasset for further investment attractiveness.
How to evaluate the attractiveness of an asset?
For example, when a new cryptocurrency with the possibility of mining (extraction) just appears, the number of coins on the market will be relatively small, and mining will not be so difficult. In addition, the very value of the newly minted cryptocurrency will most likely be initially underestimated by investors (although there are exceptions). Accordingly, the price of the asset will be low, and the opportunity to get a significant profit in the long term will be quite large. Of course, such a development of events is only possible if this Blockchain project has a unique idea for creation and can implement it.
Let's look at an example
Let's say in early 2010 you bought Bitcoin at a price when it was worth less than a dollar apiece . Since the issue of BTC is quite limited (only 21 million coins), the possibility of an increase in the price of the asset was great. So this is what happened, one Bitcoin today is worth tens of thousands of dollars. You could make a profit of millions of percent .
However, it is unlikely that if you buy one Ripple or NEM , where the total coin issue is 100 billion coins and 9 billion, respectively, the price of each will rise to tens of thousands of dollars. Here the emission is very large, so each coin of these systems will cost much less.
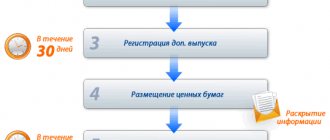
Issue timing
The timing of the issue of securities is influenced by various factors:
- how quickly the decision on the issue will be made;
- how soon will they find an intermediary and conclude an agreement with him;
- deadlines for state registration of the issue.
Deadlines for registering shares in Russia:
- issue upon establishment of a joint stock company – up to 20 days;
- additional issue – up to 20 days;
- issue during reorganization – up to 30 days;
- report on the results of the issue – up to 14 days.
According to Russian legislation, no more than 1-3 months should pass from the moment the decision on the issue is made to the registration of securities.
- no later than 1 month, it is necessary to register the issue when distributing securities among the founders, when issuing bonds or convertible shares;
- up to 3 months in other cases.
Comments: 1
Your comment (question) If you have questions about this article, you can tell us. Our team consists of only experienced experts and specialists with specialized education. We will try to help you in this topic:
Author of the article: Klavdiya Treskova
Consultant, author Popovich Anna
Financial author Olga Pikhotskaya
- Violetta
01/09/2022 at 00:32 Thank you for such a useful and informative article.
Bravo! Reply ↓
What is money emission
The issue of money (or money issue) means the release of banknotes into circulation to increase their total mass. In order not to disturb the balance and value of money, it is necessary to closely monitor its release, which is what, as a rule, entire ministries do.
Read also: “Top cryptocurrency exchanges”
The monopoly on the issue of funds in most cases belongs to the state. In the Russian Federation, these processes are in charge of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation. The only national currency in the country is the Russian ruble. Basic principles of money issue in Russia:
- Monopoly and uniqueness - funds are issued only by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in the form of unique and unparalleled banknotes (banknotes).
- Non-obligatory backing with gold - the country does not officially maintain the relationship between gold (other precious metals) and the Russian ruble.
- Unconditional obligation - banknotes are issued only in rubles.
- Legal regulation - the decision to issue the money supply or to withdraw it from circulation is made only by the board of directors of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
- Unlimited exchange - on the territory of the Russian Federation, banknotes and coins can be exchanged without any restrictions on amounts and requirements for subjects (citizens and organizations).
- The money supply (banknotes and coins) is an unconditional liability of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, and is backed by all its current assets.
Officially, the production of money is called minting coins and printing banknotes. The production of money is internal: in Russia, minting and printing are carried out at specialized facilities - mints. There are only two such facilities in the country: the mints of Moscow and St. Petersburg. The customer is the state represented by Gosznak.
The process of making money is strictly regulated. Gosznak periodically introduces new security technologies in order to suppress counterfeiting of banknotes. Counterfeiting, even at the lowest rates, seriously disrupts the exchange rate of money. As a result of this, the inflation rate increases with the subsequent depreciation of the national currency. That is why counterfeiting banknotes in any state is a serious criminal offense.
Issue of non-cash funds
The Central Bank of the Russian Federation, through repo transactions, issues non-cash loans to commercial Russian banks at the current refinancing rate. Subsequently, the issued funds are transferred to the correspondent account of the loan recipient bank. That is, the amount of the issued loan remains in the assets of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation one way or another. It turns out that a virtual amount is transferred to the bank. At the same time, the Central Bank of the Russian Federation closely monitors the level of inflation: the amount of all loans issued at the refinancing rate cannot exceed the total assets of the Central Bank of Russia.
The rest of the non-cash funds are introduced through the purchase of foreign currency by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, which replenishes the gold and foreign exchange reserves of the state. As a result, the Russian national currency also comes into circulation. Thus, non-cash cash flows are cashed out. This allows:
- Control the inflation rate.
- Increase the value of the Russian ruble.
- Replenish gold reserve funds.
- Increase the number of active loans.
- Monitor the direction of cash flows in order to prevent money laundering.
Cash money supply in Russia can only be issued by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, and non-cash money can be issued by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation and commercial banks. In the latter case, this occurs by issuing loans to the population. Moreover, such processes are necessarily controlled by the Central Bank of Russia. Interbank transfers that are made in non-cash form are also controlled by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, and their total amount cannot exceed the amount of non-cash funds placed on the correspondent account of the payer organization.
If the funds in the correspondent account of the paying bank run out, then it resorts to several options for unilateral refinancing. The Central Bank of the Russian Federation, for its part, guarantees the issuance of short-term interest-free loans to licensed commercial banks. This form of refinancing helps to increase cash flows in the country and also ensures the uninterrupted operation of credit institutions. In practice, these processes are called the banking multiplier.
Procedure for issuing funds in the Russian Federation
Coins in the Russian Federation are produced at the St. Petersburg and Moscow mints, which are under the leadership of the Goznak Joint Stock Company. Regarding documents, securities, paper money with protection against counterfeiting, they are issued in specialized printing houses.
The process of entering and producing paper money is regulated at the legislative level. In Russia, the following trends are observed when issuing cash:
- Between securities and metals. For example, there is no official ratio established by gold;
- There are no restrictions when exchanging old rubles for new ones;
- Coins and banknotes are backed by the assets of the Central Bank. His responsibilities include servicing funds, which indicates the existence of an exclusive right to withdraw or put money into circulation;
- The service life of the funds should not exceed 60 months or be less than 1 year;
- In each of the constituent entities of the federation, the national currency is the official and legal means of payment;
- Regarding legal regulation in matters of issuing additional amounts of money or withdrawing them from circulation, this is the task of the board of directors of the Central Bank.
Issue of bank cards
Emission is explained in simple terms as “to release.” This was stated at the very beginning of the article. Therefore, in this case we are talking about the issue of bank cards, which is also commonly called issuance. The subjects of these processes—issuing banks—are responsible for the balance of non-cash cash flows in the country.
In Russia, 661 credit organizations are engaged in issuing bank cards. Last year they issued 220 million bank cards - credit and debit. At the same time, our country follows the global trend, and more than 80% of bank cards issued on its territory are made by the international payment systems VISA and Mastercard.
The leader in issuing bank cards in the Russian Federation is Sberbank of Russia. This position has been held by the credit institution since 2007. Every year, the main bank of the country issues at least 20 million bank cards + 5 million are issued by its subsidiaries and affiliated organizations.
The world leader in issuing bank cards is the China UnionPay payment system (National Payment System of China). It accounts for approximately 30% of all cards issued in the world. Second place is occupied by the VISA system with 26%, and third place by Mastercard with 20%.
What will happen to the ruble exchange rate by the end of 2020?
During the economic crisis, it is difficult to predict the ruble exchange rate for the next six months and the need to print new banknotes. During the 2022 pandemic, Russians had fewer rubles, and the national currency exchange rate dropped significantly
.
There are many negative factors putting pressure on the ruble:
- record low oil prices;
- decline, economic crisis;
- minimum income of the population;
- falling demand for goods and services.
Perhaps by the end of 2022 the national currency will experience another collapse against the dollar and euro. But in any case, its rate depends on the state of the state’s balance of payments. And it is influenced by other factors:
- domestic and foreign trade;
- cross-border payments – the process of transferring salaries, dividends, interest.
The movement of all capital is reflected in the financial account. In the Russian Federation, the key factor is the current account of the trade balance and other similar ones: a high price is set for oil, this creates a positive balance, and it strengthens the ruble
.
Now oil prices have fallen to the limit, so there is a weakening of the country’s national currency. In order not to stop oil production, owners of towers and companies are forced to sell the resource at ridiculous prices.
For example, in 2022, 1 barrel of oil cost $71.5, in 2022 the price decreased by 11.2% - to $65.5, and in mid-2022 even less - to $42.4
.
What happens next depends on the market and the actions of the Russian monetary authorities. But according to expert forecasts, by 2022 a barrel should reach $44.
To release the ruble, the Central Bank simultaneously sells dollars from the National Welfare Fund and provides ruble liquidity to the banking sector.
Many will want to exchange rubles for dollars to save their funds
. But the printing press will be turned on at full capacity again - the ruble is threatened with another fall, because there will be no restrictions on converting the national currency into foreign currency.
Previously, it was believed that the fall of the ruble was a synonym for the word inflation. Now this pattern does not always work. Inflation in the Russian Federation is a complex issue. Strong factors act to suppress it, the main one being economic decline. Developed countries in 2020 are more afraid of falling prices and deflation than of declining demand and depreciation of money
.
What is an issue of securities
This process refers to the issuance of bonds and securities for the purpose of their subsequent sale to individuals and legal entities. A security or bond is a document that confirms the property rights of its owner. Emissions of this type are also controlled by state legislation.
The main purpose of issuing securities is to raise funds. In the vast majority of cases, issuers are included in this process for the following reasons:
- Formation of primary authorized capital.
- Increase the authorized capital.
- Control or splitting of previously issued securities and bonds.
- Change of organizational and legal form of a legal entity.
- Revision of the scope of property rights under previously issued securities and bonds.
- Attracting free investments (replenishment of equity capital).
- Attracting paid investments with subsequent payment of dividends.
After making a decision to issue securities, the company issues them and subsequent state registration. Violation of the procedure for issuing bonds in the Russian Federation provides for criminal liability. Information about bonds is posted on the securities prospectus for free review by all interested parties.
Emission processes: distribution of roles
The division of money issue depending on the type of issuer (money creator) is determined by the following scheme:
Central Bank:
- issues banknotes - banknotes;
- performs the function of purchasing treasury notes and issuing banknotes against them for balance;
- exercises control over the issue of securities by commercial banks, maintains their accounting and re-discounting, issuing its own money against bills of exchange;
- buys foreign currency, issuing its own against it in parallel.
Treasury Department:
- issues treasury notes;
- produces change coins.
Commercial banks:
issue loans (credit money) to economic agents such as the state, enterprises, foreign companies, and individuals.
Issue of electronic money
The most controversial and problematic type is the issue of electronic money. They are spreading much faster now than they were a few years ago. Moreover, in most civilized countries, electronic money does not have any legal basis. For example, private electronic money has become widespread in Russia, including:
- Yandex.Money is electronic money from the Russian Internet giant Yandex.
- WebMoney is a transnational electronic payment system.
- QIWI is a service launched by the bank of the same name.
- RBK Money is a service created in Ukraine and widely spread in Russia.
- Cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin, Ethereum and others.
Handling of these systems in the Russian Federation is still free. The user just needs to register in the system and upload his passport data. In accordance with recent changes in industry legislation, financial transactions between unidentified users in Russia are prohibited.
If QIWI and Yandex.Money issue electronic analogues of the Russian ruble, and legal restrictions do not yet apply to them, then with the WebMoney service everything is a little more complicated. Here, transactions are carried out using title units: WMR - the equivalent of the Russian ruble; WMZ is the equivalent of the US dollar; WME is the equivalent of the euro.
The problem is that the issuer carries out a huge number of operations, some of which are not subject to any external control. In this regard, we should expect some targeted legislative amendments in this regard.
conclusions
The issue of assets is carried out to introduce new financial instruments into use and is necessary to stabilize prices. Control over the inflation process is very important, since market oversaturation inevitably leads to inflation in the value of the asset. For potential investors, knowledge of the issue mechanism allows them to determine the possible level of inflation and factors that may affect the depreciation of a financial asset.
To date, the most correct emission mechanism has been implemented in cryptocurrency, where emission is limited and occurs in strict accordance with the underlying mathematical algorithm and cannot be revised in favor of third parties.
Emission policy in Russia
The basic principles of the emission policy in our country are as follows:
- Monopoly. Only the Central Bank regulates the volume of money supply; it injects money supply, and it also withdraws it depending on current tasks.
- The absence of the obligation to provide the gold reserve that we have in our country today is not enough for the ruble to be fully backed by gold. The situation is the same in most other countries.
- The principle of par. The ruble is the monetary unit of Russia; the manufacture of analogues or the introduction of other units is prohibited by law.
- Rubles are accepted for payment throughout the country. Banknotes are interchangeable - a 5 thousand ruble bill is always 5 1 thousand ruble bills or 10 500 ruble bills.
Mechanism
Let's see how the emission process occurs in our country. The primary one is the non-cash form and only then it is converted into cash:
- The Central Bank issues loans to commercial banks. Funds are credited to their correspondent accounts. The amount of all issued loans must correspond to the amount of assets of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
- In addition to loans, non-cash money is put into circulation through the purchase of foreign currency by the Central Bank to replenish gold and foreign exchange reserves, receiving revenue from the use of property abroad, foreign investments and loans from international organizations.
- Commercial banks also participate in the process by issuing loans to enterprises and other financial organizations.
The organization of cash circulation is regulated by the Federal Law “On the Central Bank of the Russian Federation (Bank of Russia)” dated July 10, 2002. The size of cash emission is determined through the need for it by commercial banks, which in turn is determined by the need of individuals and legal entities.
The Central Bank is the main issuer. To ensure that the regions always have a supply of cash, the Central Bank has created cash settlement centers in each region where commercial banks are serviced.
The cash issue process goes like this:
- A reserve fund and a working cash register are created in the RCC. An amount of cash is stored in reserve in case the need for it increases in a given region. This money has not yet been put into circulation and is not considered full-fledged money.
- In the working cash register, there is a constant movement of money - it comes from commercial banks and is issued by them. This is money in circulation.
- If the amount of cash received is greater than the amount issued, then the excess is transferred to the reserve fund.
- If commercial banks' need for cash increases and a situation arises when the amount of money received is less than the amount issued, then the RCC carries out an issue - transfers cash from the reserve to the working cash register. The process is coordinated with the Office of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation. The Board of the Central Bank draws up the emission balance on a daily basis.