olegas Sep 9, 2022 / 199 Views
The entire set of relations that take place during the exchange of various kinds of material and intangible goods through the mediation of money (as a universal means of payment) is usually called the financial market in economic theory.
Financial markets can be called the driving force and basis of the mechanism of the modern economy. The more coordinated and efficient they work, the faster the economy develops.
Introduction
Exchange of some economic goods for others, exchange of the currencies of some countries for the currencies of others, trading in securities, lending, etc. – all these are types of transactions performed on the modern financial market. And in the case when we are talking about such operations carried out on the scale of entire states among themselves, then we are already talking about the global financial market.
Thus, according to the scale of operations, the financial market can be divided into two main categories:
- National financial market;
- International financial market.
In the national market, transactions are carried out on the territory of a single state. Accordingly, it is fully subject to national legislation. And the international market is nothing more than the totality of all individual national financial markets and therefore cannot be subject to the laws of any individual state (it has international norms, rules and standards specially created for these purposes).
In the modern economy, there are two main models of financial markets that have developed in the countries of continental Europe and America:
- The continental model, based on bank financing, is also called the continental model or bank based financial system.
- Anglo-American model based on the securities market and institutional investors (market based financial system).
The continental model is distinguished by a less developed secondary market and non-public placement of securities (a relatively small number of shareholders and, accordingly, a high degree of concentration of share capital). In the Anglo-American model, on the contrary, the secondary market is much more developed and there is a pronounced tendency towards public offering of securities.
However, over time, these two models increasingly converge with each other and the boundaries between them are gradually erased.
Forms of existence of financial markets:
- In the form of an organized structure (for example, an exchange, where all trading operations are carried out according to strictly defined rules);
- In the form of direct agreements (for example, the interbank market);
- In retail form (for example, the market for banking services for individuals).
Finally, all financial markets can be classified by industry:
- Money market;
- Capital market;
- Stock market;
- Derivatives market;
- Currency market;
- Precious metals market;
- Cryptocurrency market.
Key rate regulation
The key rate is the main instrument of the monetary policy of the Bank of Russia. It is equal to the minimum interest rate at Bank of Russia repo auctions for a period of one week or the maximum interest rate at Bank of Russia deposit auctions for a period of one week. The key rate is set by the Board of Directors of the Bank of Russia eight times a year.
By changing the key rate, the Bank of Russia influences short-term money market rates, and through them, the entire range of interest rates in the financial sector of the economy along the entire length of the yield curve (from interest rates on market bonds to rates on deposits and bank loans).
When the discount rate increases, the demand for Central Bank loans from commercial banks falls, which causes an increase in loan rates and a reduction in their supply. In this case, deposit rates rise as banks' ability to obtain financing through other means is reduced. Thus, higher interest rates stimulate savings and weaken lending activity, thereby limiting the demand for goods and services and curbing inflationary pressures.
If the Central Bank reduces the discount rate, the demand of commercial banks for Central Bank loans increases, this expands the supply of money in the country and reduces its cost for borrowers. At the same time, deposit rates are reduced, as banks have a reduced need to attract funds from households and corporate clients. Lower interest rates have a stimulating effect on domestic demand, creating motivation to reduce savings and increasing the availability of credit. Thus, by influencing the demand for goods and services through interest rates, the central bank influences the rate of price growth in the economy. An increase or decrease in interest rates also affects the dynamics of the national currency exchange rate.
Money market
Economic relationships for the purpose of receiving or providing funds for short periods (up to one year) are called the money market.
The money market has three main components:
- Short-term securities;
- Interbank loans;
- Eurocurrencies.
All money market participants can be divided into three categories:
- Lenders or those who provide money for temporary use. This category includes banks, non-bank credit institutions, and other financial organizations;
- Borrowers or those who borrow money. This category includes individuals, state and municipal structures, various types of enterprises and organizations, etc.;
- Financial intermediaries provide a link between the two aforementioned categories of money market participants, although, in principle, their participation is not always necessary. These include banks, professional participants in the securities market (brokers, dealers), etc.
All of the above categories of money market participants have one common goal - everyone intends to benefit. Lenders make a profit due to the interest rate at which they issue loans. Borrowers intend to make a profit from the use of borrowed funds. And the benefit of intermediaries lies in the commission that they charge from lenders and borrowers for bringing them together and often acting as a guarantor of the transaction concluded between them.
Below is a picture illustrating the main money market instruments:
Risk and return
If you dream of getting a 1000% income, you must understand that the risks will increase to 99%. This is a lot, but this is what makes the blood boil in your veins. Forex is not a game, but a very complex business, with its own system and a number of rules. Any rash step that does not have a place in the plan can affect your income. We advise beginners not to play more than 18% per year - this is the same percentage at which the risks are minimal. Also, the percentage can help you avoid large losses and start stable trading. If you drive more quietly, you will come further.
Capital market
This branch of financial markets includes long-term financial transactions (loans, investments, etc.). In essence, this is the same money market described above, but only with financial maturities exceeding one year.
So-called long-term money circulates here; capital is invested in various kinds of long-term financial instruments (stocks, long-term bonds, etc.).
The capital market has the following structure:
Dividend cover
Dividend coverage measures how many times the after-tax earnings attributable to a common stock exceed, or “cover,” the gross dividend paid. In this case, the word “earnings” refers to the after-tax profit attributable to the parent company's common stock, excluding extraordinary items. Dividend coverage can be viewed as an indicator of the “margin of safety” provided by the excess of income over the gross dividend. If the dividend cover is 1.0, it means that all net income, that is, profit after taxes, was spent on paying dividends to shareholders. If the dividend cover is less than 1.0, which sometimes happens, then shareholders have actually been paid a portion of the capital value of their shares disguised as a dividend. This may be a conscious decision by the board, faced with disappointing earnings for the year, to demonstrate confidence in the future by maintaining the same level of dividend payouts in cents per share as in the previous year. The message behind this decision is: "Don't worry, the recession won't continue next year." What this does mean, however, is that to maintain dividend payout levels the company may need to increase its overdraft and will have to start the new financial year with an increased burden of interest payments on its profit and loss account. For any company, the most important source of financing is the retained earnings remaining after paying corporate taxes and eligible dividends to shareholders. A listed company should aim to pay a decent dividend and have a coverage ratio above 2.0, meaning more profits should be retained in the company to fund growth and development than paid out to shareholders as dividends.
Stock market
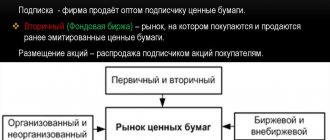
Everything related to the issue of securities and their further circulation (purchase, sale, resale) directly relates to the next branch of financial markets - the stock market.
The stock market includes not only organized trading platforms - exchanges, but also the so-called over-the-counter component. Securities of the largest and most reliable issuers are quoted on the exchange market (including securities related to blue chips), and the over-the-counter market serves as a haven for securities classified as risky (for example, shares of the second and third tier that are not listed on exchange platforms).
The securities market can be classified according to the following main criteria:
- By level of placement of negotiable financial instruments:
- Primary. Here, as the name suggests, an initial placement of securities occurs (this can be either a public (IPO) or a private placement);
- Secondary. This is the market most known to a wide range of people, where, in fact, the bulk of securities trading operations take place. It includes all stock exchange platforms;
- Third. This is an over-the-counter market and those securities are traded on it that, for certain reasons, could not be listed on official exchange platforms;
- Fourth. Large institutional investors trade here. Trading takes place electronically, in large blocks of shares (or other securities).
- By type of financial instruments traded:
- Stock market;
- Bond market;
- Derivatives market, etc.
- By degree of organization:
- Exchange;
- OTC;
- By level of globalization:
- Regional;
- National;
- International.
- By issuer of traded securities:
- Enterprise securities market;
- Government securities market.
- By longevity of traded financial instruments:
- Short-term securities market;
- Medium-term securities market;
- Long-term securities market;
- Perpetual securities market.
- By industries to which issuers of tradable securities belong.
Protection of consumers of financial services – Bank of Russia and Rospotrebnadzor
As is known, consumer rights in Russia are protected by the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare (Rospotrebnadzor). However, if the case is related to a violation of those federal laws, supervision and control over compliance with which is carried out by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, then such complaints and appeals are considered by the regulator.
The structure of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation includes the Service for the Protection of Consumer Rights and Ensuring the Availability of Financial Services, where anyone can file a complaint about the actions of financial organizations.
Complaints and appeals in writing can be sent both to service units at the regional branches of the main departments of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, and to the territorial departments of the Service in federal districts, and to the central office in Moscow, including through the Internet reception. The period for consideration of complaints and appeals is 30 days. Based on the results of the inspection, an order may be sent to eliminate the identified violations or a case of an administrative offense provided for by the Code of Administrative Offenses may be initiated.
An analysis of the results of Rospotrebnadzor’s activities regarding the consideration of complaints about violations of the rights of consumers of financial services indicates that the main group of violations consists of the inclusion in the texts of credit agreements and loan agreements of conditions that infringe on the rights of consumers (indication of the possibility of unilaterally changing the amount of the cost of borrowed funds provided, establishing jurisdiction to consider disputes at the choice of a credit institution; charging a fee for connecting to the insurance program, for issuing a loan; transferring debt to third parties who do not have a license to carry out financial activities. In addition, in the process of providing services to consumers, banks indicate the possibility of unilateral change the range of services provided to clients; establish the payment of an additional commission if the consumer refuses unnecessary services.
Together with Rospotrebnadzor, the Central Bank of the Russian Federation succeeded in suppressing the widespread practice of charging fees for considering a loan application and issuing a loan, hidden fees for bank borrowers, such as a fee for maintaining a loan account or for servicing a loan, which were sometimes several times higher than the cost of interest on the loan.
The Central Bank, by its regulations, established the mandatory provision of information to the borrower about the effective interest rate on the loan before issuing it, so that the borrower could assess the real level of the loan burden, which banks sought to hide.
Rospotrebnadzor has been fighting for many years against banks' policy of imposing life insurance on mortgage borrowers and recipients of consumer loans. This problem was helped to solve by the instruction of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, which came into force on March 2, 2016. In accordance with it, a “cooling off period” is now mandatory in a life insurance contract. This means that the policyholder has the right to cancel the contract within 5 working days from the date of its conclusion and demand a refund of the paid insurance premium. Thanks to this, imposing insurance has largely lost its meaning.
Derivatives market
This is a market for derivatives (derivative financial instruments) with a specific maturity date (hence the name). The following financial instruments are traded here:
- Forward contracts;
- Futures;
- Options.
Based on the degree of organization, the derivatives market is also divided into:
- Exchange;
- OTC.
Trading in the derivatives market is characterized by a higher degree of risk compared, for example, with the stock or bond market. This is explained by the fact that in this case leverage is used (so-called margin trading). In addition, another difference here is the possibility of opening short positions (the possibility of shorting a particular financial instrument acting as an underlying asset).
Transactions on the derivatives market are concluded for the purpose of hedging positions open on the underlying asset, in arbitrage strategies or when making money on swaps (in the foreign exchange market).
Gross dividend yield
The gross dividend rate is the income received by a shareholder in the form of a dividend (excluding income taxes), calculated as a percentage of the current market price of the stock. A logical question: why do additional calculations? The answer is simple. The dividend percentage allows comparison only with dividends paid by the same company in previous years. The gross dividend rate allows for a realistic comparison of the dividend yields received on shares of different companies.
Foreign exchange market (FOREX)
The international currency market Forex (Foreign exchange market) is a system of financial relations, the purpose of which is the purchase or sale of some foreign currencies for others. In terms of the volume of transactions performed, the FOREX market significantly exceeds all other financial markets.
The FOREX market does not have any specific trading platform (such as an exchange), it is rather the entire set of communications connecting its largest players (banks, transnational corporations, brokerage firms, etc.).
The main participants in the foreign exchange market are:
- Central banks of countries. Their main activity here comes down to managing national foreign exchange reserves in order to regulate the exchange rate of their currency. For this purpose, they can conduct so-called currency interventions;
- Banks (mostly international). This is one of the types of institutional investors in the Forex market. It is through them that the bulk of all financial flows pass here;
- Companies engaged in import-export operations, for example, for the purpose of purchasing raw materials and selling finished products;
- Various types of funds (investment, pension, hedge) and insurance companies. They conduct operations here in order to diversify their portfolios as much as possible by purchasing various types of securities outside their country;
- National currency exchanges. These operate in a number of countries and their main purpose is to quote their national currency against a foreign one, as well as currency exchange for legal entities;
- Brokerage firms and dealing centers acting as intermediaries for carrying out trading and exchange operations on FOREX;
- Finally, private individuals. The contribution of each of them individually may be completely insignificant, but in total, the financial flow from international tourism, simple exchange transactions and speculative currency transactions of individual citizens can reach very impressive volumes.
Epilogue
There is no need to rush to place bets and get involved in trades. First you need to study the business, understand the risks, clarify how high they are - this will help you avoid them and save money. Don’t forget that you first need to study the behavior and weapons of the enemy, and only then go into battle with him. This will allow you to choose the right weapon and defeat the risks in trading.
- One of the most interesting terms in the foreign exchange market is currency swap. Let's try to understand its significance for the Forex market, and also answer the question - what is it?
Precious metals market
The precious metals market can be identified as another component of the global financial market. It carries out transactions both directly with precious metals and with securities tied to them (futures, bonds, options quoted in gold, as well as gold certificates).
Based on the type of precious metal traded, this market can be divided into the following main components:
- Gold market;
- Silver market;
- Platinum Market;
- Palladium market.
Based on the type and volume of transactions carried out, the precious metals market can be classified as follows:
- International precious metals market;
- Domestic precious metals market;
- Black (underground) market for precious metals.
The international market has the maximum trading turnover; large investors, international funds, as well as central banks trade on it. The largest international trade centers are located in cities such as London, Zurich, New York, Hong Kong, Chicago, and Dubai.
Domestic markets for precious metals involve trading operations within the country. They are characterized by certain government regulation, expressed in the setting of taxes, quotas, trade rules, etc.
A black or underground market for precious metals occurs when the government places severe restrictions on such transactions. When, for example, the trade in gold is prohibited, it begins to be sold illegally (by smuggling into the country).
In addition, this market can be classified according to the purpose of the purchased precious metals:
- For investment purposes;
- For industrial use (for example, in electronics).
Types of risks
We start taking risks from the very first days of trading. Firstly, we already take risks when we choose a broker. No wonder there are all sorts of rumors about them. Brokers are very cunning for the most part and attract lovers of quick money and profit, who have no place in Forex. Trading is generally not a place for people who do not have a range of knowledge and vast experience in dealing with money games. Risks break people and take their money. This is a difficult business. Here you need to be able to combine risks with common sense, emotions with attentiveness and discipline. It is very difficult.
There are very high incomes and big money in Forex. Newbies light up when they hear about it. But profitability here also depends on the risks that traders are willing to take—no one understands or takes this into account. If a trader wants to make money, he must put himself and his money at risk. These are the rules. There is nothing to do here for those who are trying to earn money without risk. You need to come up with a strategy regarding risks. It is also important to learn how to manage your own risks. It is management that brings results that will be unlike anything else. Scientists are convinced that income has increased with the willingness to take risks and do it without panic.
Cryptocurrency market
This is the youngest financial market represented here. The history of its existence began with the emergence of the world’s first cryptocurrency in 2008 and goes back only about one decade. Its structure is currently not yet fully formed (partly due to the fact that in many countries there is no legislative framework regulating operations carried out with cryptocurrencies), but in general it can be represented as the entire set of existing cryptocurrencies and the infrastructure that provides their existence. This infrastructure includes both computing power, thanks to which new cryptocurrencies are generated and stored, as well as the entire set of organizations involved in their sale, purchase and exchange (cryptocurrency exchanges and various kinds of exchangers).
Cryptocurrency is an asset that is entirely dependent on computing power. The technology of its creation (popularly called mining) is based on blockchain computer technology. Purely theoretically, anyone with a computer connected to the Internet can mine some cryptocurrency. However, in fact, in order to earn an amount equivalent to at least a couple of American dollars in this way, it will take quite a lot of time. The fact is that the very nature of cryptocurrency is designed in such a way that the more it is mined, the more complex this process becomes, and the extraction of new coins (coins) requires more and more computing resources.
Currently, specialized mining farms consisting of many powerful video cards are used to mine cryptocurrencies. You can generate cryptocurrency either using a processor or through calculations on a video card. It so happens that the video card has the architecture most suitable for those calculations through which new coins are created.
Cryptocurrency mining farms can consist of several video cards, or thousands or even tens of thousands. Most of these large farms are located in the Asia-Pacific region, in particular in China (as of the end of 2022, about 30% of the entire global cryptocurrency market was concentrated there).
The most popular cryptocurrencies at the moment are (arranged in descending order of value):
- Bitcoin;
- Bitcoin Cash;
- Dash;
- Ethereum.
In addition, there are still a huge number of different types of cryptocurrencies in the world, many of which do not represent and, most likely, will never represent any value.
The most well-known platforms that provide the opportunity to trade cryptocurrencies (so-called cryptocurrency exchanges) are the following (arranged in descending order of trading volume):
- Binance;
- HitBTC;
- LiveCoin;
- YoBit;
- Exmo;
- Poloniex;
- Kraken et al.
You can obtain more detailed information on this topic by clicking on the following links:
- Where to trade cryptocurrency
- How to mine cryptocurrency
- How to buy and sell cryptocurrency. Step-by-step instruction
- Cryptocurrency Trading Strategies
Highlighting Financial Consumers as Economic Weaknesses
Consumers of financial services are considered an economically weak party that needs government protection. This position is shared by both the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, Rospotrebnadzor, the courts, and the media.
Inequality in the position of the consumer of financial services and the organization that provides these services is due to information and contractual disproportion. Information disproportion is due to the complexity of modern banking services for a non-specialist, therefore “... the client of a financial organization, for quite objective reasons, does not understand the content of the service provided very well. All modern legal systems recognize that a credit institution does not have the right to take advantage of this imbalance, and if it does, the client can count on protection from law and order.”
The contractual imbalance lies in the fact that all forms of contracts with financial organizations are standard, and therefore the client cannot change the terms of the contract: he can either agree to them or refuse the service he needs. Moreover, the texts of standardized contracts, as a rule, are quite voluminous and written in a specialized language, and the conditions in question are included in them so that they are not noticeable. “When concluding an agreement, a financial organization can impose conditions on a client, the meaning of which he does not fully understand, and in a dispute about the execution of an agreement, the financial organization will almost always be the winner, since it has the skill of both conducting such disputes and obtaining investment income.”
Although formally the terms of standard contracts comply with the law, for the client they are often unfavorable, which he would never agree to if he had the opportunity to choose.
Based on the presence of information and contractual imbalances, the media in Russia, as a rule, side with consumers of financial services, despite the fact that in some cases they themselves are to blame for their troubles. The most common situation is concluding an agreement “without reading the terms.” In this case, difficulties in understanding the contract are not always an excuse, since the consumer did not even try to understand it.
As a result, sometimes consumers are given a contract to sign for a different service than the one they require. For example, banks that are facing bankruptcy often organize a scam, persuading clients to renew their deposits on more favorable terms, but in reality they draw up an investment or loan agreement. Then, after the bank’s license is revoked, clients are left without insurance compensation, since it is only due under the bank deposit agreement.
Another well-known example is foreign currency mortgages. Borrowers knew about the risk associated with changes in the exchange rate, but did not take into account how great this risk was, even after the devaluation of the ruble in 2008–2009 and 2014–2015. They were unable to continue repaying the loan. There has been a debate in society for years about whether they should be recognized as the weaker side in this situation.
Therefore, a journalist who undertakes to describe a problem associated with the provision of financial services must carefully analyze whether this problem arose because the consumer really turned out to be the weak party of the contract, or whether he simply approached the matter too frivolously.
Earnings per share
Earnings per share are expressed in cents and are annual earnings divided by the weighted average number of shares outstanding during the year. Earnings per share growth is the most important indicator of a listed company's profitability as it takes into account not only sales income, but also the impact of interest payments and the company's overall tax level. Thus, profit is the entire income earned for shareholders, not just the amount of dividends paid, and, in addition, it provides financing without issuing additional shares. When additional shares are issued, for example:
- by issuing "rights" (see below) to existing shareholders to fund expansion,
- to pay for the purchase of another company, instead of paying in cash,
- for sale to managers under a share option scheme,
then the weighted average number of shares outstanding increases and, if earnings do not increase in the same proportion, earnings per share decrease. The expression “earnings per share dilution” is often used to describe this situation. A Rights issue is an additional issue of shares with payment in cash to existing shareholders in proportion to the number of shares owned by each of them. For example, a 1 for 4 rights issue means that each shareholder gets the right to buy 1 additional share for every 4 shares they already own. In a listed company, the shareholder has the option of selling “rights” rather than having to buy additional shares. At the same time, he will receive a certain amount reflecting the difference between the market price of shares and the subscription price of shares of the new issue. The aim of a listed company should be to maximize earnings per share growth over the medium to long term and to avoid declining or stagnant earnings in any year. The most successful listed companies achieve annual earnings per share growth of over 20% (compounded) for a decade or more.