Article content
Share the article, help the site!
The AMD Radeon RX 5700 XT is one of the very first graphics cards released with AMD's highly anticipated Navi architecture, which uses the 7nm process. With AMD's Navi architecture being the basis for dedicated GPUs and the next-generation PS5 and Xbox 2 consoles, this is an extremely exciting addition to AMD's graphics card lineup.
AMD is positioning the RX 5700 XT as a competitor to the Nvidia RTX 2070 with similar specs and performance for Full HD and Quad HD gaming.
However, one major problem with AMD's RTX alternative is that it lacks the technology needed to enable ray tracing, which makes games experience stunning and more realistic lighting and reflection effects.
The Radeon lettering glows red when connected to the motherboard and turned on
To compensate for this, AMD has added many additional features to its RX 5000 series cards, including Radeon Image Sharpening and Radeon Anti-Lag. The first feature aims to restore clarity to in-game images that have been negatively impacted by other post-processing effects, while the second claims to reduce the time between player input and response display by up to 31%, which should please gamers.
But let's be honest, the competition between graphics cards largely comes down to raw performance and value for money, and AMD seems confident that it's up against Nvidia's RTX lineup.
RX 5700 XT Specifications and Technologies
Below is a comparison table that compares the specs of two AMD Radeon graphics cards against Nvidia's closest competitors: the RTX 2070 and RTX 2060. AMD itself has stated that it sees these specific RTX GPUs as its biggest competitors, and judging how similar the specs are is not surprising.
| Characteristics | RX 5700XT | RX 5700 | RTX 2070 | RTX 2060 |
| Architecture | Navi | Navi | Turing | Turing |
| Base clock speed | 1605 | 1274 | 1410 | 1365 |
| Increased clock speed | 1905 | 1546 | 1710 | 1680 |
| VRAM | 8 GB GDDR6 | 8 GB GDDR6 | 8 GB GDDR6 | 6 GB GDDR6 |
| Memory Bandwidth | 448 GB/s | 448 GB/s | 448 GB/s | 448 GB/s |
| TDP | 225 W | 185W | 185W | 160W |
| Price | 25,000 rubles | 22000 rubles | 29,000 rubles | 21,000 rubles |
AMD's RDNA architecture follows a 7nm manufacturing process, which the company credits with delivering 1.25x performance per clock over previous 14nm processors.
AMD cards use a completely different architecture compared to Nvidia's RTX cards. Nvidia's RTX cards feature Turing architecture and Tensor cores, allowing for features like ray tracing and DLSS. However, AMD's new Navi RDNA architecture does not offer such luxury technology, at least not in its current iteration. Despite this, the rest of the specs for AMD Navi and Nvidia Turing cards look largely the same.
The AMD Radeon RX 5700 XT has the best clock speeds (both base and boost) of the four graphics cards reviewed. This doesn't always translate into great in-game performance, but it's still an encouraging sign.
The GPU of the video card is visible from the back and looks very cool
VRAM is identical to all but one Nvidia card, and AMD agrees that 8GB GDDR6 is the best option for average performance. AMD suggests that with the GDDR6 upgrade, performance/watt will improve by 60% over GDDR5.
All four cards offer the same memory bandwidth speed at 448GB/s, further demonstrating how similar these GPUs are. This increase in memory bandwidth comes thanks to new support for PCI Express 4.0.
On the other hand, the two AMD cards appear to be more power hungry than their Nvidia counterparts, with slightly higher thermal output. As long as you have a compatible power supply, this shouldn't be a problem at all.
Strengths and weaknesses of the predecessor
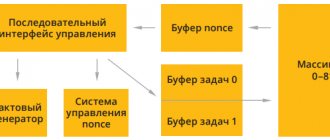
Controlling the video card directly, like in consoles, is convenient, especially when we are talking about a huge amount of calculations for each frame. Writing code for parallel execution is extremely difficult (if only for the reason that the human brain performs conscious tasks sequentially, quickly switching between contexts). Therefore, the GCN architecture was designed with an eye to predictable behavior and time costs for various types of operations. 16-bit computational units were grouped 64 into one unit and received a common 64-bit instruction scheduler. So the programmer could issue one command for four clock cycles at once to work on 64 cores.
The problem came out of nowhere: the revolution was canceled by consoles.
Due to the relatively weak hardware of the consoles, forecasts for the prospects of 3D graphics did not coincide with reality. Instead of a craze for all sorts of Ultra HD, studios rushed to develop “visual tricks”: they used low rendering resolutions and complex special effects. Even data from the previous frame was used - why waste resources on calculating something that has hardly changed? An architecture that was effective with the same load on a large number of identical cores turned out to be not the best solution in situations where it was necessary to perform various calculations on small amounts of data. On consoles this was unnoticeable due to the modest capabilities of the video core, which was loaded to capacity with rendering tasks. And with the release of PS4 Pro and Xbox One X, the general trend towards the target 30 fps continued, but at a higher resolution. Exceptions, of course, happened, but not so often.
Design - What does the RX 5700 XT look like?
The AMD Radeon RX 5700 XT design takes a fundamentally different approach to Nvidia Founder Edition boards. While GTX graphics cards put a heavy emphasis on a dual-fan setup, with a striking black and silver color combination that makes them look like they jumped straight out of a steampunk novel, the RX 5000 series cards take on a more sleek and modern look .
The word Radeon is engraved on the front and highlighted in red, while the striped chassis adds extra texture and detail to the design. There's also only one fan here, which is more powerful than any of Nvidia's graphics cards, although that means AMD cards aren't as good at cooling.
Unfortunately, the RX 5700 XT lacks USB-C, which could become a problem in the future.
Beyond those few design talents, the cards are still pretty much the same as Nvidia's alternatives elsewhere. The RX 5700 XT is about the same size as Nvidia's Founders Edition cards and offers the same 2x DisplayPort and 2x HDMI connectors, except for the lack of a USB-C port. This is a slight disappointment considering more and more VR headset setups are adopting this new optimized connection.
What awaits us?
The Reds, unlike NVIDIA, refused to use dedicated RT cores. After all, they complicate the architecture, take up space on the chip, increase the cost of production and do not perform any other tasks except ill-fated ray tracing. The necessary logic will be implemented directly into each “computing unit” - with direct access to data that is already being calculated by shader processors. This approach will save precious clock cycles on interaction with memory - operations are performed immediately, instead of copying data to a dedicated cache, applying mathematical magic and sending the results back. Using a slight modification of the universal cores will also simplify the topology of the GPU crystal. This means it will reduce the percentage of defects and reduce the final cost.
Features - What features does the RX 5700 XT have?
The AMD Radeon RX 5700 XT may not boast fancy technologies like ray tracing and DLSS, but the features it offers are still seriously impressive.
Moreover, all these features work very well at startup and do not have a significant impact on performance. While Nvidia's RTX cards feel more ambitious with their features, AMD's offerings are certainly more advanced.
Here are all the exciting features of the AMD Radeon RX 5700 XT:
Radeon Image Sharpening
Radeon Image Sharpening is perhaps the biggest new software feature for the RX 5000 series cards, as it negates the negative effects that anti-aliasing features bring to game graphics to restore image clarity.
This is just a technical way of saying that details become sharper when Radeon Image Sharpening is activated. In Division 2, the improvements AMD made to the display were barely noticeable, but welcome, the colors of the American flag looked more vibrant, the wooden bench looked sharper, and it was easier to see the details of a character standing in the distance.
RIS off
RIS enabled
However, the most surprising thing about Radeon Image Sharpening technology is that the technology is not very efficient on the GPU. After activating it in Shadow of the Tomb Raider and The Division 2 with the resolution set to Quad HD and graphics presets, the maximum drop was only 1fps and 2fps. Compare that to something like ray tracing, where the technology puts a major strain on GPU performance, and AMD's performance is very impressive.
| Games | RIS Off (fps) | RIS On |
| The Division 2 | 65 | 63 |
| Shadow of the Tomb Raider | 73 | 72 |
Another big plus is the number of games that support this technology. AMD offers any game based on DirectX 9, DirectX 12 and Vulkan graphics that can run with RIS. This covers a huge range of games including Hitman 2, Metro Exodus, Civilization 6 and many more. Again, this is in stark contrast to ray tracing, and only a few games are currently capable of supporting this technology.
Radeon Anti-Lag
Radeon Anti-Lag looks like a fantastic feature for gamers, helping to reduce input lag so that there is minimal delay between your mouse click and the resulting action on screen.
AMD claims that Anti-Lag can reduce input lag by almost a full frame, which is almost 16.7 milliseconds at 60 frames per second. This won't make much difference to the average gamer, but if you're competitive and want every little advantage to keep increasing your kill count in your favorite shooter, then any small performance advantage will certainly be tempting.
Anti-Lag works best when used with a low latency gaming rig and a high refresh rate monitor equipped with variable frame rate technology at high resolutions and graphics levels.
Since I was using a 4K monitor that refreshed at up to 60Hz for this review, I wasn't able to thoroughly test this at the time of publication, I'll update this section of the review later when I can test it with a faster monitor.
Radeon Chill
Radeon Chill is an exciting feature that lowers frame rates and reduces excessive GPU power consumption if the display is mostly static or you're away from the keyboard. This is a great way to save energy, especially if your family or housemates complain about your gaming PC's excessive power consumption.
Since the frame rate increases again as soon as the display becomes more active, the user's visual experience will not be affected. Having played with it in The Division 2, I can confirm that it performed as well as AMD claimed, transitioning smoothly from low to high frame rates as soon as I hit the keyboard.
The difference in power consumption is also significant and will increase further when playing less intensive games at high frame rates. In The Division 2, I saw a 47W drop when saving my character, but AMD claims you can see a huge 118W drop in Chill mode when playing Apex Legends.
| Games | from | On |
| Power, W) | 310 | 263 |
| Frame frequency | 43 | 30 |
This feature obviously won't improve your gaming experience, but it's still great to see AMD thinking about ways to reduce power consumption. David Attenborough would be proud.
Call of Duty: Modern Warfare (2019)
Graphics Settings
- Version 8.2.7154757.
- DirectX 12.
- The texture quality is high.
- Anisotropic filtering - high.
- The quality of the particles is high.
- Bullet marks - included.
- Tessellation - all objects.
- The resolution of shadow maps is maximum.
- Local shadow buffering is enabled.
- Sun shadow buffering is enabled.
- Particle illumination is ultra high.
- DirectX ray tracing is disabled.
- Background light shading - all objects.
- The quality of screen space reflections (SSR) is high.
- Anti-aliasing - Filmic SMAA T2X.
- Depth of field—on.
- Filmic intensity is 1.00.
- Global speed effect - enabled.
- Weapon speed effect is enabled.
- Grit – 0.00.
Performance - How powerful is the RX 5700 XT?
The AMD Radeon RX 5700 XT is marketed as a graphics card for Quad HD and Full HD gaming, and our testing confirmed this. The RX 5700 XT isn't powerful enough to play modern AAA games at 4K, but if you're not ready to make the leap to Ultra HD, our results suggest it could be one of the best cards on the market.
I also included the AMD Radeon RX 5700 in the performance tests to see if you're better off buying the cheaper AMD alternative, as well as the Nvidia RTX 2060 and RTX 2070, as AMD named them as their closest competitors.
The RX 5700 XT is capable of playing most games in Quad HD at 60fps
In fact, Nvidia will be retiring the RTX 2070 very soon and replacing it with the RTX 2070 Super Edition, but we haven't been able to test Nvidia's new line of Super cards yet. As soon as we receive them, we will definitely update this review with test results.
Note that all of the cards tested are Founders Editions, with the exception of the RTX 2070, which is an Asus ROG Strix Gaming variant, as it was the only RTX 2070 card available to us. However, the performance results of the third part of the RTX 2070 should not differ much from the Founders Edition board.
Testing methodology
We tested each graphics card on the same computer rig in our office, making sure the CPU, SSD, and RAM worked in concert to achieve fair results. The exact components can be seen below:
- Motherboard: X570 Aorus Master Gaming
- Processor: AMD Ryzen 9 3900X
- RAM: Corsair Vengeance 2666 MHz, 16 GB DDR4
- Power supply: Corsair CX750M
- SSD: Aorus NVMe Gen4 SSD 2TB
- OS: Windows 10
We also carefully selected the three games to ensure a fair test between graphics cards, so there was no unfair advantage for any specific GPU architecture. For example, Shadow of the Tomb Raider is optimized for Nvidia drivers, and so we also included the AMD-optimized The Division 2 to keep the test fair. Finally, we've included Dirt Rally as an example of a game from a few years ago that isn't as GPU-intensive as the other two games.
Each game was set to the highest graphics preset, usually called Ultra or Highest. The only custom adjustments I made in the settings was disabling Vsync, as I didn't want the frame rate to depend on our monitor's refresh rate.
Read below to see the results:
What happened before? TeraScale and GCN architectures
To understand the innovations of the RDNA architecture, you need to understand what came before it. The history of modern Radeons began with the transition to unified shaders. With their help, AMD wanted to provide outstanding GPU performance - and then let game studios decide what to use it for. It was assumed that with the move to DX10 and OpenGL 3.0, the video card would be burdened with a lot of complex tasks, so it would be much more loaded than before. Instead of dividing into vertex and fragment shaders, they used a set of universal blocks: developers themselves can write the game engine code, choosing what and at what moment the GPU will do. The use of one long instruction (VLIW) with long processing fits perfectly into the concept of “one complex operation - a lot of data,” and even on highly parallel hardware. Load distribution and optimization of such complex tasks were entrusted to the compiler and driver.
From D3D9 to D3D10 and Unified Shaders
The TeraScale architecture was developed in the 2000s with an eye toward the active implementation of technologies that were just beginning their life cycle. High resolution textures, bump mapping and normal maps, HDR and global illumination required decent bandwidth of both memory and GPU. Special effects no longer complemented the frame in individual places, but were applied repeatedly in literally every pixel.
Compare Half-Life 2 (2004) and Titanfall (2014) - how much the picture has changed. But it is based on the same engine - Source.
The hardware really turned out to be outstanding, but the driver optimization left much to be desired. The quality of the Reds' software is still remembered in a negative way - some are joking and some are serious, not having up-to-date information. With the release of DirectX11 and the advent of direct access to the GPU, it became clear that further development of TeraScale was impractical. If automation could not handle the load on the complex architecture of the graphics chip, then what can we say about manual control? The “terascale” was replaced by the Graphics Core Next (GCN) chip, which formed the basis of the Radeon 7970 and eighth-generation consoles (Xbox One, PlayStation 4).
The internal structure of the video core has become much more complicated.
To provide the same level of performance, GCN required more control logic, but the process of setting tasks for shader processors was simplified. Now developers could not only interact with models and textures, but also perform general calculations. AMD engineers planned that the central processor would be responsible for executing scripts, calculating AI, and issuing drawing commands. And photorealistic graphics, complex physics and auxiliary calculations will be carried out on the GPU.
D3D12 and direct graphics pipeline control
New APIs made it possible, at a similar level of GPU performance, to implement stunning special effects due to the efficient loading of hardware with complex mathematics. Beauty for which the computer previously did not have enough resources has become commonplace. For example, lighting with fair refraction of rays, active use of tessellation, various effects that require constant access to the depth map (bokeh, volumetric fog, long shadows), object-by-object blurring of models and even their individual parts.
Benchmark results for Shadow of the Tomb Raider - RX 5700 XT
Shadow of the Tomb Raider is optimized for Nvidia hardware even with support for ray tracing technology, so the RTX 2070 was expected to take the lead in this test. This was not the case.
The AMD 5700 XT actually delivered better performance results than the Nvidia RTX 2070 card in every 4K resolution test, although every test was tough. The fact that it lost in Ultra HD is not a big problem, since the 37 fps result that the AMD card posted is not high enough to play without technical problems.
However, the more interesting comparison is that the cheaper AMD 5700 graphics card remained within arm's reach for every test result. Based on this, I'd be tempted to choose the 5700 over the XT and save some money in the process, the performance penalty is so minimal it's unlikely to be noticeable.
Ignoring comparisons with other cards, the AMD 5700 XT benchmark results for Shadow of the Tomb Raider are very impressive, highlighting excellent performance when the resolution is set to Quad HD or Full HD.
Thermal photographs
All thermal images were taken under maximum load for a general overview and understanding of the cooling system WITHOUT overclocking the core and memory.
| Measuring point | Degrees Celsius |
| M1 | 52.6 |
| M2 | 40.6 |
| M3 | 35.5 |
| M4 | 41.5 |
By installing the thermal camera on the front side, we get the following results:
The hottest point M1 (53 degrees) is the area where residual heat is blown out.
Please note that the residual heat is dissipated satisfactorily while the coolers are running on auto.
| Measuring point | Degrees Celsius) |
| M1 | 65.2 |
| M2 | 48.5 |
| M3 | 37.5 |
By installing the thermal camera on the back side, we get the following results:
The hottest point of the M1 (66 degrees) is the GPU temperature.
Please note that the accuracy of the GPU measurement cannot be compromised since the backplate does not cover the GPU area.
Note that with overclocking under maximum load the card reaches 80 degrees!
80 degrees is a pretty bad indicator.
Division 2 RX 5700 XT Results
Division 2 is optimized for AMD GPUs, so you'd expect the Radeon RX 5700 XT to have an edge over its Nvidia competitors in this competition. It's a little disappointing that the AMD GPU delivered almost identical results to the Nvidia RTX 2070 for 4K and Quad HD tests. However, the 4K result doesn't make any difference as the 34fps result is too low for anyone to play comfortably, especially since this is an online multiplayer shooter.
It's only when you switch the resolution to Full HD that you see the Radeon RX 5700 XT take a decent lead over the RTX 2070, scoring an impressive average of 93 fps. However, the lead is only 7 frames per second, so the naked eye will almost certainly not be able to detect the difference.
The important point taken from The Division 2 benchmark is that the AMD 5700 XT comfortably exceeds the 60fps target for both Quad HD and Full HD, so performance will be smooth enough to play the online shooter without problems.
Far Cry New Dawn
Graphics Settings
- Version 1.0.4.
- DirectX 11.
- The quality of texture filtering is maximum.
- The quality of the shadows is maximum.
- The quality of the geometry of the world and vegetation is maximum.
- The quality of the environment is maximum.
- The water quality is high.
- The quality of the landscape is high.
- The quality of volumetric fog is high.
- Antialiasing - SMAA.
- Motion blur is enabled.
- The field of view scale is 90.
- Resolution scale - 1.0.
- HD textures - included.
Dirt Rally Results - RX 5700 XT
We included Dirt Rally in our test because it is a great example of a GPU-intensive game that was released a few years ago. If the graphics card can deliver decent performance with this game, it will be able to handle most games released before 2015.
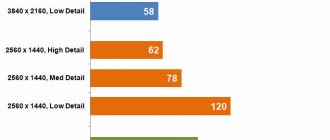
Interestingly, although the Radeon RX 5700 XT was not marketed as a 4K graphics card, with Dirt Rally it achieved an impressive 83fps average when the resolution was increased to Ultra HD. Of course, Dirt Rally is much less demanding than modern AAA games, but it's still a very encouraging result if you want to play a list of classic hits.
The AMD Radeon RX 5700 XT also delivered better frame rates in Quad HD and Full HD tests compared to the Nvidia RTX 2070 and was only 2fps behind at 4K.
However, the cheaper Radeon RX 5700 wasn't far behind its bigger siblings' scores, with a 12fps difference being the biggest advantage in each resolution test. Results like these would make me hesitant to spend another $70 on the XT.
Star Wars Jedi: Fallen Order
Graphics Settings
- Version 1.02.
- DirectX 11.
- Maximum FPS - 144.
- The graphics quality is epic.
- The viewing distance is epic.
- The quality of the shadows is epic.
- The anti-aliasing quality is epic.
- The texture quality is epic.
- The quality of the visuals is epic.
- The quality of post-production is epic.
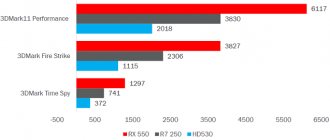
3DMark Fire Strike Ultra Test Results - RX 5700 XT
The 3DMark Fire Strike Ultra benchmark measures raw GPU performance and GPU temperature while simulating 4K gaming. This is a good way to unlock a graphics card's performance potential, although numbers should be used with caution as they do not provide an accurate indication of in-game performance.
The AMD 5700 XT came out on top in the four-path test with a performance score of 5927. The RTX 2070 wasn't far behind, though with a Fire Strike Ultra score of 5710. Interestingly, the AMD 5700 was only able to score 5351, which doesn't really reflect its excellent results in Game.
With a peak power consumption of 356 W during the 3DMark Fire Strike Ultra test, the RX 5700 XT required the most power of the quartet of video cards. This isn't necessarily a bad thing, you just need to make sure your power supply is capable of powering it.
However, this was not good news for the temperature test, as the RX 5700 XT generated the most heat over the long term compared to other graphics cards tested. With temperatures peaking at 80°C during the 3DMark Fire Strike Ultra test, temperatures rose. This doesn't mean you have to worry about this graphics card catching fire, but you want to maximize airflow and avoid using mini cases to keep that GPU in good condition.
Need for Speed Heat
Graphics Settings
- Version 1.04.
- DirectX 11.
- Motion blur is enabled.
- The texture quality is ultra high.
- The quality of the shadows is ultra high.
- Texture filtration is ultra high.
- Global coverage - HBAO.
- The quality of the effects is ultra high.
- Geometry quality is ultra high.
- Antialiasing - TAA.
- The quality of the landscape is ultra high.
- Vegetation detail is ultra high.
- The quality of post-processing is ultra high.
- The quality of reflections is ultra high.
- Depth of field is ultra high.
- The lighting quality is ultra high.
Overclocking the RX 5700 XT?
With temperatures already rising to 80°C during non-overclocked testing of the AMD Radeon RX 5700 XT, I didn't have much hope that I'd be able to squeeze much more performance out of the graphics card before seeing resistance.
My expectations were accurate, as after overclocking to 136 MHz while running Unigine Heaven, I couldn't go any further. I'm not sure if it was AMD's drivers or MSI's Afterburner overclocking software that stopped my progress, but either one is still an indication that the RX 5700 XT is starting to reach its limits.
Overclocked at 136 MHz, the RX 5700 XT achieved a performance increase of just 5 frames per second when running Unigine Heaven. There's nothing special about it, so I wouldn't waste time overclocking this card.
Innovations in RDNA
The first thing to note is that RDNA in its current form cannot be called a completely new architecture. Yes, there are a lot of changes, but this is not a total design change, as was the case, for example, in the case of the transition from DX9 to DX10 or the replacement of VLIW TeraScale with GCN. The general logic and design of the RDNA-based GPU are taken from the previous generation. The engineers simply solved the technical problems that limited the potential of the most powerful hardware - and it’s not about seven nanometers or high operating frequencies, but about the efficient loading of the video card.
End of life for current consoles. Current technologies in games
The problem of the impossibility of honest rendering of super-complex frames in high resolution was no longer solved head-on. The scientific approach to the development of scaling algorithms has given rise to many new technologies that deceive the user. Dynamically changing the rendering resolution (both general, determined by the complexity of the frame, and specific, depending on the importance of the object in the scene) made it possible not to perform unnecessary calculations where the user would not notice the difference. Training neural networks led to the creation of scaling and smoothing algorithms in conditions of insufficient data - all to effectively save resources: the picture deteriorates by 5-10%, but there are already 30-50% fewer calculations. The pinnacle of DX12 development was hardware-accelerated tracing of realistic lighting and reflections.