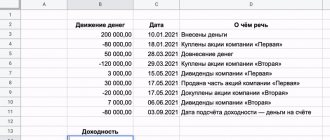
In order to get the maximum profit from such an investment, there are many things to consider. With the right steps in the stock market, such investments will bring greater profits compared to depository storage of funds in banks.
What it is
Debt yield is the amount of investment income from holding a portfolio of debt securities, which is shown as a percentage over a certain time period (usually a year). It is similar to the profitability of depositary deposits and, with certain manipulations, can bring much greater profits.
Total bond income consists of the following elements:
- the amount of coupon income;
- the difference between buying and selling or redeeming a bond;
- investor activities (tenure periods, purchase and sale operations taking into account the price of securities, investment of already paid coupons).
How to calculate risk
To calculate risk, mathematical multifactor models are used. To build these models, investors use techniques and methods applicable in mathematical statistics and probability theory. When performing complex calculations, special computer programs are used. The essence of factor analysis is that factors are summed up, and a forecast is made based on their total influence. This makes it possible not only to determine the yield to maturity of the bond, but also to predict the development of negative events, the likelihood of default or rising inflation.
Income of debt securities of Russian issuers
To invest money in bonds, you must first find out the approximate level of income from this type of investment for a certain period of time. Nowadays, some operations can be done independently, but most often all actions for buying and selling bonds are carried out through a professional specialist - a market broker.
The main types of debt securities on the Russian market can be purchased in several versions:
- federal loan bonds;
- municipal;
- corporate debt securities;
- Eurobonds.
All types of such investments have their own specifics, which must be taken into account when dealing with them.
Federal loan bonds OFZ
Federal loan bonds (OFZ) are specialized securities with government coupons issued by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
The income of these securities is formed depending on the Central Bank refinancing rate.
Their main advantage is that the profit from owning a portfolio of such debt obligations will always be slightly higher than the profit on deposits. In the current situation, the average OFZ income is measured in the range from 6% to 9% per annum.
There is a subtype of OFZ - people's OFZ (OFZ-n). The income from such securities is slightly lower (by approximately 1.5-2%). This is due to the commission of the financial agent (bank).
The main advantage of this type of investment is maximum protection from most negative factors. The rate on this investment is constant; there is absolutely no possibility that the license will be revoked or the bankruptcy process will be launched.
Since there is no possibility of problems arising with the licensing of the bank’s activities (as well as with the return of funds and making a profit), this is a profitable option for investing money if the investor wants to save funds and make some profit. The reliability of these investments is ensured by guarantees from the state itself.
Municipal
Individual constituent entities of the Russian Federation issue their own debt securities. Such issues are called municipal. The profit from this type of investment will be slightly higher than the profit from OFZ. On average, this figure ranges from 7% to 12% per annum.
For this bond, the yield is provided by guarantee obligations of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, due to which these deposits have a high level of reliability. If regions have difficulties with payments, the state intervenes and makes payments on debt obligations.
Corporate
Many large and medium-sized organizations issue their own securities, including debt, thereby attracting third-party investors to invest in their business, thereby becoming a creditor.
The Russian stock exchange shows a constant increase in this format of securities, but so far the level of corporate bonds compared to the standards of world exchanges is too unstable, that is, volatile.
The average yield on corporate bonds is in the range of 6-14%. If the income is above 14%, then such options are highly profitable, while becoming a high-risk portfolio.
Eurobonds
These are debt obligations issued by foreign companies (or their subsidiaries). These securities are denominated in the currencies of other countries. Today, such debt obligations are on average 3 times more profitable than a bank deposit. Dollar issues bring an average of 2-6% per annum, and euro issues - up to 3%.
Where and how can you buy bonds
You might be interested in: How much does a realtor earn in Moscow? How much does a realtor charge for selling an apartment?
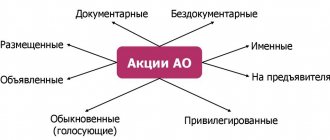
An investor can purchase debt securities from bank branches, on the stock exchange, or from individuals or legal entities that sell them outside the stock market. They can be purchased during a personal visit to the institution at the cash desk or remotely using modern communication means. Bonds can be in either documentary or non-documentary form.
Most often, securities are purchased from a bank at the current exchange rate or on the instructions of an investor or broker. A distinction must be made between speculation and investment. Speculation is carried out with the aim of reselling a security and making a profit due to exchange rate differences, while the speculator can take out a loan to purchase securities. Investments mean the purchase of bonds and other securities in an investment portfolio for long-term storage, up to the full repayment of the debt by the borrower.
Types of profitability
There are several types of profitability. Each of them has its own specific calculations.
Coupon
Most often, this type of profitability is used for calculations, which is quite simple to understand. The easiest way to understand what a coupon yield is is with an example: when a 6% coupon is issued, this means that the yield on this bond issue will be 6% per annum.
Due to the simplicity of this type, calculating the yield of this security is simple - it is the amount of coupon payments for the year. In the 6% coupon option, those who have invested in this type of asset will earn 60 rubles from 1 bond.
It must be remembered that for some bonds issuers make payments every six months or quarterly. In such cases, the amount is divided into 2 or 4 parts. That is, when the coupon has an income of 8%, and payments are quarterly, then they are paid in the amount of 2% of the investment amount.
Interest capitalization, as on deposits, does not occur for these securities.
Current yield
The current yield of a bond, unlike the coupon yield, takes into account the market value of the bond. This option calculates how much profit an investor will receive relative to their investment.
Nominal
The situation when the coupon income has already been accrued but not yet paid was not taken into account in the previous options. When the investor purchased these securities, he must pay the ICD to the previous owner.
Simple yield to maturity
The most common situation is when the investor waits until the bond matures and collects all coupon payments and face value. Most often this is the most profitable option, especially if short-term bonds are purchased. The dependence of profitability in this case occurs directly on the tenure period.
Effective yield to maturity
There is no capitalization of interest on bonds, as there is on deposits, since the investor is expected to reinvest his income. In this regard, the effective yield to maturity is calculated - when the par value, coupon and additional purchase of the same securities are added up.
When an investor receives a coupon on a redeemed bond, he or she purchases that security again. When reinvesting income, it is possible to multiply profits on more favorable terms than with a depository deposit.
To understand, let’s take examples of yields by type of Alfa-Bank-14-bob bonds:
- coupon - 8.25%;
- current - 8.2999%;
- to maturity - 8.2365%;
- effective - 8.694%.
To the offer
Offer - repurchase of bonds by the issuer. It can be forced, that is, the redemption is mandatory, and all investors must sell the securities of this issue, and voluntary. The second type is mainly produced.
Even with a voluntary offer, a disadvantageous coupon is often specifically charged, where the yield is 0.01%. These investments cease to be profitable, and investors try to sell such securities before the offer.
In such cases, it is convenient to use the calculation of the return to offer.
Bond with coupon or discount - what's the difference?
There are two main types of bonds based on the method of generating income: coupon and discount. The difference between the first and the second is that payments on coupon bonds are made twice. The first time with a coupon, and the second time entirely with paper. A discount bond is a security that is sold at a price below par, that is, the owner of such a security will receive income in the form of the difference between the purchase price and the sale price.
You may be interested in: Money of Malaysia. Malaysian ringgit - exchange rate to the ruble and to the dollar
The level of yield on both coupon and discount bonds depends on the price at which they were purchased and what their par value is. It is assumed that payments on them will be made in full within the specified period, regardless of what the situation was on the market before and at what price they were sold.
You might be interested in: How much does a pilot earn? Civil aviation pilot salary
The essence of making a profit in simple words
Let us summarize the interim results on the issues of making a profit on bonds.
The process itself goes like this:
- A bond is purchased, for example, with a face value of 1000 rubles. The total cost will be slightly higher: market price + accumulated coupon income (ACI). It will be expressed as a percentage (presumably 103%), respectively, the price of the bond will be 1030 rubles. for a unit. The NKD is paid to the current bondholder for the period.
- The main income of bonds is periodic payments for its ownership. This income is called a coupon. Payments generally occur twice a year, but can be more frequent or less frequent.
- You can receive the principal amount in 2 ways: wait for repayment and sell. Bond redemption is when the issuer buys back the bond on an exact date set in advance. This situation is borrowing from an investor. During the period, the issuer paid interest, and now it is paying off the full amount of the loan.
- The option of selling a bond is beneficial when there is still a lot of time until its maturity. Accordingly, upon sale, the investor receives the par value and the accrued income for the holding period.
The main income from a bond is coupon payments. But profits can be increased through certain actions of buying and selling debt securities.
Obtaining an increase in yield is possible by reinvesting coupon payments into the same bonds (additional purchase).
Factors influencing changes in profitability
When calculating the risk of investing in government bonds in the factor model, the following indicators are used:
- The level of growth (decrease) in the country's GDP during the reporting period.
- Inflation rate.
- The size of the state's debt.
- The presence or absence of conflicts on the territory of the state.
- The level of public confidence in the authorities (the likelihood of revolution or nationalization of the economy).
- Availability of assets: enterprises, mines, farmland, etc.
- Level of industrial development in the country.
- Stability of the exchange rate in which payments are denominated.
- Unemployment rate.
These are not all the factors that can be used in analyzing the risk of an investment. The investor assigns a numerical probability value to all of these factors. For example, it was expected that the GDP level would increase by 2%, but it grew by 4%. This means that production and tax revenues in the country are growing, that is, the issuing government will have the funds to pay bondholders. When calculating the risk of future yield to maturity, the formula is as follows:
Risk = A1+A2+A3+…+An,
where A1, A2,...An are factors that negatively or positively affect the attractiveness of a particular object for investment. Statistical data (the same Russian Rosstat) and information from rating agencies are used as sources.
What parameters to pay attention to
Key points to pay attention to when choosing bonds:
- Coupon rate. This indicator gives the buyer information about how much income he will receive while holding the bond for the period before its maturity. Cash is accrued daily (NKD), payments are made quarterly or semi-annually. The most profitable bonds are those where the coupon size is higher (compared to the purchase price).
- Market price. This indicator indicates the price of a security on the open market on a certain date or period. The higher the price, the more profitable the bond.
Type of coupon. Some coupons are changed according to special algorithms of the issuer; you need to pay attention to this possibility. There are bonds with indexation, for example, OFZ. Some securities will not have a coupon.- It must be remembered that there are bonds with an offer. Data on the offer date are always indicated in the issuer’s special booklets. After the date that is set, the bond is written off, and funds arrive within 20-25 days. The coupon exists in a stable state until the offer day; later the issuer changes the rate. This moment reduces risks, but can reduce profitability.
- Duration. This is a parameter that shows when the investment will pay off. It includes the circulation period of the paper and the possibility of reducing or increasing interest during this period of time. This parameter shows the risk of this investment.
Possible risks
Bonds are considered risk-free securities. However, the risk of loss of capital (partially or completely) exists. This is the risk of bankruptcy of the issuer (default of the country), inflation and devaluation of the national currency. A striking example is the situation with the Russian ruble. Foreign investors are in no hurry to buy ruble-denominated Russian government bonds, since the strong depreciation of the ruble has led to the fact that the OFZ yield to maturity is negative. On the stock exchange, bonds are sold with a yield of 7-8%, and the ruble has fallen against the dollar and euro over the year by 20-25%.
There is also market risk. For example, an investor bought a bond with a discount with a maturity of 1 year for 930 (nominal price 1000 rubles), and two hours after the transaction it fell in price and began to cost 870 rubles. This does not mean that the yield to maturity will become lower (the investor at the end of the term will receive a nominal value of 1000 rubles), just that the security could be bought cheaper and make a greater profit.
What formulas do you use to calculate?
When calculating the yield on a bond, the following parameters are used:
- coupon rate;
- nominal price;
- acquisition cost;
- maturity/sale date;
- sale price (if any);
- rate at the time of purchase.
There are several options for how to calculate bond yields.
Current
In order to calculate the yield of a bond, the formula used is quite simple:
(coupon/market price) x 100%.
For example: according to OFZ-24019-PK, the coupon income will be 7.35% per annum. Now the cost of this paper is 999.6 rubles. When substituting these variables into the formula, you can see that the current yield is slightly higher: (73.5 / 999.6) x 100% = 7.3529%.
Current yield does not take into account changes in the bond's market price during storage (which can also be a source of income).
To be redeemed or sold
The yield to maturity of bonds can be calculated using the formula presented below. Initially, you need to calculate the current coupon income figure - this variable is important for this formula. On the contrary, the income tax can be ignored, since the coupon payment completely eliminates it.
This formula can be used to calculate the yield to maturity, sale, and offer:
(face value - purchase price with NKD + all coupons / purchase price with NKD) x (365 / number of days until maturity) x 100%.
For example: the yield on coupon OFZ-26211-PD is 7%, the current one is 7.2202, and the simple one for redemption is 7.9863%.
Efficient
Shows the investor's total profit in case of reinvestment of funds. This method also allows you to look at the profitability of an investment.
Effective bond yields can be calculated using the formula:
EDP = ((N - P) / t + Cr) / ((N + P) / 2) x 100%, where:
- EPD - profit to maturity;
- N—bond denomination;
- P—security price;
- t — how many years until maturity;
- Cr is the annual coupon value.
Formula for calculating a speculative security
If it is purchased not for the purpose of investment, but in order to resell it, then the profitability (loss ratio) is calculated as follows:
Yield = (sale price - purchase price) / purchase price.
A negative number means a loss on the transaction. Such developments rarely happen. Losses on bond transactions most often occur due to the inexperience of the speculator or investor, his impatience, or when the bond owner urgently needed money.
How reliable is it?
Bonds are one of the most reliable ways of income for traders.
The centuries-old history of transactions has made it possible to create a wide precedent base, as well as the necessary norms for regulating relations in this area. The current state of affairs completely eliminates the possibility of fraud and ensures the safety of investors and issuers, and also proclaims the unshakable legal validity of all transactions made.
But do not forget that any investment is a risk. In order to successfully trade in the bond industry, you must be confident in your ability to evaluate and analyze the market. In addition, you need to understand the basic principles of trade and economics.
Example of risk level calculation
Government loan bonds of country N are available for sale. Below are the factors of attractiveness and unattractiveness of debt securities of this country:
- GDP growth this year was 2%, although 3% was predicted.
- Trade turnover for the current turnover increased by 7%.
- Farmers have suffered losses due to locust attacks this year. One tenth of the crop was lost.
- Inflation on basic consumer goods was only 2% instead of the expected 6%.
- The price index for shares of large companies and corporations rose by 50 points or 2.2%.
Solution.
It is necessary to determine the weight and level of influence of each factor on the financial stability of country N. In this case, two approaches are used: they use the percentage increase (decrease) that occurred or assign a certain share of value to each factor (at the discretion of the investor). Below is an example of a calculation using the first method, that is, percentages are added and negative values are subtracted.
-1 + 7 + (-10) + 4 + 2,2 = 0,8%
This means that there are more positive factors than negative ones. But this is only in a specific example. In reality, investors have to deal with even more factors. They have to process a lot of information and use various ratios to determine the relationship between the yield and maturity level and the risk of buying a bond. But this is the only way to ensure reliable storage of capital.
Current bond price
A financial calculator of the present (current, fair) value of a bond is an estimate of how much a bond, the parameters of which are known, should currently cost.
| Nominal value (rubles): |
| Required rate of return (% per annum): |
| Coupon rate (% per annum): |
| Maturity (years): |
| Number of coupon payments per year (times): |
Total: Current bond price : enter the data in rubles.