In early 2009, a mysterious cryptocurrency developer (or team of developers) working under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto released the first program that implemented Bitcoin as a digital currency. Since then, Bitcoin has not only gained widespread popularity around the world, but has also inspired hundreds of other digital currencies.
Many of these cryptocurrencies use aspects that were already inherent in Bitcoin and the Satoshi concept. Others are taking the Bitcoin model and adapting or trying to improve on it. In some cases, Bitcoin has spawned coins that are based on the same basic concept and software but are different from the original.
In these situations, the Bitcoin blockchain has undergone a process known as a fork, whereby the blockchain itself is split into two separate entities.
It was thanks to forks that various digital currencies with names similar to Bitcoin began to appear: Bitcoin Cash, Bitcoin Gold and others.
For an investor new to cryptocurrency, it can be difficult to tell the difference between these cryptocurrencies and compare the various forks on a timeline.
The table below contains information about all Bitcoin forks, and we will look at successful and popular ones further in the article .
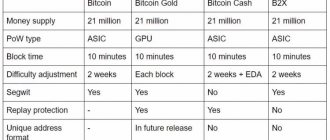
| Name | date | Block | Ratio | Status |
| Bitcoin Cash (BCH) | August 1, 2017 | 478558 | 1:1 | Active |
| Bitcoin Gold (BTG) | October 24, 2017 | 491407 | 1:1 | Active |
| Bitcoin Diamond (BCD) | November 24, 2017 | 495866 | 1:10 | Active |
| UnitedBitcoin (UBTC) | December 12, 2017 | 498777 | 1:1 | Semi-active* |
| Bitcoin Hot (BTH) | December 12, 2017 | 498848 | 1:100 | Semi-active* |
| Super Bitcoin (SBTC) | December 12, 2017 | 498888 | 1:1 | Semi-active* |
| BitcoinX (BCX) | December 12, 2017 | 498888 | 1:10000 | Semi-active* |
| Oil Bitcoin (OBTC) | December 12, 2017 | 498888 | 1:1 | Dead |
| ABitcoin (ABTC) | December 12, 2017 | 498888 | 1:100 | Dead |
| Bitcoin World (BTW) | December 17, 2017 | 499777 | 1:10000 | Dead |
| Lightning Bitcoin (LBTC) | December 19, 2017 | 499999 | 1:1 | Active |
| Bitcoin Stake (BTCS) | December 19, 2017 | 499999 | 1:100 | Dead |
| BitEthereum (BITE) | December 21, 2017 | — | 1:3.94 | Dead |
| Bitcoin Top (BTT) | December 26, 2017 | 501118 | 1:1 | Dead |
| Bitcoin God (GOD) | December 27, 2017 | 501225 | 1:1 | Semi-active* |
| Bitcoin FILE (BIFI) | December 27, 2017 | 501225 | 1:1 | Semi-active* |
| Bitcoin Cash Plus (BCP) | December 28, 2017 | 501407 | 1:1 | Dead |
| Quantum Bitcoin (QBTC) | December 28, 2017 | — | 1:1 | Dead |
| SegWit2x (B2X) | December 28, 2017 | 501451 | 1:1 | Dead |
| Bitcoin Uranium (BUM) | December 31, 2017 | — | 1:1 | Dead |
| Bitcoin Pizza (BPA) | December 31, 2017 | 501888 | 1:1 | Dead |
| Bitcoin All (BTA) | December 31, 2017 | — | 1:1 | Dead |
| Bitcoin Ore (BCO) | December 31, 2017 | 501949 | 1:1 | Dead |
| Bitcoin Rhodium (BTR) | January 10, 2018 | 501949 | 1:10 | Dead |
| Bitcoin Smart (BCS) | January 19, 2018 | 505050 | 1:100 | Dead |
| Bitcoin Interest (BCI) | January 20, 2018 | 505083 | 1:1 | Almost dead** |
| Bitcoin Lite (BTCL) | January 30, 2018 | — | 1:1 | Almost dead** |
| Bitcoin Atom (BCA) | January 24, 2018 | 505888 | 1:1 | Almost dead** |
| Bitcoin Private (BTCP) | February 28, 2018 | 511346 | 1:1 | Semi-active* |
Semi-active* - average trading volumes, but completely dead GitHub.
Almost dead** - almost no trades and dead GitHub.
What is a hard fork
Bitcoin Cash is a hard fork of Bitcoin, so first you need to understand this concept before getting acquainted with the cryptocurrency itself. A hard fork is a division of the blockchain of a specific coin.
Without delving into the depth of technical details, we can say that its essence is the adoption of a cryptocurrency update that is incompatible with the old rules. In other words, this is a strong change to the original source code. As a result, two nodes are created, one of which continues the old chain, and the second goes into a separate one.
The reason for this phenomenon is most often an excessive number of shortcomings in the network. When the transaction processing speed drops, the block size is not enough for the normal functioning of the network, transfer fees become sky-high, and ideas appear on the network to eliminate these problems.
Genesis Block
In 2009, shortly after the release of Bitcoin, Satoshi mined the first block in the Bitcoin blockchain. This is called the "Genesis block" as it represented the beginning of cryptocurrency as we know it today.
Satoshi was able to make numerous changes to the Bitcoin network early in the process. This is becoming increasingly difficult, and Bitcoin's user base has grown significantly.
The fact that no one person or group can determine when or how Bitcoin should be updated has also complicated the process of updating the system. hard forks in the years following the Genesis block .
During a hard fork, the software that implements Bitcoin and its mining procedures is updated. Once a user updates their software, that version rejects all transactions from the older software, effectively creating a new branch of the blockchain.
However, those users who retain the old software continue to process transactions, meaning that there is a parallel set of transactions going through two different chains.
Blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies. Fast start
Get the book and learn all the basics of blockchain technology and cryptocurrency in one evening
If a large number of like-minded people come up with an interesting and innovative idea, a hard fork is carried out. On some level, this is a positive phenomenon, since the network is unloaded and the above problems disappear.
On the other hand, this can be a disadvantage. No one can predict the outcome of a hard fork. It can create more problems. It could cause a complete split of the crypto-society into two categories. What happens if the hard fork turns out to be many times better than the original?
Roadmap and what to expect
Bitcoin SV begins with a simple restoration of what was the original Bitcoin protocol. The precepts set forth in the original Bitcoin document are accepted by those working on the Bitcoin SV project.
By re-enabling Satoshi op_codes, Bitcoin SV is now ready to add advanced technical features including smart contracts and tokenization. This original Bitcoin protocol is what was needed for Bitcoin to grow and prosper, and it should be allowed to exist without constant changes and modifications.
Now that this original protocol has been restored, it should remain stable. Apart from critical security fixes, there should be no required changes. By remaining stable, Bitcoin SV will ensure trust from businesses looking to build applications on top of the public blockchain. Just as the protocols that govern the Internet have remained relatively stable over the years, so too will Bitcoin SV remain stable.
Story
As you already understood, Bitcoin Cash appeared as a result of various types of flaws in the Bitcoin network. Thus, the transaction speed has become extremely low. To ensure fast transfers, users were forced to pay large fees.
Someone suggested simply increasing the block size of Bitcoin itself, but many did not agree with this, fearing that miners would leave and the network hashrate would decrease. In addition, no one could know what consequences could occur from the technical side.
However, more and more people wanted to see some kind of update to the BTC blockchain. That is why, on August 1, 2022, a fork appeared, which resulted in the emergence of Bitcoin Cash.
P2P relay of transactions with complex scripts
As of the Genesis fork, all participants are now free to use complex transaction types. Before Genesis, a participant had to find a miner to help confirm block transactions whenever complex transaction types were involved.
Like any software, we can expect the public blockchain that is Bitcoin SV to evolve over time. While technical changes are inevitable, the one thing that will not change are the rules of the underlying protocol that govern Bitcoin SV.
Development milestones
The altcoin is not even a year old yet, however, there is enough information that is subject to discussion in any environment. In fact, its development began long before its creation, in the spring of 2022, when Bitcoin began to acquire the above problems. Then a soft fork of SegWit was introduced, but it did not solve them properly. But BCH appeared, and then it began.
After this there were no significant changes. Cryptocurrency continues to develop and is under the general influence of the market situation. However, the rate remains more stable than that of Bitcoin or Ethereum.
Restoring the Originality of the Bitcoin Protocol
Bitcoin has been around for over a decade, and every year developers make changes to the Bitcoin protocol. Because of this, Bitcoin as we know it today has deviated from the original Bitcoin protocol. The Genesis hard fork on Bitcoin SV restored the original Bitcoin protocol as described in the original white paper. This essentially led to four key technical changes:
- Restoring OP_RETURN functionality: This change allows script developers to terminate scripts early and easily. Increasing the script's numeric type to larger numbers: This change allows complex mathematical calculations to be performed more efficiently. The change was necessary due to limitations of 32-bit numbers. This change returns the original design and allows complex calculations and scenarios with enhanced functionality.
- Override P2HS for new transactions: Pay to Hash (P2HS) script allows you to hide output scripts during creation. This change was made by the developers, but it contradicts the original Bitcoin protocol, which supports an honest record of events. P2HS led to poor privacy practices, and repealing P2HS will allow Bitcoin SV to return to best privacy practices.
- Recovering nLockTime and nSequence. Restoring the original use of nLockTime and nSequence will enable high-speed micropayments as envisioned by Satoshi.
The main problem is transaction repetition
BCH became a new coin, however, there was still a connection with the BTC blockchain. The main problem in this regard could be the “repetition attack”. The fact is that everyone who had regular Bitcoins at the time of the creation of Bitcoin Cash automatically received such a number of hard fork coins.
Let's say you created a transaction for 5 BTC. Since the above attack occurs, the same transaction for 5 BCH is automatically created, although the user did not intend to do so.
But this problem was avoided. BCH transactions use a different signature hashing algorithm than BTC. This prevents the possibility of a double transaction because it requires different keys.
Hash war scenario
The idea of a hash war arose in response to the lack of separation between the two chains through a technique known as replay protection. With replay protection, any transactions on one chain are invalid on the other chain, so it is impossible to spend the same coins on both chains.
What happened was that while Bitcoin ABC implemented replay protection, Bitcoin SV copied this “protection” to reverse it. This will allow you to repeat attacks.
A replay attack is when transactions appear identical on both chains and allows transactions to be replayed or repeated on both chains, resulting in doubling of costs. A similar scenario occurred in 2016 when Ethereum and Ethereum Classic split, resulting in significant losses for unprepared cryptocurrency exchanges.
Another danger of this type of split is hash war.
Ahead of the hard fork, both Bitcoin Cash ABC and Bitcoin Cash SV announced that they would use all hash power under their control to ensure they had a chain of survival. Craig Wright even went so far as to say that he would 51% launch an attack on the Bitcoin Cash network if necessary to ensure the survival of Bitcoin Cash SV.
Letter sent by Craig Wright to Roger Ver
This was all very speculative, but the Bitcoin Cash ABC side knew they had several potential responses to such an attack. They can simply wait, as the attackers give away money as long as the attack continues.
They can also use most of their own hash power, even using Bitcoin miners to mine the Bitcoin Cash ABC blockchain. Or in what is considered a “nuclear option,” they could shell out the cash again, but also change the proof-of-work algorithm to make the attack hardware incompatible with the blockchain.
Pro-SV miners are highlighted in yellow
On November 15th, the Bitcoin Cash (BCH) ledger split into 2 forks according to different consensus rules. 80% of the miners who were mining BCH until the fork went to a mine with SV consensus rules, this amounted to approximately 4000PH/s in hash. Surprisingly, another 5000PH/s hash (not previously in BCH) landed on the other hand of the fork to mine the so-called “ABC” ruleset.
In the first 24 hours, ABC hash continued to increase and peaked at around 10,000PH/s.
On the one hand we had pre-fork Bitcoin Cash miners that served the entire BCH ecosystem until November 14th. On the other hand, there was a lot of fresh hash that was apparently ready to switch to the BCH ledger and expand it according to the new ABC ruleset. While this would be a positive development if it were driven by market forces, a deeper look at the source of the ABC hash reveals that it is almost desirable.
It was almost 40% more profitable to mine BTC, but pro-SV BCH miners were mining BCH.
There is a key difference between miners mining with SV and new miners who started mining with ABC. To understand, we must differentiate the dedicated miners, who have proven that they can mine a given chain even when mining other chains is more profitable, from the pragmatic miners, who follow the profit and move from chain to chain depending on profitability.
The miners who have been mining with SV since the start of the war are miners who have already proven in the months leading up to the war that they are dedicated BCH miners. Most likely, these are companies that have invested heavily in BCH, who are not so much profiting from the sale of mined them coins, how much from building BCH-based businesses that give them a competitive advantage. Not surprisingly, among the dedicated BCH miners we find Coingeek (who owns a football team sponsored by "BCH" and builds resorts where all payments are made in BCH), BMG (an nChain miner, a Blockchain IP company whose patents are available for free on BCH ), SVPool (a pool created for all retail miners who want to support SV) and Mempool (another mining pool that openly mines SV). We will call this group of dedicated BCH miners CBSM.
On the other hand, we have a hash that didn't mine BCH before the fork, which means (regardless of this) it's either a pragmatic hash that makes money by selling the ABC coins they mine, or a hash rented by people who wanted or believed in the ABC rule set. However, following Bitcoin.com's next announcement, it became clear that most of the hash that would be mined by BCHABC on fork day would be hash stolen from Bitcoin.com miners.
Digging more below the surface, it turned out that other pools were also stealing hash from their clients and pointing them to Bitcoin.com. This included BTC.TOP, Antpool and viaBTC.
We will call this hash BABV. The main property of BABV is that it is extremely volatile, which disturbs the market.
Pool operators bring together miners from all over the world who contribute their machines to the pool, who provide the software and ensure that whatever is most profitable is mined to maximize profits for their clients. BABV is a hash based on machines pointed to the above mentioned pools (Bitcoin.com, viaBTC, Antpool) which are believed to be mining yet, but have been flagged by the pool operators at the BCHABC mine for a signal of market strength/demand for BCHABC. However, this is not a real demand, the car owners have never asked or given consent to my BCHABC. This is done behind their back while they are paid as if the machines are mining BTC, or whatever is most profitable.
Sending these machines to BCHABC against the market is expensive for pool operators. If there is no real market demand for BCHABC, the forced hash will revert to BTC and the BCHABC chain will grind to a halt because there are not enough miners to mine new blocks.
The bottom line is that BABV does not reflect short-term or long-term market demand, and it is neither a mandatory nor a pragmatic hash. This is a forced hash.
The question plaguing exchanges in those days was which one should receive the BCH ticker, the BCHABC chain, which is currently longer, or the BCHSV chain, which is backed by a verified BCH hash code?
By doing so, you are automatically converting your clients' investment on a stable and resilient chain like BCH, which has at least 4000PH of fixed hash, into a stake on a chain that at best only has about 800-1000PH/s of fixed market hash (which proven by the hash distribution before the fork) and whose length lead relative to BCHSV is due solely to forced hashing. Assigning a ticker based on forced hashing is an act of market manipulation, as the new 'BCH' holdings are not comparable to the pre-fork BCH holdings, which had 3000-4000PH/s fixed hash. Assigning the BCH ticker to ABC would most likely be accompanied by the removal of the forced hash, since its only function was to manipulate perception and steal the ticker. However, once the forced hash is removed, hash support for what will now be called "BCH" by exchanges that assigned the BCH ticker to BCHABC will suddenly drop to 800–1000PH/s from 5000PH. Given that the ABC hash support was 800 when the BCH price was around $500 and the current BCHABC price is less than $300, such a hash drop would be out of control and would result in a complete stop of what these exchanges labeled as "BCH" " chain.
This death spiral is the most likely scenario for ABC since it relies on BABV, which is an extremely unstable hash that could disappear at any time if the pool operators can no longer afford to subsidize it.
How long can Roger Ver continue to subsidize BCHABC?
So how does ABC save itself? Short answer: BCHABC is doomed because the only way to save BCHABC is for active BCH miners (CBSM) to enable ABC.
CBSM has made it clear that this will not happen.
ABC sponsors such as Roger Ver and Jihan Wu, on the other hand, showed great weakness in trying to achieve victory after 48 hours of war and trying to socially pressure loyal BCH miners to give up SV and give up on ABC. ABC's sponsors are currently in dire need of a large miner willing to mine ABC so they no longer have to subsidize it. This makes Calvin Ayre, the largest industrial miner in the crypto space, an ideal choice.
After 48 hours in the hash war, Roger Ver emerges victorious, first flirting and then trying to blame Calvin Ayre for refusing to follow ABC.
It's no surprise that Roger Ware's recent social media outings have been aimed at Ayre, culminating in a video today where Were tells Ayre that they can subsidize BCHABC 4000PH for a decade if necessary.
On other social fronts, Roger Ver has resorted to aggressive censorship in his own subreddit r/btc, where he refused to list "SV" in the sidebar, and since the hash war began, he has gone so far as to ban people from posting price tags SV memes.
Anyone who sided with or supported the SV was subject to personal attacks and declared a common enemy. People close to Roger Ver, such as r/btc lead moderator David Shares, were caught behind the scenes discrediting anyone who supported SV with personal attacks, and went so far as to attack Ryan X Charles, creator of Yours and Money Button .
Another point where ABC sponsors are trying to put pressure on exchanges. Although BCHABC is a chain currently mined through forced hashing, Kraken, an exchange known to be close to Roger Ver, today made this alarming statement in an attempt to further manipulate the market's perception of Bitcoin Cash.
Kraken's statement is an attempt to manipulate the market's perception of the MPB fork
Kraken has also openly lobbied ABC on social media, where he has issued controversial tweets and even gone so far as to threaten BCHSV holders to lose funds if the BCHABC chain is reorganized (what happens when a chain dies).
The main idea if you've gotten this far is to stay away from exchanges that try to sell ABC as "BCH" since ABC is extremely volatile and not comparable to your BCH holdings. Virtually all stable BCH miners are committed to mining BCH with the SV protocol and consider ABC to be an attack on BCH.
Differences and similarities
Since this is not just an altcoin created from the Bitcoin source code, but a hard fork of it, there are a number of similarities and differences between the two cryptocurrencies. So the BCH emission is 21 million. It is also issued by mining. It is also built on the SHA-256 hashing algorithm, respectively, the block time is approximately 10 minutes. Uses the same protection method - Proof of Work.
Among the differences, the main one is the block size, which is 8 megabytes instead of 1. This was one of the key goals of the hard fork, since the Bitcoin block size was sorely insufficient for the normal functioning of the network. The queue for transactions lasted for several days. The peak was 160 thousand unconfirmed transactions.
Accordingly, BCH has no need for SegWit since transactions are quite fast. Thanks to this, it was possible to significantly reduce the cost of commission. Thus, the minimum transaction fee on the BTC network is approximately 0.7 dollars, while for BCH it is only 0.1.
What should Bitcoin cash users do?
If Bitcoin ABC and nChain do not reach a consensus, a real war could begin. In this case, we advise all Bitcoin Cash to take the following actions:
- Do not perform transactions for several days after a blockchain split to avoid becoming a victim of a 51% attack.
- Transfer your BCH coins to a secure cryptocurrency wallet (the best option is a hardware Ledger Nano S or Trezor ).
- If you are unable to purchase a hardware wallet, use one of the software wallets: Mycelium, Jaxx, Coinomi or Exodus.
- You will need private wallet keys to receive Bitcoin SV coins , which will be released in the event of a blockchain split.
- If you are mining BCH , we recommend using the Bitcoin Cobra with replay protection. Bitcoin Cobra client is an alternative to Bitcoin SV and Bitcoin ABC , it will not implement a hard fork, so Cobra will work stably with a 99% probability.
Average rating 0 / 5. Number of ratings: 0
No ratings yet. Be the first to rate.
New toy for miners
A very important difference is mining. Yes, the hashing algorithm is the same, the security protocol is also no different. Accordingly, it is not cost-effective to mine it on a home computer using a video card, and you can also use the same ASICs that were created for Bitcoin. However, the system for changing the difficulty of cryptocurrency mining was significantly rebuilt.
Firstly, it does not change every 2016 blocks, but only every 6. The smooth change in difficulty is praised by most miners, since it is easier for the equipment to gradually accept the new load.
An analogy can be drawn with the gym. Imagine that you squat with a weight of 70 kilograms, and on the next set you immediately lift 100. It seems that this is simply impossible. And if you smoothly move from 70 to 100, adding 10 kg per approach, then it will be easier for the body and muscles.
Bitcoin hard forks 2022
As a result of the hard fork, a new blockchain network with its own rules is formed.
After unsuccessful attempts to achieve consensus in August 2017, the PTS blockchain was divided into 2 factions with different rules. Bitcoin Cash developers removed the Segwit code, while simultaneously increasing the block capacity to 8 MB. Segwit was deemed an unnecessary soft fork, and the network split before Segwit2 x (BTC 1) miners could integrate the change. In anticipation of the hard fork, the Segwit2 x developers decided to keep Segwit in the source code, but individual VTS1 miners began to deviate from the rules in order to expand the block to 2 MB.
The plan to split the network is one of the points of the NYA agreement (New York Accords and the Hong Kong Round Table), which sets out a compromise with two forks. The first part of the obligations includes the implementation of Segwit, the other is the expansion of the block to 2 MB using a hard fork.
The problem was aggravated by the lack of faith of some system participants in reaching a final consensus, and some miners refused to support the hard fork. However, by the time the changes were made, about 80% of the participants confirmed their desire to split the network and had the hashrate to realize this goal.
Blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies. Fast start
Get the book and learn all the basics of blockchain technology and cryptocurrency in one evening.
An important element of Bitcoin Cash mining is the likelihood of the difficulty decreasing, instead of increasing it. This is possible thanks to the Median Time Past protocol (aka MTP). The median represents information from the last 11 blocks that entered the chain. Thanks to it, the approximate time that will be spent opening the next blocks is calculated.
If MTP becomes more than 12 hours, mining difficulty is automatically reduced by 20%. Show me a miner who won't be happy about this. In addition, the difficulty decreases if the total number of miners in the network decreases. How does this become known, you ask? It’s very simple: the overall hashrate is falling.
It is clear that when Bitcoin Cash was created, a certain mining difficulty was set. However, many were skeptical about this hard fork, as they are about any new altcoin in principle. Therefore, there were very few miners, and accordingly, the hashrate was also small.
This caused a significant reduction in difficulty from the original one. Such information immediately attracted the attention of most miners, because they saw an opportunity to make quick money without spending a lot of resources on their equipment.
The 51% power issue has also been resolved. So, if someone in the Bitcoin network has 51% of the total hashrate, then it will become centralized, since this user will be able to solve the block faster than others. Accordingly, other miners will need to spend money on new equipment to solve this problem.
Since the difficulty of mining Bitcoin Cash can be reduced, this makes it more accessible. Therefore, it will be much more difficult to concentrate 51% of the network’s power.
Support every version
The Bitcoin Cash community was quite clear in its choice of sides before the hard fork. Of course, Bitcoin Cash ABC received support from Ver and Wu, but the Bitcoin Cash ABC network was also supported by most major exchanges. Most other Bitcoin Cash implementations, such as Bitcoin Unlimited, BCash and Bitprim, have also made their software compatible with Bitcoin Cash ABC.
The Bitcoin Cash SV adoption was most popular thanks to the CoinGeek media outlet, which is owned by billionaire Calvin Ayre. Most Bitcoin Cash mining pools also supported Bitcoin Cash SV, which gave the protocol a significant amount of hash power going into the hard fork and raised the possibility of a post-fork hash war. These mining pools represent up to 70% of the network hash power.
Team
The main developer of the cryptocurrency is Amaury Sechet. Previously, he was one of the programmers at Facebook. According to him, he has been interested in digital money and its development for a very long time. Also, as Amory said in one of his interviews, he spent a lot of time developing ways to scale Bitcoin.
He didn’t come to the idea of taking the hard fork initiative on his own. He was advised by one of the team members of the Bitmain mining equipment manufacturer. After receiving a grant from the Bitcoin Development Team, he began conducting his first research. The result is known.
Jian Wu is one of the co-founders of Bitmain. He developed an improvement for ASIC miners that reduced power consumption by 20%. An interesting fact is that he is not on the best terms with Blockstream. This company is one of the leaders in the development of blockchain technologies. They fear that mining power will be concentrated in one hand, which could be caused by ASICs.
Roger Ver is considered one of the largest Bitcoin holders in the world. According to him, Bitcoin Cash is much more in line with Satoshi Nakamoto's vision of cryptocurrencies. Another notable team member is Hypo Yang, CEO of ViaBTC.
Craig Wright vs Roger Ver
Bitcoin Cash SV proposed very few changes, the main one being the default block size of 128 MB. It also rejects CTOR and removes the size limit on scripts.
Ultimately, Wright planned to make additional changes to bring Bitcoin Cash SV closer to the 2009 Bitcoin protocol. One change would be to further increase the block size or even remove the block size limit entirely. There were additional controversial changes proposed by Wright, and he also went so far as to hint at returning coins that had not moved in a very long time (Satoshi Nakamoto's address) back into circulation.
Craig Wright (left), Roger Ver (right)
New confrontation
This cannot be called some kind of split or scandal, but the appearance of a new hard fork on the network led to the emergence of its supporters and opponents. Some exchanges, developers of mining equipment, founders of altcoins and platforms opposed it, while others, on the contrary, supported this cryptocurrency and its team.
One of the most famous opponents is the Bitmex exchange. According to their team, it is clear that they do not want to support the creation of money out of thin air. On some level, they are right, since BCH appeared through a fork in the Bitcoin blockchain. But in fact, a lot of work was done for this, so this is not “money from nothing.”
Also, the exchange’s position on Bitcoin hard forks suggests that Bitcoin Cash is not able to provide the appropriate level of protection and therefore will not be included in the exchange list. What happened in November 2017? Trading BCH futures on Bitmex.
Among the exchanges that support Bitcoin Cash and trade it on their platforms, we can highlight the following:
- Livecoin;
- Bitstamp;
- Poloniex;
- Bittrex;
- Binance;
- Kraken;
- Exmo.
There is also the CoinEx exchange, which was the first to use Bitcoin Cash as the main cryptocurrency. Interestingly, on January 10, 2018, Block Explorer announced that they only support BCH. BTC was called a blockstream fork, which is only a dead-end branch of blockchain development. The main reasons for this were quickly growing commissions and long transactions.
People behind BitcoinSV
Unlike some other cryptocurrency projects where the founders and leaders of the project are individuals or individuals, Bitcoin SV is sponsored and developed by corporate organizations.
Sponsorship for the project comes from CoinGeek, while the project's development work is being carried out by nChain, a company that has been developing blockchain since 2022, when it was founded by Craig Wright. nChain is well known for filing numerous blockchain-related patents.
The team that is developing Bitcoin SV was assembled with the full intention of following industry best practices in an attempt to provide a complete node implementation of the Bitcoin blockchain. It is also committed to maintaining the network and providing stability and unparalleled quality.
Key sponsors of Bitcoin SV. From left to right: Craig Wright, Calvin Ayre and Jimmy Nguyen
While nChain was founded by Craig Wright, who claimed to be the one and only Satoshi Nakamoto, and is currently managed by Jimmy Nguyen, development is overseen by Daniel Connolly as the lead developer at nChain.
He joins the company after two decades in enterprise systems development, holding several senior IT positions with United Nations agencies. In the past, Daniel was an anonymous backer of Bitcoin, as well as a major backer of the BitcoinJ-Cash project.
nChain's CTO is Steve Shadders, and he not only helps oversee the Bitcoin SV project, but is also responsible for interacting with sponsors and other industry participants. Steve has been involved in Bitcoin development since 2011, and was also an early contributor to BitcoinJ, in addition to creating one of the first open source mining pool engines.
Reasons for development
What's driving BCH? A good question, considering that the cryptocurrency is in the top 3 best in terms of capitalization, and in price it is right behind Bitcoin. One of the factors behind the rapid development is that more platforms and services are starting to use Bitcoin Cash.
At the time of creation the situation was different. Many services always have a negative attitude towards new altcoins, even if they are forks. This is associated with a huge risk that the project simply will not take off. However, the situation here is completely different.
The second reason is the increase in the number of miners in the network. The mining of this cryptocurrency is somehow special, which is why it attracts miners. As mentioned above, it is simpler and more profitable than Bitcoin. Also, the increased block size makes it possible to include many more transactions in it. This significantly increases the efficiency of miners.
The third, important reason is the high transaction speed. The purpose of this hard fork was to reduce the load on the network and create faster transfer processing. It can be considered that it has been achieved. And a project that has met other people’s expectations and its own plans always earns a good reputation and develops faster.
The first hash war in Bitcoin history
Any Bitcoin fork is a ledger that is regularly updated as new blocks are mined. Each new block updates user balances and takes into account transactions and trading. However, in order for the chain to continue to expand and new blocks to be added, there must be miners willing to mine the chain. Without new blocks, the chain dies, transactions accumulate in the so-called “mempool”, transferring coins becomes impossible, trust in the chain collapses, and the price of coins drops to zero.
Consequences of hard forks in the cryptocurrency world
When a system hard fork occurs, two branches are formed. If one of them does not have enough hashing power, then it dies. Moreover, the more power a given branch has, the greater the chance that they will survive, especially if they host new forks.
For example, after a hard fork occurred on the Ethereum network, two chains appeared. The new one retained the same name and abbreviation ETH, but the old one turned out to be quite independent, continued to work on the original code and was called Etherium Classic (ETC).
BTCP Rating
Of course, this is the aspect that is most difficult to predict. Looking at other BTC forks, we see that BCH is trading at $1600, Bitcoin Gold is trading at $185, even Bitcoin God (the newest fork) is trading at almost $100. All of them are 40 percent cheaper than a month ago. Let's assume that there will be a market correction and the coins will regain their former prominence. Then, by the end of February, these cryptocurrencies should be trading at a price 10-20 percent higher than the current one. None of these BTC forks have one unique property: privacy. There are cryptocurrencies created solely for the purpose of providing privacy, but now there is a privacy coin under the Bitcoin brand. Are you wondering what the brand is worth and what the specific BTC brand is worth? Then, my friend, you are living in the wrong world. Brand is everything. Look at cars, watches, perfumes. If they have the stamp of a well-known brand on them, they are worth orders of magnitude more than just things that do their job (even if they do their job well).
The most valuable brand among cryptocurrencies is, of course, Bitcoin. Bitcoin Private is deliberately trying to capitalize on the BTC branding and the BTC blockchain, and with the privacy aspect of BTC, it actually has the opportunity to do it right! A fork date has been set for BTCP (tentatively February 28, which was announced on January 28). He has a large team of developers constantly working on the project and already holding meetings in Austin and San Francisco. This fork is not one of the scams (like Bitcoin Pizza), but a cryptocurrency that could potentially become the next BCH.
Bitcoin rate after hard forks
Changing blockchain protocols is reflected in the Bitcoin exchange rate.
Understanding who, where and for what purpose is conducting a fork, network users must decide whether they support protocol changes or not. Which of the two bitcoins is stronger becomes clear based on the volume of investments. VTS is an open source protocol, so virtually any participant in the system can share the network. In a free market, users themselves determine which bitcoin will change the status quo and ensure economic independence.
Altcoins and forks - how not to get confused
In order not to get confused in forks and altcoins, I propose to start by defining what they are.
As we just said, any clone of the source code with changes made there is a fork. At the same time, Altcoin is any cryptocurrency other than Bitcoin. That is, an ordinary clone of a cryptocurrency that has already been created, without significant technical changes made to it, and uninterested in the global singularity, will not be considered an altcoin.
In fact, the same project can be called an altcoin or a fork, regardless of what it is. However, there is still a difference. Thus, Ethereum, NXT, Dash and MaidSafe should be called altcoins, since their differences from Bitcoin are significant. But the forks are Dogecoin (from Litecoin), Expanse (from Ethereum) and Stellar (from Ripple).
ZClassic and Bitcoin (ZCL and BTC)
BTCP has been discussed since early December when the price of ZCL rose from under $2 to over $100. In January, the price of ZCL approached $200, and then there was a market correction. This was due to the most anticipated January BTCP fork. As a result, ZCL lost 40 percent of its value in a matter of weeks, as did most currencies on the market. Many would say that ZCL has peaked (with a 70x increase in two months). But the fork coin from ZCL has the same value as the fork coin from BTC. The BTC coin is currently worth about $12,000, and the ZCL coin is $140. The IGNIS airdrop resulted in NXT's market capitalization being over $2 billion solely due to the FOMO (fear of missing out) syndrome associated with free coins.
BTCP will also cause FOMO, but there will also be real-life examples of the currency being used. ZCL's market capitalization is approximately $400 million. BTC's market capitalization is about $190 billion (yes, “-ards”). However, both provide the same coin, BTCP. From an investor's perspective, a fork coin is very similar to dividends, and a coin worth $140 produces the same profit as a coin worth $12,000. Discussion on BTCP valuation will come later, but whatever the price of BTCP is, it should correlate with the current minimum value of ZCL.
Many people are well aware of the problems that have plagued Bitcoin for years. These are the cost of transactions, the transparency of the blockchain (whether this is a positive or negative nuance depends on the point of view), the time required to process a transaction, the minimum number of all tokens, etc. The list of things that went wrong with Bitcoin is longer than the list of things that went right. Bitcoin was first and will always be respected (and trusted), but the purpose of forks is to improve on the imperfections in the original. To deal with the scalability issue, Bitcoin implemented SegWit. Part of the main idea was to remove signatures from each block. It is estimated that signatures accounted for 65 percent of all data processed in each Bitcoin block. With this and several other updates, the developers tried to solve the problem of Bitcoin scalability. But the Bitcoin Cash fork took a different approach to solving the BTC problem.
Bitcoin hard forks 2022
Hard forks with the advent of new bitcoins are associated with risks, but allow you to earn more money.
The first hard forks of the BTC opened a new era in the development of cryptocurrencies. Proposals to make changes to the blockchain protocol began to arrive regularly, directly affecting the prospects for the development of the cryptocurrency market. Most often, innovations are used to achieve the following goals:
- increase in emissions;
- recognition of some coins as lost with their subsequent redistribution;
- creating Bitcoin PoS or combining PoW and PoS to solve the scaling problem.
According to experts, the era of Bitcoin forks will last until an optimal alternative is found. In the meantime, blockchain participants can only closely monitor Bitcoin forks and act in the realities of the present time. Only in 2022, the list of forks was replenished with the creation of several coins, and this process will gain momentum.
- Bitcoin Pizza (BPA)
- Bitcoin Smart (BCS)
- Bitcoin Interest (BCI)
- Quantum Bitcoin (QBTC)
- Bitcoin HUSH(BTCH)
- Bitcoin LITE (BTCL)
- Bitcoin Private (BTCP)
In this regard, it is impossible not to note the difference between the appearance of Ethereum classic and Bitcoin forks. In the case of ETC, these were truly fundamental disagreements regarding the fundamental principles of the operation of digital currencies, which cannot be said about the problem with BTC. In addition, adherents of alternative versions have not answered the main question: why don’t they create a separate currency, more advanced than Bitcoin.
- 3shares
- 0
- 3
- 0
Conclusion - ZCL should grow significantly
The only way to get BTCP is to purchase BTC or ZCL and be a holder of those currencies during the fork on February 28th. Given that the price of ZCL is $140 and BTC is $10,500, the easiest route would be to buy ZCL. The value of the fork coins will be the same for BTC and ZCL, as there is a 1:1 ratio between BTC and ZCL coins purchased at the time of the fork on February 28th. With less developed forks trading between $100 and $500 and established forks trading around $1,500, BTCP looks set to have a very strong start. BTCP has already formed a large community, excited by the prospect of a privacy-focused BTC. Well, the time has come, there is less than a month left until the launch, and the only way to get BTCP is to own ZCL or BTC.
The entire market just went through a major correction, prior to which ZCL was trading at around $200 per coin. There was a correction, and now it’s at $140. The value of BTCP has not decreased since it has not even been formed yet (and will remain so for another 30 days). However, the value of the underlying asset to receive BTCP has dropped significantly (ZCL). BTC futures traders are expecting BTC to rise in value this month, thanks to the upcoming Dallas Super Conference (The Bitcoin, Ethereum & Blockchain Superconference) and many other events, as well as the cryptocurrency market recovery that follows major corrections. A sensational ZCL-related price increase is expected this month. The BTC price will likely also be subject to a trend, but if BTC rises in price by about 40 percent, then altcoins will react more actively and could rise in price by 60 percent. ZCL is considered one of these altcoins, its price directly depends on the success of the BTCP fork launch at the end of February.
Expect the overall market to rise this month. BTC will be the safest bet and ZCL could make huge profits if BTCP launches on February 28th as planned. Before the fork, there will be many catalysts that will pump up the price of ZCL, and you need to provide exit points (or buy/sell, depending on your tactics). Any exchange listing, excellent market reception, important updates, meetings and constant publicity will directly impact the value of ZCL as well as the future value of BTCP. Keep an eye on BTC and ZCL, February will be very busy with the release of a joint fork of BTC and ZCL called BTCP.
05/03/2018 in the Blog section