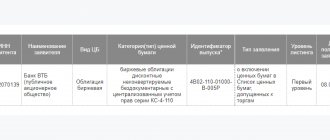
Hello, dear readers of the KtoNaNovenkogo.ru blog. There is such a thing as securities. This phrase can often be found in the media, but it is not always clear what is behind it.
In general, many financial terms are difficult to understand (volatility alone is worth it), so today I decided to devote a separate article to the concept of securities.
Let's talk about what they are, why they were invented, who issues them, and on the basis of what law the circulation of these securities is carried out. Let's also consider their types and purposes.
Securities are...
Securities (CS) is a widely used concept, which, however, does not have a strict definition. The most common definition of the Central Bank is by the functions it performs.
Securities are an easy-to-use means of confirming the receipt of money ; it is drawn up as a document (on paper), or in the form of an electronic entry in the appropriate register.
It often happens that securities existing in paper form are not handed over to the owners: then the ownership of such securities is secured by agreement for safety purposes. The issuer of securities (the one who issues them) is the state or a separate enterprise.
But even if the document meets the main feature of the Central Bank (facilitates the transfer of money), it is not necessary that it will be a security.
An example is an IOU. It cannot be called the Central Bank, because it is a variant of a civil contract. A cashier's check is not a Central Bank - it is considered confirmation of payment.
There are three main, and several more auxiliary definitions of securities . They are relevant and reflect their key feature:
- A security (CB) is a document confirming property rights and presented for this purpose;
- The Central Bank has legal force, has a certain monetary or property content, and is a business document of the established form;
- It serves as a unique form of capital, and can be turned into a commodity value, being in some way a replacement for cash.
The circulation of securities is regulated at the level of federal laws, therefore the procedure for their purchase/sale, issue, and redemption is always strictly defined.
Common types
The status of value is assigned to assets based on the domestic legislation of the country. Based on the country in which they are sold, that is, where they are issued, in accordance with what criteria they are issued, there are main types of securities, a comparative analysis of which is offered in the table.
Table of types of securities
| View | Issuer |
| Promotion | Issued by an enterprise or organization to make a profit in the market |
| Bank passbook | The bank issues to an individual |
| Bill of exchange | State or organization |
| Certificate of Deposit | Issued by the bank |
| Mortgage | Enterprise or organization |
| Investment share | Organization |
| Mortgage participation certificate | Any organization |
| Bill of lading | Enterprise or organization |
| Bond | Issued by organizations of any form of ownership |
| Issuer option | Any organization |
| Simple (double) warehouse receipt | Enterprise or organization |
| Privatization | Issuing country |
| Depository receipt | Bank |
| Savings certificate | Issued by a bank to an individual |
| Check | Bank |
When we talk about the stock market, stock trading is most often mentioned.
A share is a registered financial document that gives its holder the legal right to receive dividends in the form of income or property equivalent from the company whose shares he owns.
Distinctive features:
- has two prices: indicated and real;
- determines the receipt of part of the profit of the joint-stock company as dividends. Dividends may not always be accrued, depending on the decision of the annual meeting of shareholders;
- provides the opportunity to participate in the management of a joint stock company;
- in case of liquidation, it provides the right to return funds without fail. Liquidation of a JSC can be voluntary or forced, through bankruptcy.
The share does not have a uniform appearance, but differs according to the type of income into ordinary and preferred. Ordinary shares have all the properties described above.
Privileged ones differ:
- priority in obtaining income when selling a joint stock company;
- mandatory presence at the meeting of shareholders, while the right to vote applies only to issues of reorganization and dissolution of the company.
Bank savings book – confirms the presence of a deposit in the bank. Regulates the procedure for returning deposited funds to the depositor and paying with interest, strictly stipulated in the agreement between the bank and the depositor.
A promissory note is a monetary obligation that a borrower gives to a lender. The purpose of a bill of exchange is to serve as a means of settlement and payment.
Depending on the obligation to pay, a bill can be:
- simple - such a bill records the debtor’s promise to pay the bill in due time;
- transferable - such a bill indicates the person who is asked to pay the specified amount by the debtor within a clear time frame.
A certificate of deposit is a kind of bank certificate that establishes the fact that a legal entity has made a certain monetary deposit to the bank and regulates the process of the bank returning the deposit with charges on it.
A mortgage is a document secured by collateral, which specifies the terms of the loan agreement and the parameters of the property transferred under the mortgage. It has the property of negotiability, can be transferred by endorsement and can also be the subject of a pledge.
Collective investment is a form of investment when the funds of several investors are combined into a cash share and transferred to a manager for the purpose of investment. The founder of a mutual investment fund, that is, the investor, owns part of the property, documented - this is an investment share.
An investment share is a registered asset. Secures a monopoly on the property of the unit holder over the share of the property of the mutual fund. The fund is distinguished by its type, method of management and specialization and consists of property that is transferred by shareholders to the company manager for trust management.
As a financial instrument, it is optimal for those investors who have a small amount and are ready to invest for the long term.
A mortgage participation certificate is a type of document in the field of mortgage lending. Certifies the existence of ownership of a certain part in the common property under the mortgage. The right to own it also regulates the receipt of funds for fulfilled obligations required by the terms of the mortgage coverage.
A bill of lading is a maritime transport document on the basis of which goods are transported. A kind of sea waybill, which is accepted in international maritime transport, its use is caused by the need to carry out operations with the transported cargo while the ship is making voyages. A bill of lading is a registered type of security and is most often issued in the name of the ship's captain.
A bond is a type of debt obligation that secures for the owner the opportunity to receive annual income or property equivalent to the value of the income.
Essentially, it is a type of loan that is provided to a borrower by an investor. The borrower can be both corporations and the state. The interest, or face value, indicated on the bond is repaid by the issuer within a strictly established period. After redemption, the investor receives a coupon or discount income, so bonds are divided into coupon and discount.
By type of issuer there are:
- state - issued by the state;
- municipal - issued by local governments in order to finance local programs;
- Corporate bonds are created by businesses and companies.
An issuer option is a kind of contract for the acquisition of the right for the buyer to carry out financial activities during a certain period, therefore it is an urgent repayment type. The option is considered exercised if the acquisition is successful.
A simple warehouse receipt is a marketable type of asset that confirms the fact that the owner’s goods are stored in the intermediary’s warehouse. The denomination is a product that is in a state of alienation during storage.
Double warehouse certificate – differs from a simple one by the presence of a second part or a certificate of pledge (warrant). The owner most often needs the second part to receive a loan for the goods. In this case, the warrant is transferred to the lender and returned when the collateral is repaid. Both parts refer to financial documents and give the privilege to each of the owners to dispose of the goods.
Privatization papers - confirm the holder’s right to own part of the property in the process of privatization of state-owned enterprises.
Depositary receipt is a confirmation of the presence of shares issued by a foreign issuer, indicating the purchase of shares abroad, but is issued in the country of the depositor.
A savings certificate is a form of bank certificate, which is evidence of the availability of a freely circulating cash deposit for individuals.
A check is a kind of order that indicates an order for the bank to pay a specified amount to the drawer for the sale of assets within a clearly defined time frame.
Classification and types of securities
Central banks differ in purpose and issuer (those who issued them). Some of them indicate a business investment, while others indicate a bank deposit, while each of them provides the opportunity to receive income or profit in the future .
If we classify Central Banks according to their economic essence, we can distinguish the following types:
- Share papers: they record the relationship of share participation. As a rule, these are shares;
- Debt , it is convenient to consider them as credit instruments. These include certificates, bonds, bills, mortgages;
- Derivatives (such as futures and options). These instruments certify the right to a transaction.
There is a division into:
- Commercial (letters of credit, bills), they are traded on money markets, and are usually valid for a short term;
- Stocks (shares and bonds) are traded on the stock market and are perpetual, or designed for a period of more than a year.
Marketable securities are sold as many times as necessary, non-marketable securities - once.
| Securities (according to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) | Issuer | Properties |
| Government bond | State | An obligation given by the state to the person who purchased the securities. The most popular investment method. |
| Bond | Organization | The same, but the issuer is not a state, but a company. |
| Bill of exchange | Any person | A debt obligation that has the right to collect a fixed debt. |
| Check | Organization | Certifies the right to receive a certain amount of money from the account of the person or organization that issued the checks. |
| Certificate (deposit, savings) | Bank | Issued to a legal entity, certifying its right to withdraw the deposit after a certain period. |
| Bill of lading | Any person | Fixes the right of the owner of the security (CB) to claim his own cargo at the end of transportation (sea). |
| Promotion | Organization | Release by emission method. Traded on the stock exchange. The owner receives the right to certain dividends. |
| Privatization securities | State | Special documents could confirm the right to receive some part of state property. |
Example of use on "Secret"
“On October 28, Facebook changed its name to Meta in order to be associated not with a social network, but with a “metaverse” based on VR technologies. The company has not yet managed to change its ticker on the stock exchange, but investors have already rushed to invest in the shares. As a result, they began to buy shares of Canadian Meta Materials, which produces composite materials from metals and plastics. securities rose by 26%."
(From the news that after Facebook was renamed, investors invested in the wrong Meta.)
Securities Market Law
The information that is included in the contents of the Central Bank and its appearance is established and controlled at the legislative level. (Federal Law “On the Securities Market”).
All papers of this type are in any case :
- negotiable and can be a means of payment;
- available on the market. They can be legally bought/sold;
- serial. Securities are issued in whole batches, which allows you to purchase the quantity that is needed;
- regulated by the state;
- liquid (what is this?). This asset can be sold quickly;
- risky. There is a possibility of losing invested money;
- mandatory.
The price of securities is constantly in dynamics, their value is different at different times, which allows you to make money on transactions or long-term investing.
A security differs from a contract
Primary and secondary stock assets
Depending on the type of release, the following classification is distinguished:
- primary or fixed assets, the assets of which are directly property (movable and immovable), money, resources. All assets, except the depositary receipt, are primary;
- secondary - provide the owner with the right to own property, indirectly, through the main stock instruments. These include: warrant, depositary receipt.
A warrant can be either a primary or a secondary document. In the first case, it is a receipt confirming the ownership of the goods in the warehouse. In the second, the warrant gives the right to purchase other bonds or shares.
How to use securities
Investments
One of the main ways to use the Central Bank. The holder receives certain interest and payments, which is a way to earn money . As a rule, investments are made for a long period. The profit from this method of use is not too high, but still exceeds the yield on bank deposits.
Sometimes investing is used to gain a certain influence on a company ; for this, as a rule, you need to purchase a controlling stake of securities in the amount of 51% of the total.
Speculation
A security is bought when the price is low and then sold when the price rises. An interesting and profitable way to make money if you have the ability to determine in which direction the price will move.
Speculation is usually short-term in nature, and the profit from it is higher than from investment.
Business
Often such papers are used to more effectively conduct trade or other business. For example, buying an option on a particular commodity will help hedge risks.
Comparative analysis of financial assets
All types of financial assets can be presented in the form of a general comparative list. The table of types of securities is as follows:
| Type of financial asset | Period of existence | decor | Ownership function | Nature of capital investment | Release form | Type of issuer |
| promotion | no deadline set | varied | personal | shared | emission | bank (corporation) |
| bond | with limited and time frames | any | debt | any | ||
| bill of exchange | official document form | non-emission | ||||
| bank certificate | emission | corporation | ||||
| bill of lading | non-emission | |||||
| mortgage | personal |
To decide on an investment, it is worth considering securities from a risk factor perspective . Profitability is also important:
| Type of Central Bank | Investor's goal | |||
| Security level | Profitability | Cost growth | ||
| bonds | short-term | great | most stable | slow |
| long-term | good | stable | differently | |
| stock | privileged | high | good | variable |
| ordinary | bad | hesitates | the fastest | |
| bills | simple | above average | increased | absent |
| translated | ||||
| certificate of deposit | great | high | doesn't have | |
| futures | negative | sustainable | fast | |
conclusions
All the securities described in the article are most typical and widespread in countries with high performance market economies. This allows us to conclude that the growth and value of financial assets in Russia will only increase. It is also worth noting that the classification of securities is a very complex and multifaceted process. It is impossible to cover all the forms inherent in financial assets within one article, therefore only the most popular and well-known types of assets were touched upon.
What function does the Central Bank of the Russian Federation perform?
The Central Bank of the Russian Federation has clearly defined functions in the state market. valuable papers. Thus, he is entrusted with the role of the General Agent for servicing issues of state-level Central Banks. Supervises and controls the market. Performs financial settlements on transactions using securities. As a dealer and regulator, it conducts financial and credit policy operations.
The central bank issues securities