A newcomer to the topic of cryptocurrency faces many questions: what is Bitcoin, how to use it and store it, what does Bitcoin look like and what is needed to buy it. In this article we will talk in detail about the most popular cryptocurrency in simple language.
Images of popular cryptocurrencies in the form of coins
Strictly speaking, any cryptocurrency does not have a real physical medium. This is its main difference from the currencies we are used to, such as the ruble, dollar or euro (they are also called fiat). Therefore, Bitcoin is not a coin or a banknote. To understand what it is, let’s briefly talk about the essence and functions of cryptocurrency.
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a peer-to-peer payment system that uses cryptographic methods, and at the same time, data on transactions within it is publicly available to all participants. A more detailed description can be found on Wikipedia. The BTC cryptocurrency of the same name exists only on the Internet, in digital form, but it can be converted into any real (fiat) currencies. In simple words, Bitcoin is a digital currency and payment system that is not centralized (like in a bank), and lives through the work of many computers connected to the blockchain network (we will talk about it below).
What happens after mining 21 million Bitcoin?
Analysts say: when the last Bitcoin gets its owner, the miners will not turn off the equipment. On the contrary, they will continue to process transactions. Then it is not the Bitcoin network that will pay the reward, but the users - in the form of a commission. Naturally, by then it will increase.
They also suggested that by 2140 it will be possible to re-mined coins that were previously lost, are in wallets with forgotten passwords, or are on destroyed equipment.
According to Satoshi Nakamoto himself, by that time Bitcoin will become a means of transnational payments. Commissions will ensure the operation of the network, and the reward for the mined block will come to naught.
Who invented it?
Bitcoin is the first cryptocurrency, which appeared only in 2008, but the principles of operation of such electronic money were invented long before that, in 1998. At the end of the tenths of our century, the project was introduced by Satoshi Nakamoto. Subsequently, it turned out that this was a real figure, but in addition to him, several other developers participated in the creation of the project.
Satoshi assured the public that development began back in 2007, and the team presented a full-fledged working version of the client only in 2009. Leading financial analysts are confident that cryptocurrency, together with Bitcoin, not only does not die, but will determine the development of the global electronic economy for decades to come.
History in dates:
- On January 3, the system began working in test mode - the creators created an initial block and 50 coins.
- January 12 is the date of the first transfer between users.
- The first real exchange of BTC for real currency occurred in September of the same 2009 - approximately five thousand units were exchanged for 5 US dollars.
- May 2010 is the date of an event that would later be called one of the most unsuccessful investments in the history of cryptocurrency: an American paid with bitcoins (10,000) for two pizzas delivered to his home.
Since then, BTC has gone through many changes in its value, periods of rise and fall, but most importantly, it has created a real cryptocurrency fever on the Internet.
2008-2011: Satoshi Nakamoto appears on stage - and leaves it
In August 2008, the domain bitcoin.org was registered on the network, and soon a description (White Paper) of the Bitcoin cryptocurrency was published on it.
A certain Satoshi Nakamoto was listed as the author, and his email address was also indicated. Soon information about the project began to circulate in mailing lists and forums of cryptography enthusiasts. Source: bitcoin.org
In January 2009, the Bitcoin network was launched and Nakamoto mined the first block of the blockchain. During this early period, Satoshi actively exchanged messages with other developers and collaborated with them to improve the software for the network nodes.
In mid-2010, he sent the Bitcoin source code to programmer Gavin Andersen and transferred rights to the domains to a number of prominent members of the Bitcoin community - and stepped away from participation in the project. His last emails are dated April 26, 2011. After that, silence.
By the way, before his disappearance, Nakamoto removed his name from the copyright field in the Bitcoin software, that is, he refused the copyright on the source code, transferring it to the developer community. He really left - and, unlike Carlson, he did not promise to return.
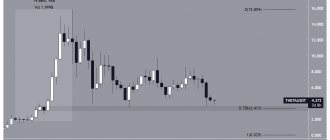
Bitcoin rate for all time
As you can see, at first the Internet community, and especially financiers working with real currency, did not take the crypto coin seriously. The computing power of computers was extremely ordinary - at the end of the 2000s, when Bitcoins appeared, such a stir simply could not have arisen.
In the first year after launch, they cost an insignificant 0.003 US dollars - such ridiculous amounts, of course, did not add confidence to the new currency. In 2010, the novelty had already reached the half-dollar mark - some real world currencies are worth less relative to the dollar. Then there was an exceptional increase in the value and popularity of the cryptocurrency.
Dynamics of the Bitcoin exchange rate against the dollar for all time
It took a very long time before BTC began to be worth any significant money, but the pace of its growth amazed analysts and forced people knowledgeable in the Internet economy to buy cryptocurrency with all available funds. In just a year, the price has risen 20 times - from 0.50 dollars to a full 10 dollars. This rate lasted until 2013, when Bitcoin rose incredibly in price (up to $600) and caused a wild stir around itself.
Due to the rising cost, novice miners began to buy mining equipment and inadvertently brought down the market for video cards - after which they increased significantly in price.
The very next year, 2014, the currency collapsed by half ($310) and remained at this level until approximately 2015 ($360). Then something happened that no one expected from Bitcoin so soon - a second colossal jump in price.
If in 2016 the price reached a thousand dollars and made brokers incredibly happy, then already in 2022 they were in for an incredible turn of events. Bitcoin officially soared to $19,000, and in the next 2022 it collapsed to $3,300. Now the rate is approximately $8,400 and it is almost impossible to predict where it will go next. Such jumps make the exchange incredibly potential, but also very dangerous. During each of the currency collapses, one could observe those who were completely burned out in their quest to make money.
/cc/ - Cryptocurrency
We trade ALGO.
In previous episodes: >>437847 (OP) Summary: We fished the bottom and successfully caught it for $0.560 . There was a pump that gave $0.883, but not a dollar. Next, we encountered a correction at $0.680, which we then carried out to $0.880 - again not a dollar and, moreover, a conditional lower high. What does this mean? For now, only about the good things: a correction awaits us, possibly a protracted one, after which we will finally take $1 .
This is a technical analysis thread where we mainly focus on
dynamic price levels , which we usually denote with a round number, for example, 0.680, while the expected closing price range for the level is approximately: “a quarter of a percent down and half a percent up,” that is, 0.678 - $0.683, tails can extend up to half a percent up and down.
Other methods of analysis are also welcome, as long as they are more than: “here is an inverted cup with a handle as part of the head and shoulders inside a bearish flag... and there is no rising wedge.” Our trading time range : something between swing trading and slow day trading: trades with a weekly outlook, but we can make several small transactions during the day.
Along the way, we also give an assessment of the state of Bitcoin, aka BTC, aka grandfather, he’s not dead yet. We do not trade it, but look at it as a market thermometer, but the analysis is still useful for those interested.
We maintain trading hygiene - we set a stop loss and understand that trading is always about guessing the outcome of an uncertain process. We formulate theories, and the course either confirms them or destroys them. Mistakes, failures, if there are no more successes and accurate hits - this is part of trading.
Now we wish everyone good luck in trading!
Missed 490 posts 37 with pictures. 2ch.hk
How does Bitcoin work and what is blockchain technology?
Cryptocoins exist only as records in the blockchain system (block chain), which stores information about all transactions and addresses in unencrypted form. However, there is no data here on how much digital money belongs to a specific user (address owner).
Addresses are generated using a pair of cryptographic keys and contain information about the balance of their owner. Any user can create an unlimited number of addresses. Those that have a non-zero balance are recorded in the transaction block chain (blockchain).
So, the address consists of a public and private key. The public key is public, and with the help of the private key, the owner gains access to his wallet and the bitcoins in it. Both keys are interconnected, and the private key decrypts the public key, allowing the owner to complete the transaction. If you lose it, then the ownership rights to the cryptocurrency will be irretrievably lost.
So, in 2013, one British owner of 7.5 thousand bitcoins, which he purchased in 2008 for ridiculous money, learned about a sharp jump in the rate. He spent a long time looking for his discarded computer with a hard drive on which that same ill-fated private key was stored. Its owner then threw away $7.5 million in the local trash, which he greatly regretted.
The blockchain system consists of a chain of blocks, which, in turn, are built from individual transactions. After the block is filled with the required number of operations, it is closed (it cannot be modified any more) and sent for verification. Verification consists of approving transactions within a block. If everything is in order, the cycle ends and the block becomes part of the chain, while users are already busy generating a new one.
The validity of Bitcoin directly depends on the amount of resources (time and electricity) invested by users in the blockchain, therefore the “length” of the chain is constantly changing upward. The more coins, the more difficult it is to mine them, so the mining process becomes more expensive and complex.
Three candidates for the role of Satoshi
Perhaps the most intriguing thing about Nakamoto is that he may have been a well-known member of the crypto community who skillfully hid - or is still hiding - the fact that he invented Bitcoin. The debate continues, but the two names that come up most often are Hal Finney, Nick Szabo and Craig Wright.
Nick Szabo (b. B) is the creator of the concept of smart contracts and the early cryptocurrency BitGold (2008), which, however, never saw the light of day. Many similarities have been noted in the style and spelling of the texts of Szabo and Nakamoto. However, Szabo is more of a researcher and academic, and the Bitcoin code was clearly written by a very talented programmer. That is, Nick Szabo would need an assistant. True, he himself denies that he is Nakamoto.
Source: CoinDesk
Hal Finney is a game developer, a prominent member of the cypherpunk movement (cryptography fans), and one of the first to pay attention to the information about Bitcoin in the mailing list. Finny became the recipient of the very first BTC transaction - 10 bitcoins from Satoshi Nakamoto. Also published were emails exchanged between Finney and Nakamoto.
Unfortunately, in 2014, Finney died from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (Lou Gehrig's disease). In one of his last posts on the Bitcointalk forum, he wrote that the true identity of Satoshi Nakamoto remained a mystery to him.
Source: Kriorus
Craig Wright - we already wrote about Wright in one of the previous articles. Unlike Sabo and Finny, he just claims and insists that he is Satoshi Nakamoto. Wright even registered copyrights on the Bitcoin White Paper and the cryptocurrency's source code. However, so far he has not provided any evidence, and a number of famous personalities have openly called him a liar and a fraudster, including Ethereum creator Vitalik Buterin.
To be fair, Gavin Andersen, to whom Nakamoto gave the source code in 2010, has long believed that Wright is Nakamoto, and said that Wright proved this to him privately. But Andersen eventually admitted that he was most likely deceived.
Source: Financial Times
By the way, Wright is the main inspirer of the Bitcoin Satoshi Vision (BSV) cryptocurrency, which is designed to bring to life “Satoshi’s true vision” (as opposed to the functionality of the current version of BTC and Bitcoin Cash that allegedly distorts his plan). At the moment, there are only about 200 nodes in the BSV blockchain (Bitcoin has over 83,000), and recently trading in this coin was blocked on a number of crypto exchanges due to code vulnerabilities.
How to mine Bitcoin and what are farms?
Mining occurs as follows: the user provides the resources of his equipment (computing power) and electricity, for which he pays. The computer solves problems that are sent to it by the system, and in return its owner receives conditional bitcoins (to a pre-created wallet and address).
Cryptocurrency is accumulated in unlimited quantities, and after a few months you can accumulate currency for exchange, provided you have a computer with a powerful video card (or a farm) and are willing to pay electricity bills.
With the growing popularity of Bitcoin, illegal mining became increasingly known - miners, realizing how much they would have to spend on electricity, connected directly to city or public networks, causing huge losses to the state or private enterprise.
Bitcoin farms are a network of interconnected computers or servers, all of whose resources are dedicated to mining. Farms are also called a collection of powerful video cards connected to one or more computers. In addition to video cards, specialized devices can be used - ASICs, the cost of which ranges from 1000 to several tens of thousands of USD.
The miner receives a commission for creating a new block in the blockchain. At first the reward was 50 bitcoins, in 2012 – 25, in 2016 – 12.5. This happens because every 210,000 blocks the size of the block reward decreases by 2 times, exponentially.
Once the blockchain reaches 21 million bitcoins, the emission of cryptocoins will be completely completed and mining will stop forever. This is done to avoid inflation.
When was 50% of the total BTC emission mined?
After the success of the first transactions, the price of the first cryptocurrency began to grow rapidly. The community grew exponentially. As a result, by 2012 the rate of one coin reached $7.50 - an increase of 75,000% in 2 years.
By that time, half of the total issue had already been produced. As a result, there were about 10.5 million bitcoins in circulation. Many investors believed that the potential of cryptocurrency had been exhausted. Its high current rate was explained by hyper-interest in the new product.
Around the same time, a series of curious events occurred. For example, an early cryptocurrency user bought two pizzas for 10,000 BTC (about $470 million at current exchange rates). Another case: a UK resident threw away a hard drive with 7,500 BTC. The owner later searched for it in a junkyard and said he would buy the Lamborgini if the search was successful.
There is also a known case where a man stopped mining in 2011–2012. He did this because his girlfriend was bothered by the noise of a running PC. As a result, the couple broke up anyway.
What is a Bitcoin address and Bitcoin wallet?
Above we talked about keys – private and public. So, a public key is a wallet address that can be passed on to other people so that they can send money to it. It consists of a unique set of characters - letters and numbers.
To use any currency online, you need a special wallet - a conditional place where the currency will be accumulated. There are a lot of services where you can create a wallet. You should choose among them very carefully, because among trustworthy online storages, protected by passwords and privacy rules, scammers are always hiding.
You need to hide your private key. Without this identifier, it is impossible to make transactions with Bitcoin.
This aspect of working with cryptocurrency will be clear to anyone who has ever dealt with electronic money, exchange and withdrawal. To make money on Bitcoin, you will need a wallet and address first.
Matbea wallet – exchange, storage of cryptocurrencies
Matbi is a wallet for storing and exchanging bitcoins, Zcash, litecoins, Dash, rubles. Here you can buy and withdraw cryptocurrencies at the most favorable market rates. There are no fees for exchanging BTC. The Matbea.com exchanger operates automatically, so it only takes a few minutes to process applications. Using the wallet is easy: you can make online purchases from your browser in 1 click.
Wrart.ru together with Matbea is giving 300 bonuses for registering using the link. 1 bonus = 1 ruble. Those. you receive 300 rubles 24 hours after you register and log in to your personal account.
What are Bitcoin faucets?
These are sites where satoshis (very small parts, approximately 1/100,000,000 BTC per hour or ten minutes) are distributed to users for performing simple operations - following links, deciphering captchas, etc.
The organizing site lives off the percentage that the user keeps from each deduction, so each faucet tries to gain as large an audience as possible. Bitcoin faucets are a harmless phenomenon. It is extremely difficult to earn a lot there; you will have to wait a very long time or continuously sit on several taps for days, turning this into your main income, which is definitely not worth doing. The main audience of such sites are users who have heard about cryptocurrency and its prospects, but are afraid to go to the stock exchange or do not want to deal with incomprehensible schemes.
Where can I buy?
You can buy Bitcoin and make money on it by reselling it when the price rises. You can both win significantly (here it is worth remembering the giant leap of this cryptocurrency in 2017) and lose – there have been enough falls. You can buy BTC:
- In online cryptocurrency exchangers . These are sites that exchange fiat money (rubles, euros, dollars, etc.) for bitcoins and vice versa. You can make an exchange from a bank card, electronic money like Webmoney and others, a mobile phone account and even cash (if the exchanger has an offline office or a courier who will pick up the cash from the client). Examples of reliable exchangers: Baksman, ProstoCash, PayBTC.Pro.
- On cryptocurrency exchanges . Exchanges typically charge a percentage for deposits and withdrawals of money from/to a trading account, as well as for each transaction of buying and selling bitcoins. Therefore, it is profitable to buy crypto coins here only if you know how to analyze the market, predict where the price will go on the chart, and make a profit on the exchange rate difference, taking into account all commissions. The best exchanges according to various ratings are Binance, EXMO, Bittrex, Bitfinex.
How to choose a reliable exchanger:
- Take advantage of exchange monitoring services. Fraudulent exchangers cannot access such sites, and if this happens, they are immediately deleted.
- Check for technical support, feedback, read reviews.
At the moment, there are dozens of exchangers where you can quickly and safely buy Bitcoin for any currency, and they can be found on the same Bestchange.
Advantages and disadvantages
Bitcoin is an amazing financial phenomenon of the last decade, and you can really make money on it by mastering the principles of accumulation and resale.
Pros:
- developed infrastructure - BTC can be easily exchanged, there are a lot of exchangers and crypto exchanges around the world;
- the finite nature of mining, which is why cryptocurrency is not subject to inflation (although other factors can cause a decrease in value);
- a well-promoted brand - Bitcoin is easier to sell than one of the little-known cryptocurrencies;
- anonymity (subject to all technical nuances, for example, when using proxies and other techniques in combination).
Minuses:
- low transaction speed – from 10 minutes to days;
- instability of exchange rates, strong fluctuations;
- Theft of funds from wallets is possible due to their insufficient security.