Venture investments are investments in promising companies and projects from the moment of their creation to the issue of securities on the stock exchange. As a rule, venture companies include enterprises with the prospect of growth to the level of large businesses. For example, an innovative restaurant chain or a new social network may be one of them, but, say, a small stand-alone convenience store is unlikely to be.
Investments in venture capital companies are associated with increased risks, but if successful, they provide a chance to earn truly large profits. To achieve this, you need to choose both a successful and innovative young company that offers the market something fundamentally new.
Concept and main features
Venture capital is a risky investment. This is how it is translated from English. These are investments in projects that offer products and services that have no analogues in the world. Business can belong to completely different areas of the economy. They have one thing in common - an innovative idea that can change the world, or at least a single industry.
Projects that offer an innovative idea, high potential profitability and the risk of loss of capital are called venture projects. And the people who are not afraid to invest money in them are venture investors.
Why are such investments considered high-risk? Imagine that you, your parents, grandparents and several other generations of relatives have used candles to light up your room all your life. Suddenly an eccentric appears who shows you some glass object and claims that its effectiveness and safety are many times higher. But you need a couple of million to launch the project.
Are there many people willing to finance the idea? However, it is precisely such enthusiasts among the generators of ideas and their investors who are an integral part of scientific and technological progress.
Here are just a few examples of venture projects:
- Google. Initial investment – $100 thousand, market capitalization as of September 2022 – $1.03 trillion.
- Facebook. Initial investment – $500 thousand, market capitalization as of September 2022 – $758.21 billion.
- Apple. Initial investment – $150 thousand, market capitalization as of September 2022 – $1.961 trillion.
It is now clear why investors who once invested in the innovative ideas of these companies do not leave the Forbes list of the richest people.
Venture investments have features compared to direct investment in the activities of an enterprise:
- High risk and no guarantee of profit. This is understood by both parties to the venture transaction – the investor and the project initiator.
- Long payback period - sometimes it can be more than 5 years. As a rule, financing begins at the research stage, then the project is implemented, the business expands, and it enters the stock market.
- Investors are interested in the success of the project, so large investors often act as business development consultants.
- It is not so much the enterprise that has value as the idea itself and the people who propose to implement it. Mark Zuckerberg did not have a profitable business in which large investors would like to invest. But he had a project that seemed promising to some.
- The investor receives a share in the business and makes money on the difference between the purchase and sale prices of shares. It is also possible to further participate in the company’s activities in order to receive dividends.
What is venture capital
Venture capital represents money invested in projects or companies experiencing funding difficulties. As a rule, these are newly created enterprises, startups, new projects. At the initial stage, the company has no revenue, and banks refuse to provide a loan, since the company has not yet developed a history on the basis of which it can be concluded about its financial solvency. This is where investors come to the rescue. Since there is no history, there is no data for analyzing key indicators, such investments are usually called venture investments (from the English venture - adventurous, risky).
Who are these adventurers? As a rule, these are large, world-famous investors who invest capital in several new projects, some of which cease to exist in the first couple of years after their creation. Other projects, on the contrary, bring high income.
Most often, the concept of “venture capital” is associated with investments in technology. This is not entirely true - investments in any startup can be considered venture capital.
Venture investment is a kind of lottery when you have to guess the potential of the company. Some investors use different business models, while others are just guessing. Why do they need this?
Firstly, if you hit the mark, investments provide super-profits. Secondly, this kind of investment brings the investor fame and glory in business circles. For people whose capital amounts to millions and billions, the desire to become famous and receive, in addition to profit, a share of power comes to the fore.
Participants
Participants in the development of a startup can be both private and legal entities. In some cases, the chain only includes the investor and the company. Venture funds participate in financing large projects.
Complete information about current strategies that have already brought millions of passive income to investors
Investor
Private investors who act on their own behalf are called business angels. They provide not only financial, but also expert support to the startup, because they have experience in management and entrepreneurial activities.
As a rule, they come into play at the initial stage. At this time, the project cannot yet attract the interest of major players, but through private investment it gets a start in development. The main characteristic feature of business angels is personal interest in the proposed idea.
Such world-famous corporations as Apple, Amazon, Microsoft, Intel, Dell, Google, etc., began their ascent to Olympus with investments from business angels.
In addition to private investors, the following can participate in financing venture projects:
- banks;
- government agencies;
- scientific institutes, etc.
Venture fund
A venture fund is specifically created for the purpose of searching for new ideas in the market and investing in high-risk projects. Unlike private investors, it can attract larger amounts for financing.
The importance of such funds for the development of the economy of any country is enormous. They participate in the development of innovative projects that cannot obtain financing from banks or other sources. And the successful implementation of an idea takes the economics of a particular industry to a completely new level.
The Foundation is a team of professionals that evaluates the prospects of a project. At the same time, she is well aware of the risk of loss of capital. The fund is not a lender, but a partner who is no less interested in developing a new business than the project initiator.
Venture company
Venture capital firms are companies that bring new technologies or products to market that have never existed before and need capital. They cannot provide potential investors (banks, investment funds, etc.) with a detailed business plan with detailed cash flows and calculations of performance indicators. They consist of a team of enthusiasts who have brilliant ideas in their heads, but often have no entrepreneurial experience.
These are the companies that business angels and funds are looking for to offer them financial, legal and other expert assistance. Together they begin to work towards achieving common goals - to bring an innovative product/technology to the market, conquer it and make money.
Statistics show that the most popular companies are from the fields of IT technology, healthcare, trade and transport.
Story
To understand the essence of investing in startups, here are some historical facts.
The Origins of Modern Venture Capital
Lawrence Rockefeller
Many people know the name of Lawrence Rockefeller, who invested in the new airlines Eastern Air Lines and Douglas Aircraft. This happened in 1938. At that time, the Rockefellers were one of the richest families in the United States and throughout the world. Another example is the creation by the Wallenberg family of the company Investor AB, which invested capital in such large Swedish projects as ABB, Ericsson, etc.
Thus, in the first half of the last century, venture capitalism was a hallmark of the richest investors who were willing to risk their money for fame and super-profits.
Jacques Doriot, who created the ARDC company in 1946, is rightfully considered the founder of venture capitalism. This company attracted investment not from the rich, but from other volunteers. Small private investors invested in businesses run by military personnel returning from World War II. Thus, in 1957, Digital Equipment Corporation was formed. Subsequently, former ARDC employees founded several venture capital companies. Examples: Greylock Partners, Fidelity Ventures, etc.
Early venture capital and the development of Silicon Valley
Silicon Valley is the area of California where the bulk of venture capital funds are concentrated. In 1962, Draper and Johnson was founded. At the same time, a form of direct investment with a ten-year cycle appeared, providing passive investors with up to 20% of income.
Between 1968 and 1980, companies were created in Silicon Valley that are still operating today:
- Mayfield Fund;
- Patricof & Co;
- Melno Ventures;
- Sevin Rosen Funds and others.
Why was Silicon Valley chosen as the base for creating venture funds?
The valley got its name in 1971 when the first microcircuit using silicon was developed by Robert Noyce. Subsequently, the silicon-rich territory began to attract engineers and entrepreneurs from all over the country, and then the world.
1980s
Since the late 70s of the last century, the main areas of interest of venture capitalists have been computer and medical technologies.
This period is characterized by a decline in private equity investment. There were two reasons:
- increased competition from firms from Japan and Korea specializing in computer technology;
- stock market crash of 1987.
Where to find startups to invest in
To invest in startups, a private investor who is not burdened with hundreds of thousands or millions of dollars can be recommended to look for such projects on crowdinvesting platforms or participate in IPOs. Many of today's large and well-known brands began their ascent with a modest couple of thousand dollars from friends and acquaintances.
Crowdinvesting platforms
Crowdinvesting is a special collective investment platform where those wishing to invest money in risky but promising projects and companies in need of initial investments meet.
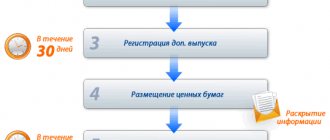
The platform acts as an intermediary. It conducts a preliminary selection of projects and provides investors with access to information:
- amount of investment;
- project implementation period;
- information about the initiator and his team;
- description of the project (idea and ways of its implementation);
- procedure for settlements between the parties.
The crowdinvesting platform has certain requirements for project registration. There are quite a lot of them on the Internet, so you first need to study the rules of the game for each of them. There is no guarantee of a refund, but sites develop their own selection systems, so completely hopeless projects do not go through it.
Examples of crowdinvesting platforms in Russia:
- AtomInvest was created with the support of Rosatom to search for new ideas and projects that can subsequently be integrated into the Rosatom State Corporation system. More than 120 million rubles have already been issued. with the participation of 2,500 investors. Investments are available from 10,000 rubles.
- “City of Money” has been operating since 2012. The minimum investment amount is 50,000 rubles. The percentage of overdue debt is 4.6%. He is a member of the working group at the Competence Center for regulatory regulation of the digital economy of the Skolkovo Foundation and the working group of the Central Bank for the regulation of crowdfunding.
- StartTrack. Investments from 100,000 rub. Almost 3 billion rubles have already been raised. The creation of the platform was initiated by the Internet Initiatives Development Fund; funding was provided from public money. Since 2013, it has attracted investments of more than 3 billion rubles.
To minimize the risk of investments, investors, as a rule, invest not in one, but in several (5-20) startups at once in small amounts.
More than 100 cool lessons, tests and exercises for brain development
Start developing
IPO
I provided this source for searching for venture projects, although it is not directly related to startups. Companies that have already occupied their niche in the market and are in need of additional financing enter IPOs. Moreover, these can be both traditional and innovative enterprises with a completely unique product or service that have passed the first stages of investment and are at the final stage.
Investments in projects do not become any less risky just because they are already at the last stage of venture investment. Therefore, I think that an IPO is a good option for participating in scientific and technological progress.
How to get venture capital
The easiest way to get funding is to apply to a venture fund. First of all, you should take care of drawing up a competent business plan that contains justification for receiving funds in numbers.
The importance of funding
For some companies, venture capital financing is the only solution to launch a business and achieve financial sustainability. In the 21st century, this type of financing is quite popular. Thus, in the United States, the revenue of companies using venture capital amounts to more than 20% of state GDP.
Stages
Let's consider the stages of investing in high-risk projects.
Stage 1. Pre-sowing (preparatory, pre-start). Involves initial marketing research and preliminary economic calculations.
Stage 2. Sowing. Creation of a prototype, testing. More detailed marketing research and assessment of project effectiveness.
Stage 3. Starting. Investments are made into mass production of the product, bringing it to market, and promoting it.
Stage 4. Development. At this stage there is expansion and growth of production. The company has firmly occupied its niche in the market, established supplies, and achieved sustainable profits. Investments are needed for further research and product improvement.
Stage 5. Final. Investors receive profit from investing in a business in the form of dividends or selling their shares as the difference between the purchase and sale prices.
Forms of venture financing
Venture capital includes the following forms of investment:
- trade loan with or without collateral;
- factoring;
- bank guarantee;
- bridge financing. This is a type of lending used in cases where the financed company has spent all its capital at the initial stage and is awaiting financial injections from another investor. Bridge financing is carried out in the form of debt obligations (notes).
Advantages and disadvantages
Venture capital is strongly associated with high-risk investments. But this area is growing every year, accepting more and more investors into its ranks. Let's hope that they have all learned the basics and intricacies of such investing, its advantages and disadvantages.
For the investor
Pros:
- return on investment can reach hundreds of percent per annum, which is incomparably higher than the return on other investment instruments;
- the period for making a profit can be extended if you remain the owner of the company and do not sell your stake;
- psychological moment - the investor will become involved in the creation of a unique innovative product (agree, it sounds when you say that you were at the origins of the creation of Apple or Google);
- the opportunity to apply your management and entrepreneurial skills by advising start-ups in their infancy.
Minuses:
- high risk of loss of invested capital;
- long payback period, because the period from the inception of an idea to its implementation on an industrial scale can be more than 5 years;
- a large entry threshold (for business angels it is measured in hundreds of thousands of dollars), small amounts can be invested mainly only on crowdinvesting platforms, but for diversification you need to select not just one, but several projects;
- It’s easy to fall for scammers, especially if you invest directly.
For business
Pros:
- companies find money to implement ideas for which they would never receive a bank loan;
- there is no collateral or guarantee, as with bank lending;
- receiving expert advice from business angels or a venture fund team;
- startups share the risk with their investors, and together they share the profit if they are successful.
Minuses:
- as a rule, investors not only want to invest money, but also to participate in the management of the company;
- the search for an investor can last for months and years; in Russia this area is poorly developed compared to Western countries.
Investment objects
Objects for placement of venture capital are:
- Newly created companies.
- Undervalued companies.
- Companies experiencing difficulties with financing for various reasons (wrong business practices, raider takeover, pressure from competitors, litigation, etc.).
- Startups.
- Innovative solutions.
- Business ideas.
Taking risks together
The third working and popular option is syndicates in the early stages. They exist with both crowdfunding platforms and seed funds. This way you can conduct syndicated deals together with Angellist or choose someone from domestic investor clubs. If there are high risks at the seed stage, this option provides access to higher-quality startups. Both syndicates and clubs reduce risk by allowing you to invest with professional investors. Of course, this will cost you additional costs - usually administrative and legal fees, tax fees and success fees.
The perfect storm
In dollar inflation, a perfect storm emerged when several reasons overlapped each other at once. In addition to long-term quantitative easing, the following drivers were added to the process: the disruption of global supply chains due to the pandemic and the resulting shortages of goods and rising prices for them, the accumulation of excess savings among citizens due to generous benefits, the phenomenon of early mass retirement generated by the pandemic and the resulting rise in wages, rising energy prices - partly due to underinvestment in previous years, partly due to the ESG agenda. Some of these drivers will go away with the pandemic, but some will remain after.
Inflation can be curbed by a sharp rise in rates, but this could throw economies weakened by Covid into recession and make servicing government and corporate debt problematic. This cannot be allowed, as China continues its “offensive” and threatens to seize global dominance. It turns out that rates cannot be raised significantly either. The situation is stalemate, but one way or another, the decision to raise dollar rates is overdue, and it will have to be made, otherwise the entire developed world will have to remember that inflation has such bad epithets as “galloping” and “hyper.”
Material on the topic
For a time, developed countries were able to export inflation to developing economies, seriously weakening local currencies. Central banks of developing economies responded by raising rates, but now the Fed, ECB and Bank of England unanimously announced the winding down of monetary support measures and raising rates. The Bank of England has already raised the rate from 0.1% to 0.25%.
These trends will also affect the venture capital industry, which is expected to mature and become more complex.
Alternative assets
Many classes of traditional assets consistently show negative returns (especially currencies, bonds, shares of the “old” economy), and this fact forces managers to look for investment points for capital in alternative classes. Large capital has experienced significant migration over the past two to three years. Investments in shares of private companies, LBO operations (acquisition of a controlling stake in a company using borrowed funds), shares of startups, non-bank credit instruments, cryptocurrencies and crypto-assets have increased multiple times. Venture investing is experiencing a real boom, because previously one could not even dream of such an influx of liquidity. Nowadays the most fantastic ideas and directions are generously funded.
Principle of operation
The work scheme boils down to the following points:
- Company employees find potentially attractive companies or consider an application from the project initiator (startup owner).
- A comprehensive analysis of the project is being carried out.
- Capital is generated for investment in the approved project.
- Funds are invested in the project. At this stage, documents are drawn up that establish the responsibilities of the parties and the degree of participation of the management company (fund management) in the activities of the financed organization.
In the future, if necessary, the fund invests additional funds in the project at different stages of its development. For several years, management monitors the activities of the funded organization.
As soon as the profitability of the project reaches its maximum value, the venture fund sells its own share.
Industries of the future
In the industrial context, attention is drawn to projects around the metaverse, crypto-assets and related services, space, and new fintechs. It will also be necessary to look at the direct beneficiaries of inflation, including among the underinvested sectors of the “old” economy. For example, this could be the production of durable goods, as well as resources in demand in the new economy, for example, those associated with the production of components for electric batteries and cars: lithium, graphite, manganese, cobalt. As internal combustion engines are replaced and the overall energy transition continues, the demand for new materials will only increase.
So in the coming years, the alternative investment industry will continue to receive large amounts of capital under management, but it will also become seriously more complex in terms of tools, geography, industrial specialization and requirements for asset managers.
Large industrial company, corporation, holding
Why do they need this? A corporate venture investor enters the market for the following reasons:
- Availability of sufficient capital.
- Stable but insufficient profitability of your own business (average or below average).
- Possibility of using your own innovative developments.
- Limited opportunities for business development in your own and related segments (geographical and industry). High competition. The impossibility of extensive growth through the absorption of competitors.
Examples
Examples of venture financing include such big names of companies as Apple, Tesla, Intel, etc. There are other examples.
So, in 2009, former Yahoo employees invested 18,750,000 rubles. ($250,000 or UAH 7,250,000) to the WhatsApp project, which was recently purchased by Facebook.
In the same 2009, the Russian fund AlmazCapital bought a minority stake in Yandex, which was sold to Yandex NV 3 years later. The profit from the deal was more than 1000% (about $4.5 million).
In 2011, the American fund Benchmark financed Uber and eBay and received super profits.
In 2012, Facebook bought Instagram, founded in 2010 by Kevin Sister and Mike Krieger, for $1.1 billion.
Alternatives to Venture Capital
Venture funds have fairly strict requirements for the source of funding. Therefore, some are private investors. Strictly speaking, a business angel is also a source of venture capital, but it will not require as much financial documentation as a fund.
Another alternative is buyer financing. Sometimes companies offer benefits or discounts to customers in exchange for a subscription or deposit. By purchasing a product or service with prepayment, you become a VIP client and gain certain privileges.
And the third alternative method is crowdfunding (collective financing). This is also raising funds from end consumers, but here they act as investors. Read more in the article “Crowdfunding”.
Geographical differences in venture capital
Let's compare the features of venture capital in different parts of the world.
USA
This is the most extensive venture investment market, where the world's funds are concentrated. Here are some examples: Accel Partners, Sequoia Capital, DCM, etc. Every year, venture capitalists invest billions in new businesses using private equity methods. At the same time, 2/3 of investments come from non-profit organizations.
The largest site is Silicon Valley, located in California. Tens of thousands of specialists work there, whose knowledge allows them to create technologies that are ahead of the future.
Europe
The largest industry for investment is the IT sector. 2020 also saw pharmaceuticals and biotech come to the fore. The European market accounts for 10% of the total volume of venture investments in the world. Sources of investment are distributed as follows:
- 30% – non-profit organizations;
- 20% – private investors;
- 50% – credit organizations.
Russia
There are about 200 venture capital companies operating in the Russian Federation. Examples: Runa Capital, Primer Capital, QIWI Ventures. About ¼ of the funds receive funding from the state.
A considerable share of funds comes from foreign investors. Sanctions have a negative impact on the development of the venture capital market.
In 2022, the volume of the Russian venture investment market amounted to 8.3 billion rubles, including:
- RUB 5.2 billion funds came from foreign investors;
- RUB 3.1 billion - from the state.
Asia
Southeast Asia's venture capital volume in 2022 has caught up with the US market, according to sources. In particular, there are 172 funds operating in China. The predominant industry is biotechnology (HealthCare). The main regions where venture capital companies are concentrated are Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen.
Middle East and North Africa
The venture capital market in the Middle East and North African countries is developing at a rapid pace. Thus, in 2022, the volume of transactions increased by almost 30% compared to 2022. The most actively participating countries: UAE, Egypt, Lebanon. The predominant industry is financial technology.