Bitcoin mining is the main process through which the blockchain exists. This process has several key features inherent in the Bitcoin program code. One of these features is the complexity of the Bitcoin network, which changes periodically and depends on the total amount of computing power of the network. Miners around the world constantly monitor the complexity of the Bitcoin network, because the cost of mining and the efficiency of the equipment used essentially depend on this. But for those who are learning how to trade Bitcoin, information about the complexity will not be superfluous.
Mining difficulty as a limit on emission?
Mining, at its core, is the discovery of a new block in the blockchain chain. To generate a new block, you need special equipment that performs calculations. For this, miners receive rewards. The more powerful and productive the equipment is used, the higher the miner’s income, but in this way it is impossible to generate an infinite number of coins. Their emission is limited; this limitation was initially included in the source code. For example, for the Bitcoin cryptocurrency, the maximum possible emission until 2140 is 21 million coins, but if miners begin to intensively mine Bitcoins, their number will exceed the permissible value by the specified date. To prevent this from happening, emissions must be monitored and managed.
Mining farm on ASIC
Today mining is at the peak of popularity. New, powerful equipment is being developed that is used specifically for cryptocurrency mining. More and more users are interested in cryptocurrency and are starting to mine it. This leads to an uncontrolled increase in emissions. To prevent this and control the number of coins issued, developers use mining difficulty. Opening a new block becomes more difficult, requiring more time or using more powerful computing equipment.
For the Bitcoin cryptocurrency, it is established that it takes 10 minutes to open one new block, regardless of the number of users who will be involved in this process. That is, mining 2016 coins should take 14 days. It is these figures that are taken as the basic indicator.
The algorithm analyzes emissions over 14 days and determines deviations from the nominal indicator. If more coins were minted than planned, the mining difficulty increases.
Today, such situations are becoming more common, as interest in mining grows and more and more users are attracted to cryptocurrency mining. Accordingly, developers need to constantly monitor emission volumes and, depending on this, change the mining difficulty. Production volumes are not constant, they are constantly changing and can increase or decrease. For Bitcoin, recalculation is carried out after every 2016 coins are mined. If this process took less than 14 days, then the complexity increases, if more than 14 days, it decreases. In this way, developers can adjust emissions so that they do not go beyond the target.
Forecast for 2021-2022
In the near future, devices with fundamentally higher computing power are not expected to enter the market, so a global recalculation of the hashrate is hardly possible. Most devices based on this algorithm quickly become outdated and start to work at a disadvantage.
Several episodes of sharp declines in the value of Bitcoin make mining a less popular activity. From a process accessible to every home computer owner, cryptocurrency mining has long turned into a complex business with a fairly high entry threshold. Now this is a network of large organizations that have access to relatively inexpensive electricity. Such companies, thanks to a large number of devices, can mine many coins. For individuals, Bitcoin mining is not a promising business, and its profitability will decrease even more in the future. But you can pay attention to less expensive “secondary” coins, where the entry threshold is lower.
How does changing difficulty affect miners?
Increasing complexity means that calculations take longer to complete. Accordingly, over the same period of time, the miner will earn fewer coins. Although the process can be reversed - if the emission is insufficient, the developers reduce the complexity of mining and the extraction of cryptocurrency proceeds faster, which means that the miner will earn more coins over the same period of time.
Changing the complexity allows developers to make adjustments to emission volumes. Calculations are carried out that show how much the number of actually issued coins per unit of time differs from the planned one. Depending on this, the difficulty changes. That is, if the emission deviation was 12%, then the difficulty will also be changed by 12%.
What affects difficulty?
There are a number of factors that directly or indirectly affect the difficulty of mining. Of these, two main ones stand out:
- network hashrate – shows the total power of the equipment that is used for mining a specific cryptocurrency;
- time to open the previous block of the chain.
These indicators are interconnected. In other words, when one of them changes, the other also changes. An increase in hashrate indicates that the number of users engaged in mining a certain cryptocurrency has increased. This suggests that the total power of the equipment has also increased, as have calculations, and, accordingly, the generation of blocks will proceed much faster.
It means that:
- with an increase in hashrate, cryptocurrency mining occurs faster, which means the difficulty will increase;
- with a decrease in hashrate, cryptocurrency mining is slower, and accordingly, the difficulty will be reduced.
Difficulty is calculated using special formulas. They are based on an equation that shows the relationship between the main indicators.
B=C/X,
Where:
B – time spent on opening a block of the chain;
C – mining difficulty;
X – hashrate.
The base difficulty is one. If it takes 30 seconds to open 1 block, then the calculated hashrate should be 3H. With this figure, equality will remain at difficulty 90.
If we assume that the number of miners has increased and the hashrate has increased to 5, then to maintain equality it is necessary to change the difficulty so that the time to generate the next block is still the same 30 seconds. In this case, equality will be maintained if the complexity is changed to 200 N/s.
This example shows how time to mine one coin and hashrate are related. Changes in any of these indicators will necessarily provoke a change in the other to maintain equality.
But not every cryptocurrency has the same mining difficulty. The more attractive and promising a cryptocurrency is, the more miners give it preference, but there is another side to the coin - as soon as the number of miners begins to grow, and accordingly the hashrate, the difficulty of mining immediately increases.
The hashrate is dynamic and changes frequently, followed by increases or decreases in mining difficulty. These are already established rules, since developers must control the emission of cryptocurrency. If this is not monitored, the consequences can be very unpredictable.
So - the difficulty of finding a block
Let's summarize - the difficulty of finding a block is based on the total hashing power of the network and is adjusted every two weeks to maintain a stable rate of 1 block every 10 minutes. This gives the network time to synchronize and update the blockchain ledger globally and is critical to ensuring the security of the ledger ( orphan blocks reduce the security of the network as they can become invalid even after they have been verified as valid ).
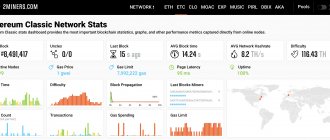
The more miners that join the network, the more aggregate computing power will be spent on finding eligible signatures, and the faster blocks will be added to the blockchain if the difficulty of solving blocks is not changed. Therefore, the difficulty increases when the total hashing power increases, and conversely, when the complexity decreases, the hashing power also decreases. As you can see below, the total hashing power (hashrate) currently stands at 51 billion GH/s. The higher the hashrate, the higher the block difficulty.
Date - Date Difficulty - Difficulty Change - Change Hash rate - hashrate
As illustrated below, block 100 (back in 2009) required a signature that began with only eight consecutive zeros, while the latest block as of this writing (block 542865) required a signature that began with at least 18 zeros. following each other. The number of zeros is what reflects the level of difficulty. Finding output with that many consecutive zeros requires either much more time or much more hashing power. And today, the difficulty of finding a block is much higher, for the simple reason that the Bitcoin blockchain uses significantly more hashing power (due to the increased number of miners).
The difficulty of block 100 was 8 consecutive zeros.
The difficulty of block 542864 was 18 consecutive zeros.
As you can see, the total hashing power on the Bitcoin blockchain in 2022 is many, many times greater than it was in 2009. Quick note: The graph below only shows the ever-increasing difficulty of mining Bitcoin through March 2022, but it has been declining since October 2018, when miners were forced to stop mining because their operating costs began to exceed mining profits as Bitcoin prices fell rapidly.
The difficulty of mining Bitcoin has increased significantly since its inception because more miners have joined the network since then (hash power has increased).
Why do different currencies have different mining difficulties?
The emission and hashrate of each cryptocurrency are different, and accordingly the difficulty of production also varies, but users do not need to carry out the calculations themselves. Today there are special resources that publish important information in the context of cryptocurrencies, including indicators of mining difficulty for each. The calculation is carried out in real time, but it is not entirely accurate, since the hashrate changes quickly, followed by difficulty. Experienced miners use data from multiple sources. They analyze them, calculate the average value, thus obtaining a more accurate result.
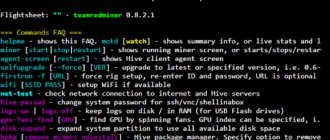
One of the most popular thematic resources among miners is CoinWarz. Here you can find a lot of useful information, including the level of complexity in the context of cryptocurrencies.
The disadvantage of this site is that it does not have a Russian-language version, so users from the CIS countries prefer another resource - Bitinfocharts. If you go to one of these resources and analyze the difficulty for some cryptocurrencies, it becomes clear that:
- Popular cryptocurrencies have a higher complexity, since they are mined by a larger number of users;
- Difficulty is affected by the market value of the cryptocurrency - the higher it is, the higher the difficulty of mining.
What is mining (aka hashing) - let’s refresh our memory
Let's quickly go over this topic again. If you have read my article How Mining Works and How Transactions Are Processed, you already know that a block of transactions will only be accepted by the rest of the network if it has a signature (hash) that meets the established requirements (for example, in the Bitcoin blockchain The block signature must begin with a certain number of zeros). In order to find such a signature, miners spend their computing power (hashing power) on performing many predefined operations on random numbers until they find the required number, which will ultimately lead to a certain output number, which will meet the specified criteria. Finding an output that is a number that starts with only one zero is much easier (and usually more common) than looking for a numeric output that starts with five consecutive zeros (this is quite rare, so you'll need significantly more time to find the desired number, which will lead to such output data).
Why does mining difficulty matter so much?
For miners, difficulty is one of the most important indicators. The number of coins that the user can receive in a certain period of time directly depends on it. The higher the difficulty, the fewer coins, and with regular increases in difficulty, sooner or later there will come a time when the available equipment can no longer cope with the calculations and becomes ineffective. The change in difficulty and earnings are in equal proportion. This means that increasing the difficulty by 10% reduces the miner’s earnings by 10% and vice versa. The dynamics may be different; in some cases, in just a month the drop can be 50% or more.
Mining farm on video cards
But there are other factors that slightly neutralize the impact of complexity on income - this is the cryptocurrency exchange rate. If the difficulty of mining has increased, it means that interest in the coin has also increased. An increase in demand necessarily entails an increase in prices. Yes, with increasing difficulty, the user will be able to mine fewer coins over a certain period of time, but in fiat money their value will remain the same or even increase. Although many experts argue that the connection between the rate and the difficulty of mining is indirect. This means that you should not hope that due to the growth of the exchange rate the negative impact from the decrease in the number of mined coins will be smoothed out.
Quotes are influenced by a large number of factors that do not depend on the issue. That is why their connection with complexity is called strained. Experienced miners do not count on compensation due to the growth of the exchange rate, but prefer to mine several currencies, diversifying risks.
Natural limitation of bitcoin mining
The main limitation of the network is related to the technical equipment used for mining. At first, ordinary computers were enough for users. Anyone could earn bitcoins, but their cost was too low. As the popularity and rate of the cryptocurrency grew, more and more new users began to connect to the system. This increased the difficulty: mining required fast graphics cards. Costs grew, but so did profits.
The races did not stop. The system constantly gained momentum, moving from the category of hobbies into a full-fledged business. Expensive technical means began to be used for extraction: they were more energy efficient and productive. Users were divided into several categories: some had resources to invest (they began to use ASIC modules designed specifically for Bitcoin mining), others began to join pools to achieve any results.
The ratio of the required power, the cost of Bitcoin and income is the natural limiter of the chain. The greater the resources, the higher the return - without a contribution to the system, no user receives unreasonable income.