Proof-of-Stake (PoS) is a type of consensus algorithm through which participants in a cryptocurrency network strive to reach consensus. In PoS-based cryptocurrencies, the creator of the next block is chosen through various combinations of random selection: a period of frozen coins or wealth (i.e. staking).
Simply put, the concept of Proof of Stake (PoS) states that a person can mine or validate block transactions based on how many coins they hold. This means that the more bitcoins or altcoins a miner owns, the more mining power they have.
Simple POS operating principle
This is similar to Bitcoin's Proof-of-Work consensus, in which miners perform expensive calculations using mining hardware to earn coins.
If a user is selected, they will validate transactions similar to how miners do in Proof-of-Work.
Comparison of POW and POS
Proof-of-Stake can be thought of more as a mechanism to resist a Sybil attack, it ensures that the people creating blocks act in the best interests of the network.
Anyone who has followed Ethereum closely is well aware that the community has been pushing to move towards Proof-of-Stake for quite some time.
Features of Ethereum mining in 2022
Initially, the Ethereum blockchain uses the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus algorithm - proof of work. With this mechanism of network functioning, the creation and verification of new blocks occur by solving mathematical problems. This process requires enormous computing power. It can be performed using special equipment:
- processors;
- video cards;
- ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit).
It is worth considering that in this case we do not mean processors and video cards from a regular PC. Such equipment has significantly higher productivity and is created specifically for mining. This technique provides the level of computational processes needed to solve a cryptographic problem.
As soon as the problem is solved, the created block is accepted into the general chain. And the one who managed to get a solution is paid a reward. The same principle of adding blocks is used in the Bitcoin blockchain.
The main disadvantage of Proof-of-Work is that it forces miners to buy expensive equipment. Unlike the BTC blockchain, Ethereum developers have made this process more accessible, since this network uses a slightly different hashing algorithm - Ethash. However, with the growing popularity of the Ethereum cryptocurrency, the complexity of its production has increased significantly, and also requires enormous power.
Today, for mining BTC you need to use only ASICs, and it is advisable to assemble farms from them to obtain a high hashrate. But AMD and Nvidia graphics processors (GPUs) are also suitable for mining coins on Ethereum. So you still have to spend money on hardware.
It should be noted that the mining process in the Ethereum blockchain is gradually ceasing to be fair. Miners with funds to spare buy special integrated circuits designed for ETH mining. This gives them the ability to mine blocks faster than GPU users.
As a result, ordinary GPU miners began to earn less money, and some of them switched to mining other assets. Many users began to express their indignation at the fact that the Ethereum technical document says that the network is resistant to ASIC mining, but in reality everything is different.
The only way to compete with ASICs is to collect farms, which not everyone can afford. An alternative option is to combine your technical capabilities by forming mining pools.
Ethereum transition to PoS
Ethereum developers are aware of the problem with mining difficulty and are planning to replace the consensus mechanism. Around the 3rd quarter of 2022, the Ethereum blockchain will switch to the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) algorithm.
This is an alternative way to add a new block to the chain. When using it, there is no need for powerful equipment - no more complex problems need to be solved. Any users will be able to participate in coin mining, including those with regular PCs or smartphones.
Despite the fact that the difficulties with buying expensive equipment will go away, a new problem will appear - the need to have a large amount for staking and mining, since when using PoS there is a greater chance of mining a block from someone who holds a lot of coins. That is, the share of assets is used as evidence (instead of solving problems). Accordingly, users will now have a new goal: to obtain more Ether tokens to increase their chances of making a profit.
In addition to changing the proof of work algorithm to proof of stake, sharding will appear in the second version of Ethereum. This is the name for dividing a single set of data and storing it in the form of multiple databases. The main advantage of sharding is that it allows you to increase the speed of transactions by 64 times.
The updated network will be called Ethereum 2.0, and validators will take responsibility for its security.
When will Ethereum 2.0 come out and why is a network update needed?
The Ethereum blockchain is capable of carrying out up to 15 transactions per second, which is 2 times faster than the Bitcoin network. For comparison, the Visa payment system processes 24,000 transactions per second.
The more Ethereum users become, the more transactions compete with each other to be included in the blockchain. Because of this, the workload of miners is growing: to generate new blocks, they need more and more computing power. Therefore, the number of transactions processed can drop to 10 per second. To maintain network performance at the current level, transaction fees have to increase.
The main purpose of update 2.0 is to avoid problems associated with user growth. The first change the developers came up with was a new consensus algorithm. Blockchain participants agree on each new block before it is created. The security of this process is now ensured by the work of miners. In the future, this will be done by validators - users who have contributed to the deposit contract. If a validator tries to harm the blockchain, he will simply lose his invested funds.
The second change is to create fragmented chains. The blockchain user checks the relevance of his version by comparing it entirely. The more blocks there are in the blockchain, the longer this process will take. Dividing the blockchain into fragments will allow comparisons to be made within a small area. Ethereum 2.0 will be divided into 64 fragments, which will allow 64 blocks to be created simultaneously instead of one. This will reduce the confirmation wait time by several times.
The blockchain chains in each shard operate independently and communicate with each other only when necessary. This makes it possible to speed up the transaction confirmation time
As a result, Ethereum 2.0, as a platform for decentralized applications, should become cheaper and supposedly 64 times faster. Such changes will affect not only developers, but also all participants in the crypto industry, since the majority of decentralized applications operate on the Ethereum blockchain. Therefore, the crypto community is waiting and regularly wondering when Ethereum 2.0 will be released.
What should ETH miners do in 2021?
Those who mine coins on Ethereum 1.0 need to think about moving to the new consensus mechanism. Until the end of this year and in the first half of the next, ASICs and video card farms will still be able to generate ETH. But then the PoW mining method will no longer be available. As a result, the purchased equipment will have to be used for mining in other networks. Some experts are focused on moving to working with cryptocurrencies such as Ravencoin and Ethereum Classic.
If your goal is to mine ETH, then you should stock up on coins now, which you can then stake (freeze). Without locked tokens, you will not be able to mine Ether and receive rewards for working as a validator.
Validators are network participants who check the generated blocks for compliance with the blockchain requirements. To obtain this status, you need to block 32 ETH. At the current ETH/USDT rate, this is approximately 140 thousand dollars. And at the ETH/RUB rate – more than 10 million rubles.
If a verifier allows a bad block into the system, they will lose all locked coins. For this reason, none of the validators are interested in violating the requirements in favor of any network participant. All this should make the Ethereum 2.0 blockchain significantly safer.
According to Ethereum developer Tim Beiko, miners now need to begin the process of abandoning the use of ASICs and video cards. A gradual transition to working with a new consensus mechanism will be less painful than a sudden change in mining method.
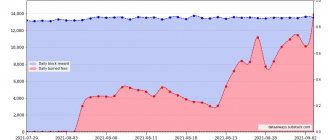
Certain changes have been made already this year. In August, the developers launched the EIP-1559 update. Now work with gas is automated. In addition, the process of burning Ether tokens was launched, due to which the number of coins in circulation is reduced. And this is one of the ways to encourage miners to refuse to work in PoW mode.
Sanctions for violators of network rules
There are three scenarios where stakers are penalized:
- The block producer offers two conflicting blocks in one timeslot.
- Sending by a staker two votes containing conflicting references to checkpoint block transitions at the same block height.
- Casting two votes with overlapping links to checkpoint block transitions. For example, a voice indicating the transition from checkpoint block 1 to checkpoint block 4 and a transition from checkpoint block 1 to checkpoint block 4, and a voice referencing the transition from checkpoint block 2 to checkpoint block 3.
It can be assumed that this rule will subsequently be replaced by a more logical one, according to which all references to block transitions must be sequential, however, it is possible that an honest node may skip a checkpoint block, and the result of a sequential vote may turn out to be legitimate. Here's a diagram illustrating this scenario:
Source: BitMEX Research
Pros and cons of switching to PoS
Implementing the Proof-of-Stake consensus algorithm in Ethereum has a number of important advantages:
- the system will become more reliable due to the work of validators;
- mining will be available to users with any equipment;
- abandoning powerful equipment will reduce the level of electricity consumption in the process of mining blocks by approximately 99.95%;
- The Ethereum 2.0 blockchain will become noticeably faster;
- the ability to increase your chances of mining blocks using expensive equipment will be neutralized;
- new roles (validators) will appear in the system, providing additional income in the form of a commission for work performed;
- due to sharding, the decentralization effect will increase;
- commissions will be reduced several times.
Ethereum's transition to PoS also has its downsides:
- the need for start-up capital to mine blocks. When using PoS, mining efficiency is directly affected by the number of locked tokens;
- inability to quickly withdraw invested funds. Users planning to become owners of tokens in Ethereum 2.0 need to be prepared for the coins to remain locked for 1-1.5 years. The reason is the time required for a full merger of the first and second versions of the Ethereum blockchain. Until this merger ends, you will not be able to withdraw your tokens;
- low staking profitability. In a PoS-based network, the profit from locked tokens will be in the range of 1.8% - 18.1% per annum. According to Ethereum developer Justin Drake, the average level of profit from staking will be 5% per year. For example, on the Binance platform you can find fixed staking at a rate of up to 100% per annum.
Some disadvantages can be circumvented. For example, use services that allow you to stake small amounts of ETH. But there is still a risk that some users will lose interest in mining in the PoS format.
Low profitability can be compensated by a significant increase in the cost of tokens of the second version of Ethereum. The main problem with Ethereum 1.0 comes down to low throughput and high fees. All this interferes with the scaling of the project. Against the backdrop of such disadvantages, second-level networks, as well as competing blockchains (lighter and cheaper), are gaining popularity.
After the transition to PoS and the introduction of sharding, the efficiency of Ethereum will reach a new level. The network will become much faster, commissions will be greatly reduced. According to analysts, such changes will allow the blockchain to gain an even stronger foothold in the first place in the altcoin ranking.
ETH mining after the merger
The Ethereum blockchain update should solve 3 key problems of the existing network:
- low transaction speed due to the massiveness of the system;
- reducing the level of stability of the block chain;
- high requirements for ETH mining equipment.
Thus, by introducing the Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism, competition between miners will be neutralized.
Those who want to be a validator, but do not have 32 ETH in their account, can use the services of cryptocurrency services that provide staking with minimal amounts. For example, on the Binance Staking platform there is a special staking pool. The minimum amount to participate is 0.0001 ETH. In dollars it is 0.44 USD. Profits are distributed according to the shares of the participants. Another advantage of working through an exchange is that you can periodically receive bonuses subject to full verification. The profitability of such pools is 5-20% per annum.
Those with 32 ETH can become validators of the network directly. In this case, it is better to store the coins in a hardware wallet - you still don’t need to use them. To obtain validator status, you must go to the official website of the project.
There you will need to perform the following steps:
- click on the “Become a validator” button;
- study the instructions (10 sections) by clicking “I accept”;
- select one of the proposed Eth1 clients and configure the node;
- read again the 10 sections of the instructions for working with Ethereum 2.0;
- select an Eth2 client and configure a node;
- indicate the number of validators that will be launched: each will cost 32 ETH;
- select the operating system of your device and the OS for running the node;
- connect a crypto wallet.
After this, the user will become a validator and will be able to receive ETH cryptocurrency for confirming blocks.
In the second network, the scheme for generating new blocks will be different, but the principles of entering mining will remain the same: either large starting capital or joining a mining pool.
One way bridge
Since the launch of Beacon Chain, two networks have been operating in parallel: Eth1 and Eth2. Initially, users are given the option to convert Eth1 coins to Eth2 coins, but not vice versa, so in theory the coins should trade at a price less than or equal to Eth1 coins. However, it is unlikely that the new coins will be valued or accepted on exchanges in the early stages, since the only use case for them is staking. Even basic transactions between users are not yet possible.
Transfer of coins from Eth1 to Eth2 is done through a smart contract on Eth1. This smart contract destroys coins on Eth1, and then a record of this can be used as confirmation to issue new coins on Eth2. The coins are permanently burned, although they can be restored by changing the protocol through a hard fork.
Coins transferred to Eth2 automatically go into the validator pool.