Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is an electronic database system distributed across multiple network nodes or devices. Thus, it is distinguished by the absence of a single regulatory body. Therefore, DLT technology allows information to be recorded and stored in a network that is both decentralized (data is stored on several servers) and distributed (these nodes are interconnected and interact with each other). Such networks can be either private or public.
Sponsored Sponsored
How does DLT work?
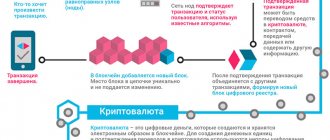
Networks based on a distributed registry system do not have a single control center. Instead, information is stored on several nodes of a peer-to-peer network at once, and an automatic consensus algorithm is used to update the data.
Data is transmitted over the nodes that form the network, duplicated on them and synchronized. This way, each node independently updates itself to a complete copy of the registry. All nodes then vote to update the ledger and reach consensus on one of its copies.
Sponsored
Sponsored
Each such update is protected by a unique cryptographic signature. All this determines the security of the database and at the same time its transparency.
What is blockchain
The first step in stopping people from saying “blockchain” instead of “bitcoin” is to understand what blockchain is.
People usually use this word to mean “the ledger on which Bitcoin operates.” In fact, Bitcoin and its blockchain are inseparable from each other, since they cannot exist separately.
A non-cryptocurrency blockchain is simply a centralized database that can be distributed among different locations and nodes using cloud computing. Moreover, a cryptocurrency owned by a small group of people is simply a digital currency that we were already familiar with.
The definition of blockchain that most of you will likely like is: decentralized consensus through a distributed, censorship-resistant protocol that allows data not to be shared with third parties .
No more, no less.
It's easy to create a private database, kept under the tutelage of your private nodes/servers, that works almost like a blockchain, but without the actual cryptocurrency. But it would really just be a database (like Oracle or SQL) owned by a group of individuals. You may have read-write access to this ledger, but there will be no decentralization because there will be no monetary incentive.
The most important part of the blockchain is Bitcoin. It would seem a trifle, but it was he who gave birth to decentralized money, for which bankers and representatives of large corporations now want to strangle him.
Are DLT and blockchain the same thing?
The two terms are often used interchangeably because they both refer to a system for recording and storing information in a transparent, decentralized network that has no central control node.
However, in reality, blockchain is just one type of distributed ledger.
Its key functional feature is the grouping and organization of all data into a cryptographically protected block chain. It is important that new blocks of data can only be added to such sequential chains, but already recorded data cannot be corrected or deleted. Additionally, blockchains, unlike other types of DLT, are generally open public networks and do not require special permission to access.
All this makes the blockchain the optimal cryptographically secure network for recording, storing data and freely tracking transaction history.
Commonly used data structures
Before we get into how to differentiate between blockchain and DLT, here are the most commonly used data structures:
- Data arrays are the simplest and most widely used structure. Other data structures, such as stacks and queues, come from arrays.
- Stacks allow you to store previous states of your work (which are limited to a certain number) in memory so that the latest state appears first. This is not possible if you just use arrays.
- Queues, which are similar to stacks, are another linear data structure that stores elements in a specific sequence. The only significant difference between stacks and queues is that instead of using the LIFO (last in, first out) method, queues implement the FIFO (first in, first out) method.
- Linked lists are like a chain of nodes, where each node contains information such as data and a pointer to the next node in the chain. There are head pointers that point to the first element of a linked list, and if the list is empty then they simply point to zero.
- A tree structure is a hierarchical data structure consisting of vertices (nodes) and edges that connect them. It is similar to a graph, but the key difference from a graph is that a tree structure cannot have a cycle.
- A graph is a collection of nodes that are connected to each other in a network. Nodes are also called vertices. The pair (x, y) is called an edge, which indicates that vertex x is connected to vertex y. An edge may contain parameters such as weight/cost, indicating the cost of moving from vertex x to vertex y.
- The loaded/prefix tree is a variant of the tree data structure that should be considered separately. It is quite effective for solving string problems because it provides fast searches. The main uses of the prefix tree are for looking up words in a dictionary, providing automatic suggestions in a search engine, and for IP routing.
- Hash Tables: Hashing is a process used to uniquely identify objects and store each of them in some pre-computed unique index called a key. Thus, an object is stored in the form of a key-value pair, and the collection of such elements is called a dictionary. Every object can be found using this key. There are different data structures based on hashing, but hash tables are the most commonly used.
So, having studied the above, we can come to the conclusion that the blockchain corresponds to hash tables with a hierarchical tree format - they contain blocks with transaction inputs and outputs (UTXO), registered and placed in chronological order.
An important takeaway from this section is that cryptocurrency blockchains can use different types of data structures to achieve similar goals, but the unifying factor in all cases will be the underlying cryptocurrency associated with the blockchain.
Advantages of DLT:
- High level of transparency, efficiency, automation. Control of the network is transferred to the users themselves and distributed throughout the network.
- Potential for fast and cheap transactions due to the elimination of the need for intermediaries, third parties or a central regulatory authority.
- High level of security thanks to an innovative information storage system in a database distributed throughout the network. Such a system is extremely difficult to hack, and data to change or falsify.
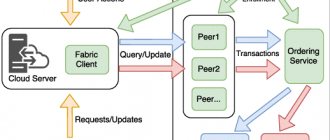
What is a distributed system
To explain what a distributed system (DLT) is in one sentence, it can be something like this: it is a system of several participants acting as a single unit in relation to an external user. Such a system may consist of several entities that perform different roles at different times: they replace each other, interact with each other, relay messages, temporarily store information for others, but ultimately strive for a single goal.
In other words, these are several participants/parties/processes, as well as connections between them.
Areas of application of DLT
- Finance – Cryptocurrencies operating on the basis of decentralized DLT technologies increase the security and transparency of financial transactions.
- Voting – DLT technology can provide a secure, confidential and at the same time transparent voting system, solving many problems associated with unfair elections.
- Healthcare – Access a patient’s medical history from anywhere in the world and significantly improve diagnostic tools.
- Supply Chains – Increasing the transparency and efficiency of global supply chains, as well as increasing consumer awareness of product quality and safety.
- Oil production
- Army
- Agriculture
Killer cryptocurrency app
If we want to understand how this decentralized ledger can change the world, we need to imagine its properties and think about how they can be used to run a business.
As you know, decentralization means that all people can participate in all aspects of government. You may have wondered how effective a democratic system really is. (And you had to think about this precisely because it is ineffective.)
There is no way to ensure a better distribution of wealth - even with the most efficient system.
Most organizations have no reason to move from conventional IT infrastructures to blockchain systems unless they themselves somehow want to decentralize value.
Taking this into account, we come to two important conclusions:
- DLTs are great for centralized organizations and products;
- blockchains are optimal for decentralized organizations and products.
Now that the whole picture is in sight, it becomes clear what a killer app is. This is something that changes the structure of organizations and creates value.
By combining the power of distributed infrastructure with decentralized governance and autonomous consensus rules that ensure trust between peers, we can achieve a completely new and unprecedented way of creating and distributing value.
This applies not only to money, but to literally everything we strive for.
Sure, it's great to track the origin of products on a public registry or securely store personal identification data in a place where only you can access it; These are great and revolutionary ways to use technology to better distribute value among network participants.
And the path to the new Internet must be paved with a fundamentally new approach to earning/receiving value.
But what will it look like?
Prospects for DLT
Distributed ledger technology continues to be a relatively new and still evolving phenomenon. DLT technology has become widely known worldwide thanks to blockchain and Bitcoin. However, in addition to the sphere of cryptocurrencies and financial transactions, it has a wide range of potential applications in a wide variety of areas of the real economy.
PS Don't agree with the author? Join our telegram chat.
Disclaimer
All information on our website is published in good faith and for general information purposes only. Any action based on information published on this site is taken by the reader solely at his own risk. In our Knowledge Base section, our priority is to provide high quality information. We carefully identify, research and create educational content that is useful to our readers. To maintain these high standards and continue to produce quality content, our partners may compensate us for featuring them in our articles. However, such payments do not in any way affect the processes of creating objective, honest and useful content.
Blockchain today
The key to power is knowing how to maintain that power.
Google and Microsoft were once “disruptors” trying to change the world in their own way. I believe that they were able to achieve this by giving billions of people cheap access to information. However, this information is kept under their watchful eye, and now it's time to pay for the free cheese.
There are several new regulations, such as the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), that are trying to solve this problem. Although in the end, as is usually the case with EU legislation, such rules can make the entire Internet less efficient, and leaks will not go away. Information will be stored in the same place as before - on the servers of large private companies.
Have cookie conventions caused your web browser to stop storing them? No. They've just made it harder to navigate the web, and now it takes up more of your time.
The bottom line is that we do not benefit from having our data stored in different places, nor are we compensated for participating in different networks.
If information is power, those who have it have power. Instead of simply making money from the sites you visit and analyzing your online habits, some companies make this information into a neat package and sell it to the highest bidder.
You probably believe that companies should give you back control over your data, and you believe that you can achieve this. But how? Will the EU or anyone else be able to confirm your claims?
The abundance of websites from different jurisdictions makes it difficult to remove your data from the Internet and prevent it from being sold without your permission.
Rhetorical question: do you think GDPR will be the solution to the problem of information abuse?
Relatively stable value with constant growth
One of the main reasons why merchants do not yet use cryptocurrencies is high volatility. Radix protects the price stability of its token while offering maximum growth potential.
Radix DLT protects against large price fluctuations using elastic supply. Today's coins have large fluctuations in price. But the Radix cryptocurrency will be more stable. Instead, the level of supply will fluctuate. This way, when the demand for Radix increases, instead of the token increasing in price, more Radix tokens will be provided to holders. If demand decreases, Radix will reduce the supply of all tokens. (Tokens will not be removed from holders’ wallets. More details about the economic system, and how this will be implemented, are not yet entirely clear).
This will allow for bulk confirmations to be accepted as suppliers will not have to worry about their Radix tokens decreasing in value once the item has been paid for.
The difference from a technical point of view using an example
To prevent the article from being amorphous, you first need to make a technical comparison and define the concepts.
DLT is an information storage technology, the important features of which are the absence of a central authority, the sharing and synchronization of information according to a consensus algorithm and, most importantly, the distribution of this database in different geographical locations.
The frequently used words register, book and journal are abstract implementations of the concept “DLT table”. DLT table is a technical term that defines a two-dimensional array data structure created long before Bitcoin.
The differences are best seen with examples. Current examples of DLT include Ripple, because just two weeks ago Bank of America filed a patent application for a settlement system based on Ripple distributed ledger technology. Ripple's developments are great for banks and really have practical applications, so their technology is worthy of being a representative of DLT.
Classic examples of blockchain are Bitcoin and Ethereum, so they will be representatives from the blockchain family.
The presented table clearly shows the difference between DLT and blockchain, the explanation of which will be discussed further.
Radix debit cards that work on existing PoS
Existing solutions do not provide a truly decentralized and independent form of payment solutions for merchants. They have to depend on partnerships with existing payment providers (such as Visa) to complete the transaction.
If Visa terminates the partnership, operations stop. Moreover, there are enough cases of unsuccessful partnerships with Visa. Radix allows you to use debit cards that will be completely independent from any payment provider. In fact, anyone can make a Radix debit card, and it will cost pennies. How this happens is described in the video.
Most modern blockchain solutions require merchants to use new hardware. Radix can be used on standard everyday Point Of Sale solutions that are already in use. The protocol's features reduce contention and speed up confirmation.
Radix will use a standard EMV card for transactions to the Radix public network (or bank). The transaction will be verified on the Radix network.
Energy
Beijing-based Energy Blockchain Labs Inc used IBM blockchain technology to develop a DLT platform for carbon trading. The platform aims to bring transparency and streamline efforts to limit greenhouse gas emissions by allowing high and low emitting countries to exchange carbon credits through smart contracts, ensuring compliance with government-set Certified Emissions Reduction (CER) quotas. Chinese company Hyperchain (Hangzhou Qulian Technology) is developing a solution for the state-owned network corporation of China that will include the Internet of Things (IoT).
Basis and status of China's regulatory framework for DLT
China filed more patents in blockchain technology - 58,990 - than any other country in 2022, making it clear that DLT initiatives are becoming an increasingly important part of China's technology landscape. We then discuss the location, status, and regulatory framework of these initiatives.
Typically, DLT initiatives have been concentrated in China's eastern coastal region and Sichuan province. China has four main blockchain hubs located around its major cities: Sichuan and Chongqing, Guangdong centered in Shenzhen, the Yangtze Delta centered in Hangzhou and Shanghai, Xiong'an New Area, and Beijing. Sichuan and Chongqing boast favorable policies and low energy costs, while Guangdong is a center of innovation and industry. The Yangtze Delta is a strong economic powerhouse and a center of globalization, and Beijing is home to leading universities and produces some of the best technical talent. In regions such as the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, DLT projects such as the People's Bank of China (PBOC) Trade Finance Pilot Platform have been launched. The Greater Bay Area has been at the forefront of the collaborative blockchain group with the creation of the Guangdong-Hong Kong Macau Greater Bay Blockchain Alliance in November 2022. More than 150 DLT initiatives have been developed in the Greater Bay Area, while the Hong Kong Innovation and Technology Fund has funded 67.2 million US dollars within 18 DLT projects.
Read other CHINA NEWS News about quantum achievements in China for November 01, 2021
The Chinese government aims to promote the further development of DLT through the creation of a national blockchain-based service network, a hosting platform for small and large companies participating in DLT. Such developments demonstrate how China is seizing opportunities for DLT initiatives to emerge and coexist with existing infrastructure. The primary government regulator for DLT is the Cyberspace Administration of China, which requires all DLT initiatives to be registered with the agency. Other regulatory authorities in the DLT space include the PBOC, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, the State Administration of Industry and Commerce, and the China Banking Regulatory Commission.
DLT continues to be practiced in pilot sandboxes being used in major cities in China. These pilot projects began in December 2022 and include Shenzhen, Shanghai, Guangzhou, Suzhou, Chongqing, Hangzhou, Beijing, Chengdu and Xiong'an New Area. The sandbox is helping cities create DLT, especially in the fintech space. The pilot projects will allow buyers, sellers and other intermediaries to conduct contactless digital transactions.
Government-sponsored pilot blockchain projects
In line with its ultimate policy goal of expanding technology innovation, the Chinese government is promoting the use of DLT in several key areas. The central bank has created a DLT system that digitizes checks. The Supreme People's Court has said it supports the use of blockchain in storing digital evidence. Local governments at both the provincial and city levels have also adopted the technology. More than 30 provincial and city governments have introduced more than 40 policies to support new technologies, including DLT.
Read more CHINA NEWS A comprehensive guide to electronic signatures from a legal perspective. Part 1
The cities of Guangzhou, Beijing, Shanghai, Suzhou, Xiong'an and others have given priority to the development and integration of DLT. Guangzhou has included DLT in its development zone. Beijing has created the Zhongguancun Blockchain Alliance to promote the development of this technology. Shanghai has set up an incubation base in the Baoshan area. Suzhou has established a training base to train hundreds of DLT technicians. Xiong'an New District has established a blockchain platform to manage the Xiong'an Land Requisition and Demolition Fund to track relocation and resettlement and related cash payments. The requisition and demolition fund management platform was created by the Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC). The platform tracks application contracts, fund approvals, disbursement instructions and fund transfers.
Medicine
The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated five major challenges facing the healthcare supply chain: varying product requirements, payment security, supplier reliability, end-to-end tracking and customs certification. Blockchain is a potential answer to solve these problems, especially with a focus on streamlining medical processes and ensuring the protection of personal data. China's DLT initiatives in the medical industry have continued since the 2022 launch of Alibaba's blockchain project to protect medical data. Other large companies using DLT solutions in the medical field include Baidu and Tencent, which have also developed platforms for sharing medical data between multiple organizations. For example, Baidu launched XuperChain, an open-source blockchain platform, to store medical data (such as diagnoses and treatments) in Yuzhong District, Chongqing. XuperChain is expected to expand to other regions in the coming years. Further evidence that Chinese companies are using DLT to streamline medical processes includes a joint pilot project between Ant Financial and Huashan Hospital 2022 that tracks prescriptions throughout the supply chain to provide tamper-proof protection and prevent prescriptions from being abused for unauthorized refills.
Smart contracts Scrypto
Radix already includes smart-contract. The developers created dApps using Scrypto, a decentralized application development language from Radix. Scrypto is based on JavaScript/TypeScript, so the learning curve is almost non-existent. In addition, the platform will have its own debugging tools and can be used on existing JavaScript IDEs. Essentially, if a user knows JavaScript, then he can develop applications in Radix.