This article is a summary of the results of research and study of the Bitshares protocol. The decentralized platform of the same name implements cryptocurrency, smart contracts, a trading platform and much more interesting functionality. The material may be useful if you are already familiar with the operating features of the Bitcoin protocol, but have not heard of Bitshares, which in turn is an accounting system with a good compromise between decentralization and throughput. In addition, the Bitshares protocol was taken as a basis in other decentralized systems: Steemit, EOS. The idea of the Bitshares protocol is to create a tool with which it would be possible to trade different assets and currencies in a decentralized environment, without actually depositing them on the trading platform. The idea itself belongs to a programmer named Daniel Larimer. He proposed it in 2013 and actively discussed it on forums for five weeks. This is how Daniel Larimer met another active cryptocurrency activist named Charles Hoskinson, who helped develop a business plan and attract investments. Daniel Larimer in the school cafeteria
Purpose of the Bitshares platform
Daniel Larimer, also known as Bytemaster, is the main ideologist and developer of the protocol.
The Bitshares platform allows anyone to create user issued assets (UIA), or digital tokens. Thus, the platform takes into account the base currency, i.e. the cryptocurrency with the ticker BTS and a variety of user tokens. The protocol implements a decentralized exchange where these digital assets can be traded. When designing the accounting system and the consensus mechanism, the developers placed great emphasis on throughput. As a result, Bitshares positions itself as a decentralized alternative to the Visa accounting system. While Visa claims it can process a couple of tens of thousands of transactions per second, Bitshares talks about the ability to process a hundred thousand transactions per second, in a decentralized manner with an open database and auditability.
In addition, Bitshares positions itself as a smart contract platform. True, smart contracts here are pre-installed and their number is limited - the most popular contracts are implemented. But they are more energy efficient and therefore cheaper in terms of fees.
Another feature of the platform is support for payments with an increased level of user privacy, which can be used optionally. In Bitshares this technology is called Stealth Transfers.
Buy BitShares LIVECOIN: goo.gl/pzXEzS BINANCE: goo.gl/GEHpHx Trade on decentralized exchanges RUDEX: t.co/GoinFNjFc4 BITSHARES: t.co/KAKEkySfLq OPENLEDGER: t.co/o3JRB9o7m2 = What is BitShares? BitShares (symbol BTS), formerly known as Protoshares (PTS), is both an industrial-grade “crypto-share”, a peer-to-peer distributed ledger, and a delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) network. It was created in 2014 by a visionary named Dan Larimer (“Bytemaster”), co-founder of Steemit, EOS and Cryptonomex.
BitShares is built on Graphene, an open-source blockchain technology in C++, as a consensus mechanism. Graphene is also used by several other real-world projects - Steemit.com (a decentralized Reddit-like blogging platform) and PeerPlays.com (a gaming site and PPY tokens).
BitShares works more like a stock than a traditional “currency”, since BTS tokens act as collateral when using various decentralized financial services: smart contracts, decentralized exchanges, banking, or the creation of derivatives (linked to the bit asset market – “bitAssets”).
BitShares Specifications
Consensus algorithm: Delegated Proof of Stake, DPOS Block creation time: 1.5 seconds on average, 3 seconds maximum, ~1.5 seconds delay up to 99.9% irreversibility Block reward: 1 BTS (from the Reserve pool) Irreversible blocks: (2 * BLOCK_INTERVAL * WITNESSES / 3) ~ 34 s Coins outside the reserve fund: 2,599,900,000 BTS (September 30, 2017) Coins in the reserve fund: 1,000,668,097 BTS (September 30, 2017) Total coins: 3,600,570,502 (constant quantity) Maximum number of transactions per second: potentially more 100,000 (tested 3400+ TK/sec)
Notably, it is a lightning-fast blockchain with an average block creation time of 1.5 seconds and a throughput of 100,000 transactions per second—more than all credit card transactions worldwide combined.
BitShares are governed by a decentralized autonomous company (DAC), a framework that allows BitShares holders to make decisions about the future of BTS. Although DAC operates independently, it is in tandem with an open source code base that is constantly being improved.
Your wallet address is your username
This is much more convenient than long, cumbersome strings of letters and numbers that literally attract negative user experiences and errors. Your username is your wallet address (like your login on social networks or Google). It is much easier to remember and write “john-smith” than 21x9d8sv37sd6m282u4j2hg9h4orbjht2u98f3.
Financial services offered by BitShares
BitShares competes with banks by providing the ability to issue market-linked, collateralized, and stable bitAssets (also called smartcoins).
This means that such crypto assets are pegged to the value of real world market assets. So, for example, the nominated “bitAsset” of USD is bitUSD. It tracks the movement of the dollar by collecting information from various sources carried out by the BitShares community.
This smartcoin token is always collateralized with at least 175% (or more) of its value in BTS, the main currency of BitShares, into which it can be converted at any time, since the loan collateral in the smart contract is managed by the blockchain.
What makes this platform truly unique is that while it provides collateralized credit, it remains free of counterparty risk. This is possible due to the fact that the protection of collateral and settlements are carried out by the network (and software protocol).
Objectives of smartcoins (bitAssets) with a stable price:
- A relatively reliable solution for predicting the future value of a token
- Unit of account other than assets with capital gains/losses (resulting in increased tax liability)
- Hedging against volatile cryptocurrency markets and price action
- Predicted stable price with reduced volatility
BitShares market pegged assets (MPAs) can be thought of as a contract between an asset buyer who cares about price stability and a short seller who is looking for the best deal when the price of BTS fluctuates.
Figure 2: Shows price discovery and a short seller betting to profit from the price change of BTS, providing liquidity with a 24-hour forced call (selling the position) from the time of the call. BitShares as lender
BitShares offers the ability to pledge your BTS holdings with a customizable reserve level (from a minimum of 175% to 1000 or even 2000%). BitShares integrates with any stock, commodity or currency pair as long as quotes are available. Additionally, bitAssets, including bitGold, bitSilver, bitOil and other commodity-focused cryptocurrencies, can also participate in this model.
This is a working, dynamic “smart” economy that adapts to the needs of the market. To maintain price stability, loans can be created with large collaterals (10-20x), allowing them to exist almost forever.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEX)
By accepting fiat money and issuing IOUs, traditional exchanges expose your funds to counterparty risk.
Conventional exchanges require a clearing house to deal with buyers and sellers. And although they provide the services the market requires, their performance can be significantly improved, since centralized management is inherently risky from a security point of view.
Exchanges set withdrawal limits and other regulatory restrictions, and often require customers to provide identification, payment accounts and other documentation.
How traditional cryptocurrency exchanges work:
- Receive cryptocurrency or fiat and issue IOUs instead
- They buy back these IOUs and allow them to be exchanged
- Processing the stock order book
Exchanges issue and redeem IOUs and maintain a market ledger
Have you ever thought that doing all 3 steps above by one person creates a conflict of interest? Not to mention the risk of a security breach. The same people are responsible for the safety of funds and for the order books of the entire market.
The BitShares Financial Services White Paper states the following: “There is no objective reason for the same person to be responsible for both the issuance of IOUs and the processing of orders. Moreover, combining such actions is a disadvantage from a security point of view.”
Decentralized exchanges (DEX) offer the opportunity to eliminate single point of entry and counterparty risk
Having these two functions performed by one party leads to centralization, especially in the case of cryptocurrency exchanges. This fact has been problematic in many cases where exchanges have made mistakes in handling wallets, keys or other vulnerable infrastructure components (resulting in breaches of obligations, hacks and loss of assets, as was the case with Mt Gox, Bitfinex or Mintpal).
Entry and exit from different asset pairs via gateways
Gateways act as reliable portals for trading various assets via the BitShares blockchain. Under your control, the gateway buys coins and then sends them to your wallet. It doesn't hold them for you like Coinbase and other exchanges do. This is a much safer option than letting third parties hold your coins, as only you have the private keys.
Open Ledger is a project by a Danish company that allows users to buy various assets (called open assets), which, like any gateway coin, are IOUs (which is similar to buying assets on any other exchange like Bitfinex). The platform helps you easily create and launch ICOs in a secure and decentralized manner.
DEX eliminates high-frequency trading, front-trading and order hiding
DEX creates a level playing field for trading, eliminating the possibility of Wall Street style shenanigans. In their system, savvy insiders deploy their trading infrastructure close to exchanges to increase the speed of order execution, coupled with trading algorithms that displace most ordinary people.
You can trade various crypto instruments and other derivatives
Positions such as silver, gold, oil and other crypto derivatives, including stocks, bonds and other market baskets. These pairs can be traded with each other, so you can sell silver for gold or bitUSD for BTC.
Smartcoins are market-pegged assets (MPAs) backed by the value of real assets.
Using these built-in functions, assets such as bitUSD are linked to the value of the fiat US dollar. 1 bitUSD can always be redeemed for at least $1. Price parity is maintained due to the flow of quotes supported by the Witnessers. All this opens the door for collateralized shorts and options to enter the derivatives market, allowing BitShares to take a piece of the $1 quadrillion pie.
No trading restrictions and low fees create a new level of financial freedom
Most exchanges require the provision of personal information, accounts, tax documents and other data as required by their “Know Your Customer” policies, anti-money laundering policies and a variety of other regulations. A DEX doesn't have the same restrictions, and you don't have to go through all the trouble of starting your own trades.
BitShares DEX GUI Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) and Governance
The problems with expensive, energy-intensive proof-of-work and the inherent power of the elite
Proof of work (PoW), as the Bitcoin example clearly shows, consumes a significant amount of energy to solve mathematical problems. For most people this is not sustainable in the long term. In addition, the increase in complexity took out a lot of those who could not solve the issue of finances or scalability. As a result, miners themselves decide whether to support the network or not, since the basis of the security and reliability of the blockchain is their machines.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
Traditional Proof of Stake (PoS) is powered by coin holders, who thereby create additional coins. Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) eliminates Proof of Work by adding a new Governance layer to the traditional Proof of Stake architecture. Users “delegate their shares” and allow them to select Authors who collect transactions, form them into blocks and broadcast them to the network. The work of witnesses is paid from the reserve pool.
Proxy voting allows voters to give power to Witnessers, as well as take it away
On the BitShares network, 1 vote = 1 BTS. For most users, the voting process is burdensome, so it was decided to vote by proxy. This helps reduce voter apathy and allows shareholders to respond quickly to pressing business and security issues. The formalism inherent in any bureaucracy makes management slow. With delegated Verifiers, you receive centralized control under a temporary contract that you can revoke at any time, thus maintaining decentralization.
Authors aggregate and verify transactions, publish quote feeds (providing the basis for the bitAsset market), maintain the blockchain, and improve the BitShares ecosystem.
Committee members
Committee members are responsible for regulating transaction fee rates, keeping them low if the price of BTS increases. During the election process, the protocol calculates the difference between upvotes and downvotes for each committee member (similar to voting for a post on Reddit). As a result, users with the highest average rating become members of the Committee.
The code acts as a channel for making suggestions, increasing the value and earning BitShares
To offer your services to the network, you can set up a “worker” - a special BitShares account. You need to provide a work plan, start/finish dates and your payment rate; This information is then sent to the owners of BTS tokens. They receive a work proposal and hold a vote, which can result in the proposal being accepted or rejected. A counter-offer may also be made to the applicant (including the amount of payment).
BitShares shares a percentage of the commissions collected by the network among members
BitShares allows you to purchase memberships, for example, “lifetime” gives you reduced rates for using BitShares features. In addition, there is a one-level referral program for members that provides reduced commissions and pays a percentage of your referrals' commissions.
Problems and risks
Sounds great, but what about the downside? After all, she is always there...
Collateral risk in case of a “black swan” (sudden price collapse)
Market-linked assets track the price of real assets using cryptographic derivatives backed by collateral with an established market value. Ultimately, all bitAssets are denominated and backed by the BitShares token (BTS). But these tokens are not immune to price action, including sharp declines in value.
The presence of a built-in function for triggering a margin call (selling a position to cover the original amount) does not guarantee complete reliability. The biggest risk is the price falling too quickly when there is no longer enough collateral to buy the asset. This is as if the value of the home drops below the total loan amount due to a downturn in the market.
While the overall market capitalization of cryptocurrencies is increasing exponentially, it is not without periodic shake-ups. A Black Swan event can severely undermine trust in a system and disrupt the ability to conduct secure transactions (such as loans), especially on a large scale.
People and businesses (especially banks) are sensitive to their money, so systems must work flawlessly. These are still very experimental technologies that the “big money bags” continue to be wary of.
Bittrex delisting took the market and community by surprise, causing massive FUD
FUD (Fear, Uncertainty and Doubt) is one of the community's favorite words. This is when people create a barrage of negative messages about a coin (or anything else). Markets are very sensitive to FUD (especially smaller caps) and can decline significantly as a result.
For unknown reasons not stated by Bittrex, Bitshares was listed for delisting from the exchange on October 13, 2022 (but has not been definitively delisted to this day). Some argue that the reason was the decentralized nature of the BitShares DEX as an exchange. Others call this FUD a way to push the price down. Then a version appeared that the nodes were “too big” to work.
All of the above are unconfirmed hypotheses. All we know is that Bittrex announced the removal of Bitshares, but what is the explanation for the exchange's clients or the BitShares team?
Exchange users are fickle and whether it was BitShares fault or not, most speculators behaved like a herd of sheep that quickly dumped on the back of the news, thereby causing the price of BitShares to collapse.
What really stands out against the backdrop of negative news is the presence of buying activity and “support” (many other excluded coins collapsed or died altogether).
No one can prevent the possibility of unexpected failures, software bugs or vulnerabilities
However, this argument applies to any modern project, including Bitcoin. As can be seen from the story of the DAO hack for $53 million of ether, they had to carry out a hard fork of the network, which led to a split into two different coins: Ethereum and Ethereum Classic.
What about the recent Parity fiasco? (Vulnerability that led to the freezing of $300+ million in ether.)
User error is widely recognized as the leading cause of IT and cybersecurity problems. This is an eternal threat not only to cryptocurrencies, but to technology in general. Any technology in the crypto world is experimental, so you should always exercise caution and healthy skepticism.
Final Thoughts
BitShares is definitely leading the way in terms of thinking and architecture
To summarize the ideas mentioned above:
- BitShares is an industrial-grade decentralized network, protocol and platform based on the Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) algorithm and Graphene technology (the backend engine of Steemit) capable of processing over 100,000 transactions per second.
- BitShares offers a variety of decentralized financial services - issuing smartcoins bitAssets, including market-pegged asset (MPA) and other crypto pairs from recognized real-world assets (e.g. gold, oil, S&P 500)
- The Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) algorithm adds a layer of governance - building on the traditional Proof of Stake model, which produces and multiplies coins based on ownership.
Despite all the risks and difficulties mentioned, the team perseveres, grows and constantly solves problems that arise along the way. Their services are simply amazing (despite certain risks and pitfalls). I have personally used their DEX and found it to be intuitive, smooth and fast.
As the platform becomes more mature and experienced, more players from the fintech and financial services sectors will begin to show interest in it.
I generally place a very strong emphasis on projects that promote decentralization and are usable in the real world. The current ICO craze is often downright sickening (Paris Hilton, are you serious?! LOL) and the industry is in dire need of high quality projects.
Fickle market sentiment, weakening tokens, hacker attacks, hidden regulation and other unforeseen pitfalls are all waiting for us (and frankly, many “coins”, or even most of them, will not last long).
Therefore, it is important that we focus on and support the creation of meaningful and meaningful communities and projects that focus on longevity.
I consider BitShares to be one of them.
Translated by @blockchained
Original post: HERE
= link =
My Telegram channel: t.me/cryptothrash = My Twitter: www.twitter.com/uberipuzo = List of promising crypto projects (updated periodically): goo.gl/u5hgK2 = All latest distributions of free tokens (airdrops): goo .gl/uvLnVh = "Cloud mining". HASHFLARE: t.co/wk7ETJPwkg GENESIS MINING: t.co/BJOb65tFeZ = 3% Discount - Uv31rm CCG Mining: t.co/MlRRKzr71G NuVoo Mining: t.co/ofRkZZz2rb Hashing24: t.co/FCwKosNyAh = Power Exchange = Hardware Crypto -wallets. LEDGER NANO S: goo.gl/i4XNom = Wallets and payment systems. PAYEER: goo.gl/tDavne (exchange BTC,ETH,USD,EUR,RUR) ADVCASH: goo.gl/qTy5z5 = Crypto exchanges. YOBIT: goo.gl/irx0NL EXMO: goo.gl/cMhZR6 CEX: goo.gl/b7A3hS = Margin Trading BITFLIP: goo.gl/Fd5Ppj BINANCE: goo.gl/GEHpHx Bit-Z: t.co/vp3W1CN27u BitMEX: t .co/awr9FXHqnP = Leverage x100 = Decentralized exchanges. RUDEX: t.co/GoinFNjFc4 BITSHARES: t.co/KAKEkySfLq OPENLEDGER: t.co/o3JRB9o7m2 BANCOR: www.bancor.network/ = Exchange cryptocurrencies for fiat. LOCALBITCOINS: goo.gl/v2hNf6 BTC banker: goo.gl/59Z9QD P2P-Bridge: t.co/k7gZuGVOwi P2P-Bridge-BOT: t.co/dngfE93uus = Directory - Exchanges and other services for transactions with Ethereum and ERC tokens 20: t.co/KrNVlnayC9 = Directory - Exchanges and other services for operations with BitShares: t.co/lueLVb6Z1d = Instructions - How to short bitAssets on the decentralized crypto exchange RuDEX: t.co/kv9kwbLOVD = Brief overview of decentralized crypto exchanges on the BitShares blockchain: t.co/VenerCsECO = Instructions - How to create your own token on the BitShares blockchain in 5 minutes: t.co/xT824vAZJy =
History of development and launch
Let's briefly get acquainted with the history of the launch of this decentralized platform.
The amount of work to create the planned platform was very large. The creators decided to start attracting people and distributing coins of the future cryptocurrency in advance to understand whether the project would attract enough attention and whether it was worth further supporting. So, in November 2013, the idea of Bitshares PTS, which means protoshares, was born. Its essence was that the distribution of coins would begin using mining based on a simple protocol, and at this time a full-fledged version of Bitshares would be developed.
To implement Bitshares PTS, we made a fork of Bitcoin (a clone of the repository with the source code), made minor changes to it and launched a new network. Anyone who was interested in the project could install a full node of the Bitshares PTS network on their computer, mine coins, exchange and trade them. Competition for the extraction of these coins grew, and very soon participants had to join together in mining pools.
Later, the developers presented the Bitshares protocol version 1.0 and announced in advance the release date of the last block in the Bitshares PTS blockchain. Since the new version of the protocol was written almost from scratch and uses completely new data formats, the update has its own characteristics. A snapshot of the state of all unspent coins is taken at the time of the last block of the old blockchain and transferred to the Genesis Block of the new blockchain. It turns out that all correspondences between public keys and balances are preserved, i.e. you can continue to use coins using the same private keys. Thus, on December 14, 2014, users switched to a new version of the protocol, where consensus is already achieved according to delegated proof-of-stake rules, and mining and issuance of new coins are not provided.
In October 2015, there was another major update to the Bitshares protocol to version 2.0, which went through a similar process.
It is worth noting that the Bitshares developers created the very core of the decentralized platform as part of a separate project called Graphene. Graphene is the foundation for building next-generation decentralized accounting systems. In addition to Bitshares, Graphene has formed the basis of several other projects.
general information
BitShares is more than just a cryptocurrency under the ticker symbol BTS. This concept hides a whole system that has great potential for use in various fields of activity. These areas include:
- finance;
- storage and transfer of valuables;
- attracting investments;
- guaranteed safety and transmission of data;
- cryptocurrency exchange and others.
Figure 1. Crypto project logo
The new project was conceived to improve existing blockchains and bring technologies to a new level. It was designed to solve problems inherent in Bitcoin:
- centralization, which manifests itself in the accumulation of power by large mining pools. Because of this, there is fragmentation in the Bitcoin ecosystem, as community members often cannot come to a common agreement on improving the technology. As a result, the emergence of numerous forks of the main cryptocurrency;
- low throughput of the Bitcoin blockchain;
- high volatility of the coin exchange rate;
- increasing service fees for miners.
Account model
Now let's look at how accounts are structured in the Bitshares 2.0 protocol. It uses elliptic curve cryptography, and the curve itself is exactly the same as in the Bitcoin protocol. There is an address format that uses a hash value of the public key, a base 58 number system, a BTS prefix, and does not contain a checksum. But this format is rarely used because the platform's overall database is optimized in such a way that each object, including the user account, has its own unique identifier, which is actually an 8-byte (or 64-bit) integer. In normal transactions of sending a payment, this is the account identifier indicated. In addition, the protocol supports the registration of unique names. Similar functionality was first implemented in the Namecoin protocol. Thus, in Bitshares you can register a human-readable string that will be unique within the corresponding blockchain and link it to your account to use this name instead of Account ID.
Transaction model
Let's take a closer look at the transaction model in Bitshares.
The diagram shows that the transaction body consists of five main fields.
The first two fields of a transaction are necessary in order to link it to a specific block. This is necessary to determine the block chain in which this transaction can be added, since according to the rules of the protocol, a transaction cannot be confirmed in a chain to which it is not linked. The expiration_time field specifies the time until which a transaction can be added to a block. If it has not been confirmed before this time, then it is considered invalid and can no longer be included in the blockchain. The operations_vector field is special. This feature is that many different operations can be placed in it. Operation is another key object in the Bitshares protocol. Let's name a few of the most popular types of operations: transfer (transfer), account_update (account update), asset issue (token issue) and order (trade offer). Each operation has its own format and necessary parameters. For example, a transfer operation requires specifying the sender's account, asset type, transfer amount, and recipient's account. The operations themselves are independent of each other, but can only be performed together if the transaction is accepted.
The extensions field is needed so that the current version of the software can process transactions of the new version, where additional fields may be added. Of course, the old software will not know how to correctly verify additional fields of new transactions, but at least it will be able to correctly process transactions according to the old rules.
This is an unsigned transaction format. In order to sign a transaction correctly, you need to analyze all operations from the operations_veсtor field and compile a list of accounts that must confirm this transaction. Then it will become clear which keys need to be used to sign the transaction. All necessary signatures are placed in a separate field - signatures. If even one signature is missing, the entire transaction will be considered invalid.
Note that by optimizing the size of identifiers, the final size of a transaction that contains one operation will be approximately 100 bytes. This is indeed a very compact transaction when compared to transactions in other protocols.
When it comes to fees, the Bitshares protocol takes a special approach. Each operation requires a certain payment, which is withdrawn from the initiator’s account balance at the time the transaction is confirmed. The commission for transactions may be constant or may change. As a rough comparison, fees for regular transfers and trading are significantly lower than fees for issuing new assets and registering a new account.
Cold wallets
In addition to those mentioned, it is possible to create a so-called “cold” Bitshares wallet, or paper wallet. This is a means for offline storage of assets without wallet access to the Internet, providing a high level of security. There is no need to install additional software.
To create a cold wallet, you can use the resource https://paperwallet.bitshares.eu/:
Figure 9. Cold wallet registration.
Here you set your login and password. After entering the data, a “cold” wallet will be generated, which can then be printed to choose from - with or without a password.
Figure 10. Generated Paper wallet.
Decentralized asset exchange
Now let's figure out how trading works for assets that are issued and accounted for on the Bitshares platform.
The user can create a transaction with such an operation where he declares that he is ready to exchange one asset for another asset in a certain ratio and for a certain amount. This transaction is propagated throughout the network and receives confirmation, after which another user can in the same way declare that they want to exchange the same assets in the same ratio. At the moment the second transaction is confirmed, according to the protocol, the balances of these two users are updated, i.e., assets are actually exchanged, based on the fact that both users have signed exchange statements that satisfy each other. Since such trading is carried out on the basis of a decentralized accounting system, this trading platform is called a decentralized exchange.
The purpose of creating “smart” coins (bitAssets)
Smart coins were created for a specific purpose and have a number of advantages and distinctive characteristics:
- predictable stable price with reduced volatility;
- a relatively reliable solution for predicting changes in the token rate in the future;
- a unit of account other than assets with the potential for capital appreciation or depreciation;
- hedging against the instability of cryptocurrency markets and price fluctuations of digital money.
Essentially, they represent a kind of contract between a buyer seeking asset price stability and a seller aiming to increase the price of BTS.
Account management flexibility
Another important feature of the Bitshares protocol is the possibility of flexible account management. The dynamic account permissions system allows you to set account management using several keys, using the multisignature principle. It is designed in such a way that each account can be controlled by a weighted combination of other accounts or electronic signature keys. This approach allows you to create a hierarchical management structure, the organization of which is similar to the permission system in real life. It turns out that it is possible to organize multi-user management of an account and its balances, where each user will have a certain weight in decision making. Moreover, different criteria can be set for different operations. This management mechanism can significantly reduce the risks of asset theft and loss of control over the account.
Let's imagine this schematically. At the top of the hierarchy there is an account on behalf of which it is impossible to authenticate a transaction with a single key. This can only be done by confirming several other accounts and keys. Participants at lower levels of the hierarchy are usually called signers. Each of them has its own weight in confirming the operation. For example, in this scheme, signatories have a weight of 25, 40, 35 and 40 units, and the required threshold for confirming a certain type of transaction may be 50, 60 or 70 units. At the same time, other types of operations may have a different distribution of weights and a different threshold value.
How does this work at the transaction level? One of the signers creates a transaction with certain operations and certifies on behalf of his account. The transaction is confirmed, but the operations included in it are not executed, but are waiting for confirmation. Other signers then see the offer and can either confirm it or reject the offer on behalf of their account using transactions containing special operations.
UIA emission
Let’s take a closer look at the features of issuing user assets on the Bitshares platform.
Anyone can create a transaction to create a new asset, pay a certain commission, set the parameters of this asset and begin issuing the corresponding tokens. This protocol functionality is implemented as a pre-installed smart contract and has some special features. At the request of the issuer, it is possible to satisfy the KYC (Know Your Customer) requirements using the white list mechanism (list of allowed accounts) and additional confirmation of the issuer. The white list contains accounts that the issuer of the asset gives permission to receive and hold its tokens. And the additional confirmation mechanism allows the issuer to control each transaction of transfer or trade of tokens (he can reject or approve each transaction with his asset).
In addition, the issuer may limit trading of tokens and allow only storage and transfers, or limit transfers and allow only trading. The issuer may also set additional fees for transfers and trading of tokens.
Another feature is that the issuer can activate the function of withdrawing and redistributing tokens. This works for cases when it is necessary to support external mechanisms for condemning transactions and rolling back payments. It is also worth noting that all settings of user assets are specified in the form of smart contract parameters and the issuer sets which properties it can change and which will be constant. For example, he may limit himself to additional issuance of tokens, or may leave the possibility of arbitrary issuance. And these contract parameters will be visible to all users.
An interesting property of tokens that are issued on the Bitshares platform is that when performing transactions with them, the user can pay a commission either in the base currency or in these same tokens. Conversion is performed based on the exchange rate set by the issuer.
Voting mechanism
When exploring the Bitshares platform, it is imperative to mention a mechanism that helps make decisions in a decentralized environment - voting.
Committee members, validators (witnesses) and developers (workers) are elected by voting. Committee members are needed to vote on changing some protocol parameters, such as commissions, the number of validators, etc. Validators, also known as delegates, are needed to verify transactions and generate blocks. And developers offer software improvements. If they get enough votes and meet the development deadline, they receive a reward. When voting, the weight of each account's vote is proportional to its balance in the base currency. At the same time, the proxy voting option is supported, which allows you to give your vote to another voter. This is convenient in cases where the user himself does not know which candidate is better to vote for, and gives this right to a more competent user. In general, voting is very important to ensure the high reliability of the Bitshares platform.
"Road map"
To date, there is no official roadmap for the BitShares project. The first version was released in 2014 and was designed for the next two years. All stated points of the “road map” were completed on time.
The lack of a roadmap may be due to the fact that the introduction of fundamentally new technologies and functions in BitShares is not expected. The developers declare their intention to concentrate efforts on promoting and popularizing the platform, using marketing techniques in order to arouse interest among ordinary users and large technology companies.
Commission mechanism
Now let's look at the mechanism for collecting transaction fees and rewards for active network participants. There is a balance that does not belong to any of the users of the platform, and it can be managed exclusively according to the rules of the protocol. This balance is called Reserve Pool. The rules stipulate that commission fees for all transactions from all accounts go to the Reserve Pool. Validator and developer accounts are paid rewards from the Reserve Pool as a percentage of its balance. In addition, the collection and distribution of commission fees may be subject to the rules of the referral program, which is also supported by the platform (you can read about it separately).
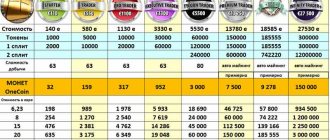
It is worth mentioning the maximum number of coins of the base currency. A total of 3.6 billion coins have been issued and no additional issue is planned. At the same time, at the time of 2022, about 2.6 billion coins are in free circulation, and about 1 billion are in the Reserve Pool.
Where can I buy
As of March 22, 2022, the crypto asset is traded on 18 crypto exchanges. Among the platforms with the highest turnover are Binance (for BTC, ETH, BNB), Poloniex (BTC). The largest daily volume is shown by the ZB.com crypto platform (USDT, BTC).
The largest selection of cryptocurrency pairs is provided by their own decentralized crypto exchanges Wallet.Bitshares, BitShares Asset Exchange (in pairs with assets) and Openledger DEX. Many coins can be added for intra-account trading. The cost of the transaction at the time of preparation of the review was only $0.015, for withdrawal of funds – $0.14.
Figure 9. Rudex interface
A good option for buying an altcoin for rubles is the decentralized exchange Rudex, which has an entry point into the Bitshears blockchain and its own ruble gateway. In addition, the interface is made in Russian.
Important! To replenish your account in Rudex, methods such as Alfa-Click, VTB24, Russ.Standard, Sberbank, Tinkoff, Kukuruza, payment systems Yandex.Money and Qiwi are available. Fiat deposit fees are only 1%.
In the next video you can see how a deposit is made to a Rudex account in rubles
The Bitshars coin is traded in pairs with BTC on the Russian crypto platform Livecoin. Here you can first enter the ruble and exchange it for Bitcoin, then buy BTS. There is no commission for replenishing using Capitalist, AdvCash – 10%, Qiwi – 9%.
SmartCoins
Before this, we talked about a smart contract that implements regular tokens, and now we’ll talk about another smart contract that implements market pegged assets, tokens that are price-linked to some external asset. They are also called SmartCoins. It works on the principle of contract for difference, i.e. contract for difference. Accordingly, anyone can issue these tokens by simply freezing a certain collateral amount, for example in the base currency. In this case, the collateral coefficient is significantly higher than one, and 2 or more is recommended. Here everything works according to the principles of margin trading, where margin positions and automatic margin calls are used. In order for the platform to have data on the price of an asset in external markets, trusted parties are used to post data about the price of the asset on the Bitshares blockchain using a special type of operation. In this case, these trusted parties are the validators themselves.
A country
The BitShares ecosystem may reach a point where government influence on the lives of ordinary citizens is eliminated. In fact, the platform itself is a state. It consists of a community that issues its own currency and operates the network. All functions of the state, for example, approval and enforcement of laws, control and regulation of the financial sector, conflict resolution, etc., can be performed by smart contracts, an insurance system and other features of BitShares.
Block Header Format
The block header in Bitshares has a simpler structure and smaller size than the block header in Bitcoin.
The following fields are included: previous block ID, timestamp, creator ID, hash value of incoming transactions, and an extensions field to maintain compatibility with new versions of the block header.
A complete block will include the block title, the signature of the validator who created the block, and a list of transactions that are included in that block.
Within the Bitshares protocol, there are 4 concepts that play a key role in the operation of the platform: blocks, transactions, operations and objects. The objects here are account, asset, balance, offer, etc.
Mining
The concept of mining Bitshares is different from that of Bitcoin. If in the latter case anyone with equipment with sufficient computing power can mine, bitshares uses a different principle. Its basics:
- Only delegates chosen by the community can mine;
- In theory, any user can become a delegate, although in practice this is unlikely for a beginner;
- delegates sign transactions and monitor the operation of the network as a whole, receiving commissions in BTS;
- The work of community-selected delegates is carefully reviewed.
To become a miner, you need to receive votes from other participants in the system. Each token owner casts a vote for one candidate or another, and the winners based on the total number of votes become delegates. The number of such is 101, this number seemed optimal to the developers.
In addition, a referral program is built into the code, which allows you to earn income from attracting new users to the system.
Many operations and features of their implementation
Let's take a closer look at the concept of an operation in the context of this protocol.
Bitshares has about 40 different types of operations as of 2022, and new types can be added with new protocol updates. Operations allow you to initiate some simple changes to the accounting system and more complex mechanisms such as pre-installed smart contracts. It was already said above that one transaction can contain several operations, which, if successful, will be executed simultaneously. Here is a small list of the most popular operations:
- transfer_operation transfers a specific asset from the balance of one account to another;
- limit_order_create_operation creates an asset exchange order object; limit_order_cancel_operation cancels such an order;
- fill_order_operation is executed automatically when two orders satisfy each other, and it does not require creating a transaction, so it is also called a virtual operation;
- account_create_operation creates a regular user account;
- blind_transfer_operation makes a confidential payment;
- asset_create_operation creates a new asset object;
- asset_update_operation changes the smart contract parameters of an existing token;
- asset_issue_operation issues tokens of an existing asset;
- witness_create_operation creates a candidate validator account.
As for statistics, we can say that the load on the Bitshares network in terms of the number of transactions is comparable to the load on the Bitcoin or Ethereum network. Moreover, at some points in 2022, the Bitshares platform processed more transactions than Bitcoin and Ethereum combined. And the results of load testing show that the maximum throughput of the Bitshares network is hundreds of times greater than the maximum throughput of the Bitcoin and Ethereum networks.
According to the analytical resource blocktivity.info, as of July 2018, the Bitshares platform processes more than 60% of the total number of transactions confirmed by all decentralized platforms.
Computer wallet
The main way to store Bitshares is in a desktop wallet. You can download the bitshares wallet application from the official website https://bitshares.org/download/:
Figure 1. Downloading the program.
The site presents client programs for the main popular PC platforms - Windows, Mac and Linux. The software has the following functions:
- wallet;
- Bitshares block explorer;
- exchange interface.
The software must be downloaded to a PC, then run the executable file and go through the installation, registration and configuration process (instructions are given below).
Database organization
Now let's look at one important architectural feature of the Bitshares protocol that helps achieve such high throughput.
The diagram on the left shows a method of organizing a database called blockchain, which is usually used to store the entire transaction history. On the right is another way to organize a database - Ledger. It is usually used to store correspondences between identifiers and states (for example, an account and its balance).
Blockchain properties make it easy to verify the integrity of the database and the history of its changes, as well as easily organize synchronization and achieve consensus in a decentralized environment.
Ledger is convenient because it stores the latest state of the database in a compact way while providing fast search, reading and updating of records. That is why they fundamentally have a higher throughput. Ledger is usually used in centralized accounting systems.
The idea behind Bitshares is to take advantage of both ways of organizing a database at the same time. Thus, a complete network node keeps records simultaneously using two databases organized as Blockchain and Ledger, respectively. At the same time, nodes synchronize data with each other using blocks and update a local copy of the blockchain, and they verify and accept transactions based on the latest state of the database stored by Ledger. Moreover, the size of all the data that makes up the Ledger is optimized in such a way that the network nodes keep it in RAM. This allows you to significantly speed up the process of verification and acceptance of new transactions.
Optimizing the execution of business logic
Many accounting systems use a general purpose scripting language to define all transactions.
These accounting systems ultimately use the "business logic processor" as a virtual machine, and all transactions are defined as scripts that will be executed by the virtual machine. This approach takes the thread synchronization mechanisms of the real processor and combines them, executing all instructions through the virtual processor. A virtual processor, even with Just-In-Time compilation, will always be slower than a real processor, but the resulting computational rate is not the only problem with the everything-is-script approach. When transactions are defined at such a low level, it means that most of the static checks and cryptographic transformations remain in the business logic processing, and overall throughput drops. To improve the performance of the accounting system and quickly execute business logic, you need to move all static checks, including all cryptographic transformations, outside the scope of the business logic module.
Another optimization step is storing data of the final state of the accounting system in RAM. This means that the business logic processor can quickly follow memory pointers and directly obtain the data it needs, rather than having to perform time-consuming database queries. This also means that the data can be accessed without being copied, and that the data can be changed in place. This optimization provides performance gains over using a database-based approach.
Thus, creating an accounting system with high performance does not require complex technologies and separation of processes among network nodes. All that is needed to create a high-performance validator is to separate all independent calculations from the main business logic, execute it in a single thread without interruptions for synchronization, and store all verification dependencies in RAM.
Flaws
Like any phenomenon, the Bitshares cryptocurrency has its own disadvantages. Of course, through the efforts of a powerful development team, the number of negative qualities of their project was reduced to a minimum. Among the known and main disadvantages the following points can be identified:
- Low prevalence when compared with competitors and industry leaders.
- There are few places where you can pay with such a coin.
- This network does not have administrators, therefore, the user himself is responsible for managing income and assets. If he loses his password for the virtual wallet, it will not be possible to recover it.
Options to enhance user privacy
It was noted above that the Bitshares accounting system uses accounts and balances, unlike Bitcoin, where accounting is based on unspent transaction outputs.
Increasing the level of privacy on the Bitshares platform is not a trivial task, since in the case of accounts and balances it is even easier to de-anonymize users than in Bitcoin. But the Bitshares developers solved this problem in an interesting way. They implemented the ability to specify multiple inputs and outputs within a single operation. It is now possible to include many inputs and outputs in a single transaction, making cash flow analysis more complex and increasing user privacy.
Additionally, these operations default to techniques such as Confidential Transaction and Stealth Addresses. Confidential Transaction hides the amounts of the transaction's inputs and outputs, but uses proof that the sum of the outputs does not exceed the sum of the inputs. And Stealth Addresses hides the relationship between the public key, which is used as the recipient's identifier, and the address that is actually specified in the transaction output.
Bitshares uses regular (non-private) payments by default, but users can use Stealth Transfers if they wish. Thus, coins are accounted for on the platform in two different ways.
There is such a thing as transferring coins from one accounting method to another. For this purpose, separate operations are implemented:
- transfer_to_blind_operation is used to transfer coins from open circulation to hidden circulation;
- blind_transfer_operation is for transferring coins in a hidden manner, and transfer_from_blind_operation is for transferring coins from hidden circulation to open circulation.
It is clear that these operations are larger in data volume than usual and, accordingly, require a larger commission.
It is noteworthy that anyone can calculate how many coins went into hidden circulation, which is why there is such a thing as Stealth supply (the number of coins in hidden circulation). But there is one practical downside to the privacy option in Bitshares at the moment (July 2018). The fact is that there are still no convenient graphical interfaces for simple work in enhanced confidentiality mode.
Team
Initially, the co-founders of BitShares were Dan Larimer (who also participated in the creation of Steemit and EOS) and Charles Hoskinson. They developed a business plan and thought through the first stages of the project. However, Hoskinson left the team back in 2013; the reasons for his departure were never given.
The current composition of BitShares developers is not presented on the official website. Since the project operates on an autonomous basis, the size and composition of the team changes frequently. The most complete information about the people taking part in the promotion of BitShares can be found on github.com - on the page dedicated to the ongoing development of the platform.
Current Bitshares Development Team